|
WASP
A wasp is any insect of the narrow-waisted suborder Apocrita of the order Hymenoptera which is neither a bee nor an ant; this excludes the broad-waisted sawflies (Symphyta), which look somewhat like wasps, but are in a separate suborder. The wasps do not constitute a clade, a complete natural group with a single ancestor, as bees and ants are deeply nested within the wasps, having evolved from wasp ancestors. Wasps that are members of the clade Aculeata can sting their prey. The most commonly known wasps, such as yellowjackets and hornets, are in the family Vespidae and are eusocial, living together in a nest with an egg-laying queen and non-reproducing workers. Eusociality is favoured by the unusual haplodiploid system of sex determination in Hymenoptera, as it makes sisters exceptionally closely related to each other. However, the majority of wasp species are solitary, with each adult female living and breeding independently. Females typically have an ovipositor f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hymenoptera
Hymenoptera is a large order of insects, comprising the sawflies, wasps, bees, and ants. Over 150,000 living species of Hymenoptera have been described, in addition to over 2,000 extinct ones. Many of the species are parasitic. Females typically have a special ovipositor for inserting eggs into hosts or places that are otherwise inaccessible. This ovipositor is often modified into a stinger. The young develop through holometabolism (complete metamorphosis)—that is, they have a wormlike larval stage and an inactive pupal stage before they mature. Etymology The name Hymenoptera refers to the wings of the insects, but the original derivation is ambiguous. All references agree that the derivation involves the Ancient Greek πτερόν (''pteron'') for wing. The Ancient Greek ὑμήν (''hymen'') for membrane provides a plausible etymology for the term because species in this order have membranous wings. However, a key characteristic of this order is that the hindwings are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eusociality
Eusociality (from Greek εὖ ''eu'' "good" and social), the highest level of organization of sociality, is defined by the following characteristics: cooperative brood care (including care of offspring from other individuals), overlapping generations within a colony of adults, and a division of labor into reproductive and non-reproductive groups. The division of labor creates specialized behavioral groups within an animal society which are sometimes referred to as 'castes'. Eusociality is distinguished from all other social systems because individuals of at least one caste usually lose the ability to perform at least one behavior characteristic of individuals in another caste. Eusocial colonies can be viewed as superorganisms. Eusociality exists in certain insects, crustaceans, and mammals. It is mostly observed and studied in the Hymenoptera ( ants, bees, and wasps) and in Blattodea (termites). A colony has caste differences: queens and reproductive males take the roles of the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
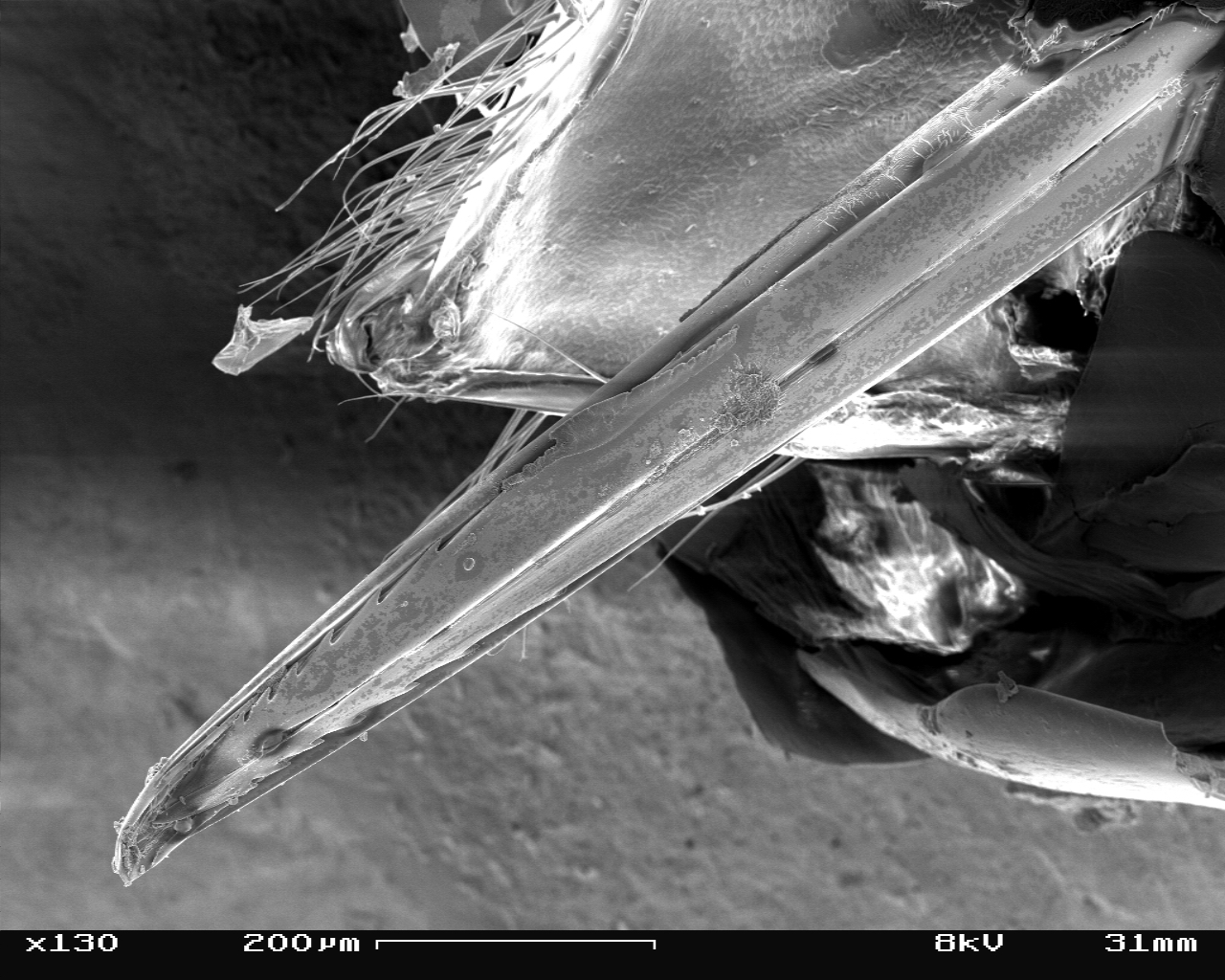
Ovipositor
The ovipositor is a tube-like organ used by some animals, especially insects, for the laying of eggs. In insects, an ovipositor consists of a maximum of three pairs of appendages. The details and morphology of the ovipositor vary, but typically its form is adapted to functions such as preparing a place for the egg, transmitting the egg, and then placing it properly. For most insects, the organ is used merely to attach the egg to some surface, but for many parasitic species (primarily in wasps and other Hymenoptera), it is a piercing organ as well. Some ovipositors only retract partly when not in use, and the basal part that sticks out is known as the scape, or more specifically oviscape, the word ''scape'' deriving from the Latin word '' scāpus'', meaning "stalk" or "shaft". In insects Grasshoppers use their ovipositors to force a burrow into the earth to receive the eggs. Cicadas pierce the wood of twigs with their ovipositors to insert the eggs. Sawflies slit the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
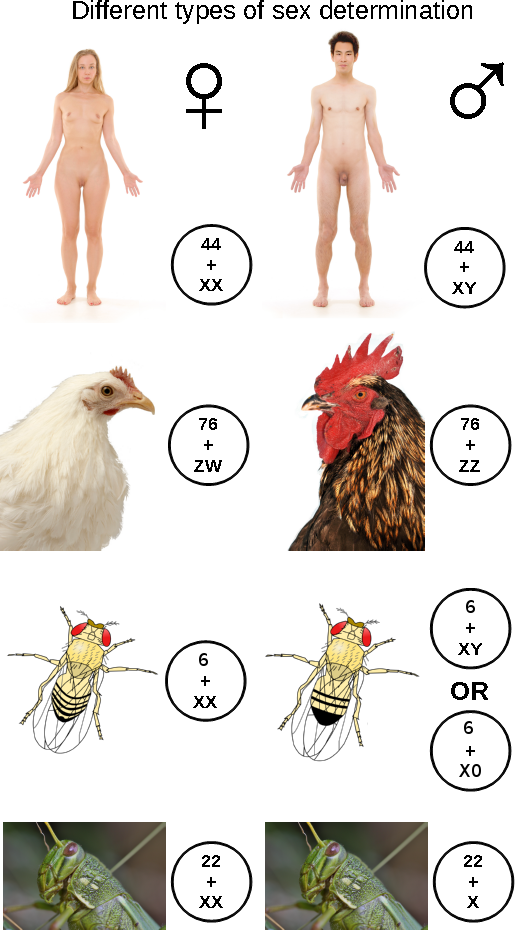
Sex-determination System
A sex-determination system is a biological system that determines the development of sexual characteristics in an organism. Most organisms that create their offspring using sexual reproduction have two sexes. In some species there are hermaphrodites. There are also some species that are only one sex due to parthenogenesis, the act of a female reproducing without fertilization. In some species, sex determination is genetic: males and females have different alleles or even different genes that specify their sexual morphology. In animals this is often accompanied by chromosomal differences, generally through combinations of XY, ZW, XO, ZO chromosomes, or haplodiploidy. The sexual differentiation is generally triggered by a main gene (a "sex locus"), with a multitude of other genes following in a domino effect. In other cases, sex of a fetus is determined by environmental variables (such as temperature). The details of some sex-determination systems are not yet fully under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haplodiploid
Haplodiploidy is a sex-determination system in which males develop from unfertilized eggs and are haploid, and females develop from fertilized eggs and are diploid. Haplodiploidy is sometimes called arrhenotoky. Haplodiploidy determines the sex in all members of the insect orders Hymenoptera (bees, ants, and wasps) and Thysanoptera ('thrips'). The system also occurs sporadically in some spider mites, Hemiptera, Coleoptera (bark beetles), and rotifers. In this system, sex is determined by the number of sets of chromosomes an individual receives. An offspring formed from the union of a sperm and an egg develops as a female, and an unfertilized egg develops as a male. This means that the males have half the number of chromosomes that a female has, and are haploid. The haplodiploid sex-determination system has a number of peculiarities. For example, a male has no father and cannot have sons, but he has a grandfather and can have grandsons. Additionally, if a eusocial-insect colo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eusociality
Eusociality (from Greek εὖ ''eu'' "good" and social), the highest level of organization of sociality, is defined by the following characteristics: cooperative brood care (including care of offspring from other individuals), overlapping generations within a colony of adults, and a division of labor into reproductive and non-reproductive groups. The division of labor creates specialized behavioral groups within an animal society which are sometimes referred to as 'castes'. Eusociality is distinguished from all other social systems because individuals of at least one caste usually lose the ability to perform at least one behavior characteristic of individuals in another caste. Eusocial colonies can be viewed as superorganisms. Eusociality exists in certain insects, crustaceans, and mammals. It is mostly observed and studied in the Hymenoptera ( ants, bees, and wasps) and in Blattodea (termites). A colony has caste differences: queens and reproductive males take the roles of the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vespidae
The Vespidae are a large (nearly 5000 species), diverse, cosmopolitan family of wasps, including nearly all the known eusocial wasps (such as ''Polistes fuscatus'', ''Vespa orientalis'', and ''Vespula germanica'') and many solitary wasps. Each social wasp colony includes a queen and a number of female workers with varying degrees of sterility relative to the queen. In temperate social species, colonies usually last only one year, dying at the onset of winter. New queens and males (drones) are produced towards the end of the summer, and after mating, the queens hibernate over winter in cracks or other sheltered locations. The nests of most species are constructed out of mud, but polistines and vespines use plant fibers, chewed to form a sort of paper (also true of some stenogastrines). Many species are pollen vectors contributing to the pollination of several plants, being potential or even effective pollinators, while others are notable predators of pest insect species. The subf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hornet
Hornets (insects in the genus ''Vespa'') are the largest of the eusocial wasps, and are similar in appearance to their close relatives yellowjackets. Some species can reach up to in length. They are distinguished from other vespine wasps by the relatively large top margin of the head. Worldwide, 22 species of ''Vespa'' are recognized.A.H. Smith-Pardo, J.M. Carpenter, L. Kimsey (2020) The diversity of hornets in the genus ''Vespa'' (Hymenoptera: Vespidae; Vespinae), their importance and interceptions in the United States. Insect Systematics and Diversity 4(3) https://doi.org/10.1093/isd/ixaa006 Most species only occur in the tropics of Asia, though the European hornet (''V. crabro''), is widely distributed throughout Europe, Russia, North America, and north-eastern Asia. Wasps native to North America in the genus '' Dolichovespula'' are commonly referred to as hornets (e.g., baldfaced hornets), but are actually yellowjackets. Like other social wasps, hornets build communal n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yellowjacket
Yellowjacket or yellowjacket is the common name in North America for predatory social wasps of the genus, genera ''Vespula'' and ''Dolichovespula''. Members of these genera are known simply as "wasps" in other English-speaking countries. Most of these are black and yellow like the eastern yellowjacket ''Vespula maculifrons'' and the aerial yellowjacket ''Dolichovespula arenaria''; some are black and white like the bald-faced hornet, ''Dolichovespula maculata''. Others may have the abdomen background color red instead of black. They can be identified by their distinctive markings, their occurrence only in colonies, and a characteristic, rapid, side-to-side flight pattern prior to landing. All females are capable of stinger, stinging. Yellowjackets are important predators of pest insects. Identification Yellowjackets may be confused with other wasps, such as hornets and paper wasps such as ''Polistes dominula''. A typical yellowjacket worker is about long, with alternating ban ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stinger
A stinger (or sting) is a sharp organ found in various animals (typically insects and other arthropods) capable of injecting venom, usually by piercing the epidermis of another animal. An insect sting is complicated by its introduction of venom, although not all stings are venomous. Bites, which can introduce saliva as well as additional pathogens and diseases, are often confused with stings, and vice versa. Specific components of venom are believed to give rise to an allergic reaction, which in turn produces skin lesions that may vary from a small itching weal, or slightly elevated area of the skin, to large areas of inflamed skin covered by vesicles and crusted lesions. Stinging insects produce a painful swelling of the skin, the severity of the lesion varying according to the location of the sting, the identity of the insect and the sensitivity of the subject. Many species of bees and wasps have two poison glands, one gland secreting a toxin in which formic acid is one r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clade
A clade (), also known as a monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that are monophyletic – that is, composed of a common ancestor and all its lineal descendants – on a phylogenetic tree. Rather than the English term, the equivalent Latin term ''cladus'' (plural ''cladi'') is often used in taxonomical literature. The common ancestor may be an individual, a population, or a species (extinct or extant). Clades are nested, one in another, as each branch in turn splits into smaller branches. These splits reflect evolutionary history as populations diverged and evolved independently. Clades are termed monophyletic (Greek: "one clan") groups. Over the last few decades, the cladistic approach has revolutionized biological classification and revealed surprising evolutionary relationships among organisms. Increasingly, taxonomists try to avoid naming taxa that are not clades; that is, taxa that are not monophyletic. Some of the relationships between org ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |