|
Władysław Syrokomla
Ludwik Władysław Franciszek Kondratowicz (29 September 1823 – 15 September 1862), better known as Władysław Syrokomla, was a Polish romantic poet, writer and translator working in Vilnius and Vilna Governorate, then Russian Empire. Biography Syrokomla was born on 29 September 1823 in the village of Smolków, in the Minsk Governorate of the Russian Empire (now Smolhava, Minsk Region, Belarus), to an impoverished noble family. His parents were Aleksander Kajetan Kondratowicz (d. 1858) and Wiktoria (née Złotkowska). His uncle was Hilary Kondratowicz (1790–1823), a Polish teacher of maths in gymnasium in Vilnius, who published some articles in '' Wiadomości Brukowe''. A year after his birth his parents moved to another village ( Jaśkowicze). In 1833 he entered the Dominican school in Nesvizh (Nieśwież). He had to give up his studies due to financial problems. In 1837 he began work in a Marchaczewszczyzna folwark. Between 1841 and 1844, he worked as a clerk in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lyuban District
Lyuban District (Lyubanski rayon, Lyubansky raion) is a district of Minsk Region, Belarus. The capital of the district is Lyuban. Notable residents * Władysław Syrokomla Ludwik Władysław Franciszek Kondratowicz (29 September 1823 – 15 September 1862), better known as Władysław Syrokomla, was a Polish romantic poet, writer and translator working in Vilnius and Vilna Governorate, then Russian Empire. Biogr ... (known in Belarus as Uladzislaǔ Syrakomla) (1823, Smolków estate – 1862), poet, writer and translator References External links Districts of Minsk Region {{Belarus-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
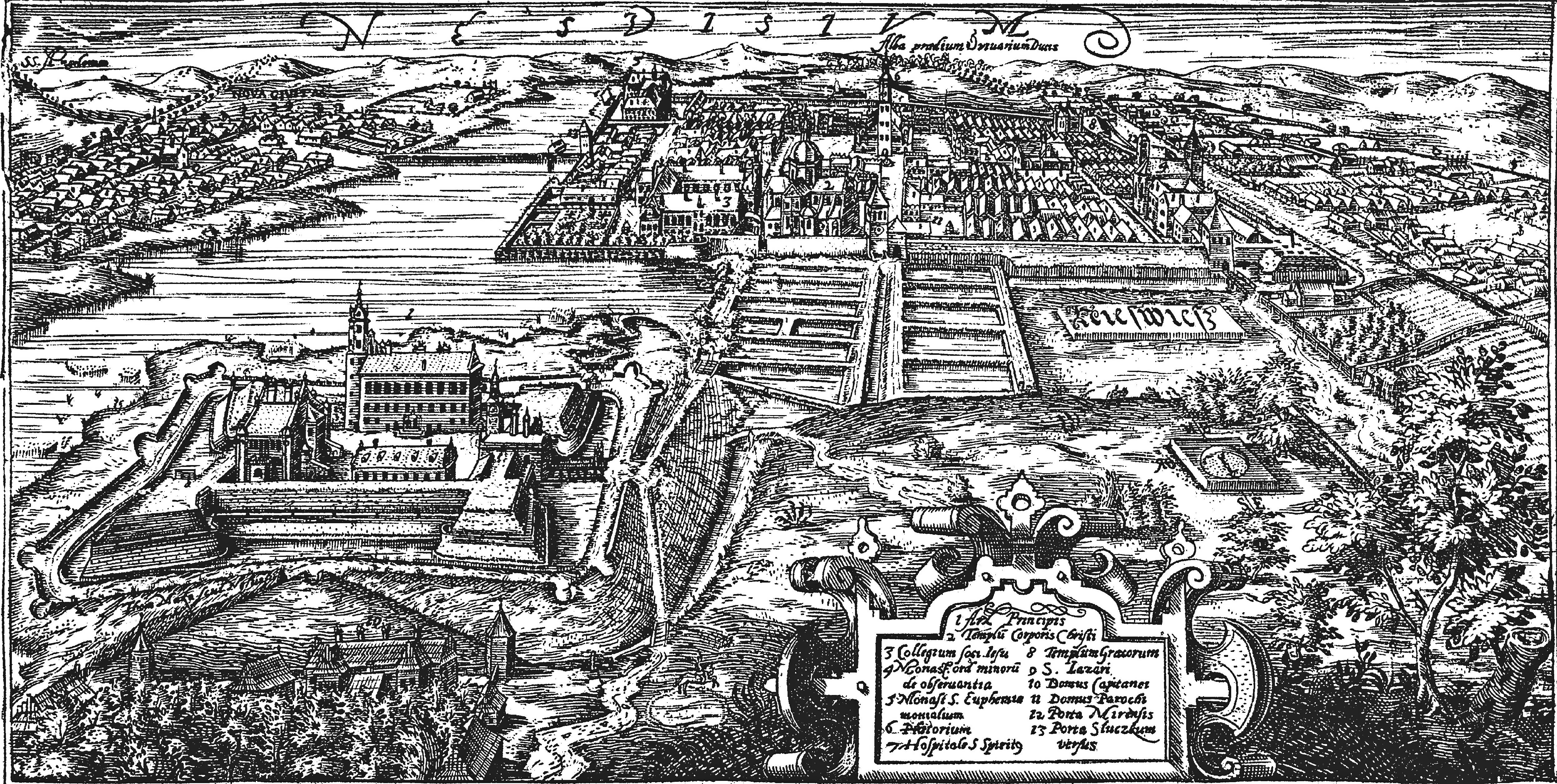
Nesvizh
Nesvizh, Niasviž ( be, Нясві́ж ; lt, Nesvyžius; pl, Nieśwież; russian: Не́свиж; yi, ניעסוויז; la, Nesvisium) is a city in Belarus. It is the administrative centre of the Nyasvizh District (''rajon'') of Minsk Region and site of Niasviž Castle, a World Heritage Site. Its 2009 population is 14,300. History Nesvizh was first documented in 1223. It was part of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania until 1793, but the Grand Duchy was part of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth since 1569. In the 15th century, while still a minor town, it belonged to the Kiszka family and later to the Radziwiłł family, and remained the family's seat until 1813. In 1561 or 1562 Maciej Kawęczyński founded the print works of the Polish Brethren. The first Belarusian language book printed in Latin script, a catechism by Symon Budny, was published in Nesvizh in 1562. The ''Nieśwież Bible'' ('' Biblia nieświeska''), one of the oldest Polish translations of the Bible, also b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stanisław Moniuszko
Stanisław Moniuszko (; May 5, 1819 – June 4, 1872) was a Polish composer, conductor and teacher. He wrote many popular art songs and operas, and his music is filled with patriotic folk themes of the peoples of the former Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth (mainly Poles, Lithuanians and Belarusians). He is generally referred to as "the father of Polish national opera". Since the 1990s Stanisław Moniuszko is being recognized in Belarus as an important figure of Belarusian culture. Life Moniuszko was born into a noble landowning family in Ubiel, Minsk Governorate (now Belarus). He initially took piano lessons with his mother and then continued his musical education in Warsaw, Minsk, and in Berlin under Carl Friedrich Rungenhagen. In 1858 he was appointed conductor at the Warsaw Opera and later became professor at the Warsaw Conservatory. He died in Warsaw, Congress Poland and was buried at Powązki Cemetery. Works For a complete list, see List of compositions by S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eustachy Tyszkiewicz
Count Eustachy Tyszkiewicz, Leliwa coat of arms, (18 April 1814 – 27 August 1873) was a Polish noble from the Tyszkiewicz family. He was an archaeologist and historian of the former Grand Duchy of Lithuania and White Ruthenia, then part of the Russian Empire. He is considered the first archaeologist to have undertaken a systematic study of historical sites in Belarus and Lithuania, and was highly influential on succeeding generations of archaeologists. In 1855 he founded the Museum of Antiquities in Vilnius (Vilna, Wilno), which is regarded as the predecessor institution of the National Museum of Lithuania. He donated his personal collection of archaeological and historical artifacts to start the museum. He was a younger brother of historian Konstanty Tyszkiewicz. Biography According to his memoirs, Tyszkiewicz was born in Minsk, not in Lahoysk, as researchers believe. Tyszkiewicz was the younger son of Pius Tyszkiewicz and his wife, Augusta, née Plater-Broel. He spent his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Czesław Miłosz
Czesław Miłosz (, also , ; 30 June 1911 – 14 August 2004) was a Polish-American poet, prose writer, translator, and diplomat. Regarded as one of the great poets of the 20th century, he won the 1980 Nobel Prize in Literature. In its citation, the Swedish Academy called Miłosz a writer who "voices man's exposed condition in a world of severe conflicts". Miłosz survived the German occupation of Warsaw during World War II and became a cultural attaché for the Polish government during the postwar period. When communist authorities threatened his safety, he defected to France and ultimately chose exile in the United States, where he became a professor at the University of California, Berkeley. His poetry—particularly about his wartime experience—and his appraisal of Stalinism in a prose book, ''The Captive Mind'', brought him renown as a leading ''émigré'' artist and intellectual. Throughout his life and work, Miłosz tackled questions of morality, politics, history, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Okhrana
The Department for Protecting the Public Security and Order (russian: Отделение по охранению общественной безопасности и порядка), usually called Guard Department ( rus, Охранное отделение, tr= okhrannoye otdelenie) and commonly abbreviated in modern English sources as Okhrana ( rus , Охрана, p=ɐˈxranə, a=Ru-охрана.ogg, t= the guard) was a secret-police force of the Russian Empire and part of the police department of the Ministry of Internal Affairs (MVD) in the late 19th century and early 20th century, aided by the Special Corps of Gendarmes. Overview Formed to combat political terrorism and left-wing revolutionary activity, the Okhrana operated offices throughout the Russian Empire, as well as satellite agencies in a number of foreign countries. It concentrated on monitoring the activities of Russian revolutionaries abroad, including in Paris, where the Okhrana agent Pyotr Rachkovsky ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warsaw
Warsaw ( pl, Warszawa, ), officially the Capital City of Warsaw,, abbreviation: ''m.st. Warszawa'' is the capital and largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the River Vistula in east-central Poland, and its population is officially estimated at 1.86 million residents within a greater metropolitan area of 3.1 million residents, which makes Warsaw the 7th most-populous city in the European Union. The city area measures and comprises 18 districts, while the metropolitan area covers . Warsaw is an Alpha global city, a major cultural, political and economic hub, and the country's seat of government. Warsaw traces its origins to a small fishing town in Masovia. The city rose to prominence in the late 16th century, when Sigismund III decided to move the Polish capital and his royal court from Kraków. Warsaw served as the de facto capital of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth until 1795, and subsequently as the seat of Napoleon's Duchy of Warsaw. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kraków
Kraków (), or Cracow, is the second-largest and one of the oldest cities in Poland. Situated on the Vistula River in Lesser Poland Voivodeship, the city dates back to the seventh century. Kraków was the official capital of Poland until 1596 and has traditionally been one of the leading centres of Polish academic, economic, cultural and artistic life. Cited as one of Europe's most beautiful cities, its Old Town with Wawel Royal Castle was declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1978, one of the first 12 sites granted the status. The city has grown from a Stone Age settlement to Poland's second-most-important city. It began as a hamlet on Wawel Hill and was reported by Ibrahim Ibn Yakoub, a merchant from Cordoba, as a busy trading centre of Central Europe in 985. With the establishment of new universities and cultural venues at the emergence of the Second Polish Republic in 1918 and throughout the 20th century, Kraków reaffirmed its role as a major national academic and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kurier Wileński
''Kurier Wileński'' (literally: ''Vilnian Courier'') is the main Polish-language newspaper in Lithuania. Printed in Vilnius, it is the only Polish-language daily newspaper published east of Poland. A direct descendant of both the 19th-century newspaper of the same name and the ' newspaper, created by the Soviet authorities in 1953 as a means of Sovietization of the Polish diaspora left in the Polish areas annexed by the Soviet Union. The newspaper is a member of the European Association of Daily Newspapers in Minority and Regional Languages (MIDAS). According to TNS Gallup media research, ''Kurier Wileński'' 36,800 people or 1.4% of Lithuania's population read at least one issue out of the last six in summer 2008, but that measure dropped to 0.3% in spring 2010. History Early history The newspaper was first founded under the name of ''Kurier Litewski'' in 1796 in Grodno (modern Hrodna). The following year it moved to Vilna (modern Vilnius, Lithuania), where it became one of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bareikiškės
Bareikiškės is a village in Vilnius district municipality, Lithuania. According to the 2011 census, it had population of 78. There is a library and cottage-like block of flats in Bareikiškės. A museum of Władysław Syrokomla Ludwik Władysław Franciszek Kondratowicz (29 September 1823 – 15 September 1862), better known as Władysław Syrokomla, was a Polish romantic poet, writer and translator working in Vilnius and Vilna Governorate, then Russian Empire. Biogr ... in a manor, that belonged to him, is situated in Bareikiškės. Stanisław Moniuszko was a frequent visitor of Bareikiškės manor. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Bareikiškės Villages in Vilnius County Vilnius District Municipality ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Załucze
Załucze is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Niedrzwica Duża, within Lublin County, Lublin Voivodeship The Lublin Voivodeship, also known as the Lublin Province ( Polish: ''województwo lubelskie'' ), is a voivodeship (province) of Poland, located in southeastern part of the country. It was created on January 1, 1999, out of the former Lublin, C ..., in eastern Poland. It lies approximately south of Niedrzwica Duża and south-west of the regional capital Lublin. References Villages in Lublin County {{LublinCounty-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syrokomla Coat Of Arms
Syrokomla - is a Polish coat of arms. It was used by several szlachta families in the times of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. History According to the legend, the coat of arms was granted to certain knight named Syrokomla of Abdank coat of arms after he won a duel with a pagan Old Prussian warrior in 1331 during the reign of Ladislaus the Short. After this victory he was awarded with a right to add a golden cross to his coat of arms, to underline that he is one of the defenders of Christianity. Blazon Gules, Abdank (''W-shaped symbol'') Argent, with a cross Or (sometimes Argent) attached above. In the crest the symbol repeated. Notable bearers Notable bearers of this coat of arms include: * Michał Grocholski * Franciszek Grocholski * Władysław Syrokomla (1823-1862), writer External links * Syrokomla Coat of Arms & bearers. * See also * Polish heraldry * Heraldry Heraldry is a discipline relating to the design, display and study of armorial bearings (kn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |