|
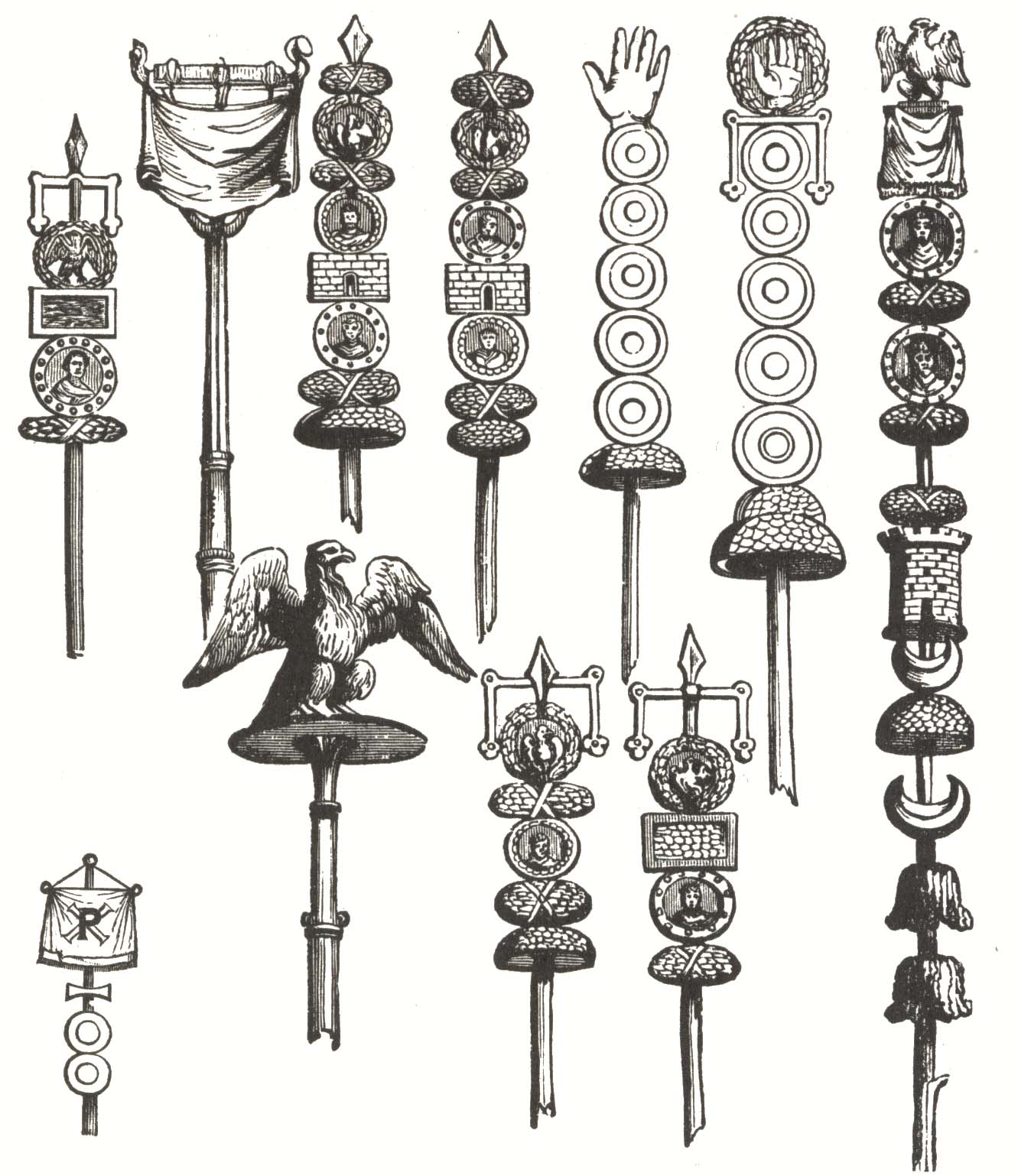
Vexilloid
A vexilloid is any flag-like (vexillary) object used by countries, organisations, or individuals as a form of representation other than flags. American vexillologist Whitney Smith coined the term ''vexilloid'' in 1958, defining it as This includes vexilla, banderoles, pennons, streamers, heraldic flags, standards, and gonfalons. Examples include the Sassanid battle standard Derafsh Kaviani, and the standards of the Roman legions such as the eagle of Augustus Caesar's Xth legion and the dragon standard of the Sarmatians; the latter was allowed to fly freely in the wind, carried by a horseman, but depictions suggest that it bore more similarity to an elongated dragon kite than to a simple flag. The use of flags replaced the use of vexilloids for general purposes during late medieval times between about 1100 to about 1400. However, vexilloids still remain in use for specialised purposes, such as for some military units or to symbolise various organisations such as frater ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flag
A flag is a piece of fabric (most often rectangular or quadrilateral) with a distinctive design and colours. It is used as a symbol, a signalling device, or for decoration. The term ''flag'' is also used to refer to the graphic design employed, and flags have evolved into a general tool for rudimentary signalling and identification, especially in environments where communication is challenging (such as the maritime environment, where semaphore is used). Many flags fall into groups of similar designs called flag families. The study of flags is known as " vexillology" from the Latin , meaning "flag" or "banner". National flags are patriotic symbols with widely varied interpretations that often include strong military associations because of their original and ongoing use for that purpose. Flags are also used in messaging, advertising, or for decorative purposes. Some military units are called "flags" after their use of flags. A ''flag'' (Arabic: ) is equivalent to a b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sassanid
The Sasanian () or Sassanid Empire, officially known as the Empire of Iranians (, ) and also referred to by historians as the Neo-Persian Empire, was the last Iranian empire before the early Muslim conquests of the 7th-8th centuries AD. Named after the House of Sasan, it endured for over four centuries, from 224 to 651 AD, making it the longest-lived Persian imperial dynasty. The Sasanian Empire succeeded the Parthian Empire, and re-established the Persians as a major power in late antiquity alongside its neighbouring arch-rival, the Roman Empire (after 395 the Byzantine Empire).Norman A. Stillman ''The Jews of Arab Lands'' pp 22 Jewish Publication Society, 1979 International Congress of Byzantine Studies ''Proceedings of the 21st International Congress of Byzantine Studies, London, 21–26 August 2006, Volumes 1–3'' pp 29. Ashgate Pub Co, 2006 The empire was founded by Ardashir I, an Iranian ruler who rose to power as Parthia weakened from internal strife and wars with t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vexillum
The ''vexillum'' (; plural ''vexilla'') was a flag-like object used as a military standard by units in the Ancient Roman army. Use in Roman army The word ''vexillum'' is a derivative of the Latin word, ''velum'', meaning a sail, which confirms the historical evidence (from coins and sculpture) that ''vexilla'' were literally "little sails": flag-like standards. In the ''vexillum'', the cloth was draped from a horizontal crossbar suspended from a staff. That is unlike most modern flags in which the "hoist" of the cloth is attached directly to a vertical staff. The bearer of a ''vexillum'' was known as a '' vexillarius'' or ''vexillifer''.Vexillum ''Flagspot.net'', retrieved March 18, 2011 Just as in the case of the |
Narmer Palette
The Narmer Palette, also known as the Great Hierakonpolis Palette or the Palette of Narmer, is a significant Egyptian archeological find, dating from about the 31st century BC, belonging, at least nominally, to the category of cosmetic palettes. It contains some of the earliest hieroglyphic inscriptions ever found. The tablet is thought by some to depict the unification of Upper and Lower Egypt under the king Narmer. Along with the Scorpion Macehead and the Narmer Maceheads, also found together in the main deposit at Nekhen, the Narmer Palette provides one of the earliest known depictions of an Egyptian king. On one side, the king is depicted with the bulbed White Crown of Upper (southern) Egypt, and the other side depicts the king wearing the level Red Crown of Lower (northern) Egypt, which also makes it the earliest known example of a king wearing both types of headdress. The Palette shows many of the classic conventions of Ancient Egyptian art, which must already have been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Derafsh Kaviani
Derafsh Kaviani ( fa, درفش کاویانی) was the legendary royal standard Derafsh (in Latin: vexilloid) of Iran (Persia) used since ancient times until the fall of the Sasanian Empire. The banner was also sometimes called the "Standard of Jamshid" (''Drafš-ī Jamshid'' ), the "Standard of Fereydun" (''Drafš-ī Freydun'' ) and the "Royal Standard" (''Drafš-ī Kayi'' ). Meaning and origins The name ''Drafš-e Kāvīān'' means "the standard of the kay(s)" (i.e., "kings", ''kias'', ''kavis'' ) or "of Kāva." The latter meaning is an identification with an Iranian legend in which the ''Derafš-e Kāvīān'' was the standard of a mythological Persian blacksmith-turned-hero named Kaveh (Persian: کاوه), who led a popular uprising against the foreign demon-like ruler Zahhak (Persian: ضحاک). Recalling the legend, the 10th-century epic ''Shahnameh'' recasts Zahhak as an evil and tyrannical ruler, against whom Kaveh called the people to arms, using his leather blacksm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fraternal Organisation
A fraternity (from Latin ''frater'': "brother"; whence, " brotherhood") or fraternal organization is an organization, society, club or fraternal order traditionally of men associated together for various religious or secular aims. Fraternity in the Western concept developed in the Christian context, notably with the religious orders in the Catholic Church during the Middle Ages. The concept was eventually further extended with medieval confraternities and guilds. In the early modern era, these were followed by fraternal orders such as Freemasons and Odd Fellows, along with gentlemen's clubs, student fraternities, and fraternal service organizations. Members are occasionally referred to as a ''brother'' or – usually in a religious context – ''Frater'' or ''Friar''. Today, connotations of fraternities vary according to context including companionships and brotherhoods dedicated to the religious, intellectual, academic, physical, or social pursuits of its members. Additionall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staff Of Office
A staff of office is a staff, the carrying of which often denotes an official's position, a social rank or a degree of social prestige. Apart from the ecclesiastical and ceremonial usages mentioned below, there are less formal usages. A gold- or silver-topped cane can express social standing (or dandyism). Teachers or prefects in schools traditionally carried less elaborate canes which marked their right (and potential threat) to administer canings, and military officers carry a residual threat of physical punishment in their swagger sticks. Orchestral conductors have in their batons symbols of authority as well as tools of their trade. Ecclesiastical use Churchwardens (and sometimes sidesmen) traditionally carry staves or wands on special occasions as an emblem of their office. In the Eastern Orthodox Church and some of the Oriental Orthodox Churches an ecclesiastical walking stick is used by bishops, archimandrites and hegumens (abbots) when walking outside. It is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gerzeh Culture
The Gerzeh culture, also called Naqada II, refers to the archaeological stage at Gerzeh (also Girza or Jirzah), a prehistoric Egyptian cemetery located along the west bank of the Nile. The necropolis is named after el-Girzeh, the nearby contemporary town in Egypt. Gerzeh is situated only several miles due east of the oasis of Faiyum. The Gerzeh culture is a material culture identified by archaeologists. It is the second of three phases of the prehistoric Naqada cultures and so is also known as Naqada II. The Gerzeh culture was preceded by the Amratian culture ("Naqada I") and followed by the Naqada III ("protodynastic" or "Semainian culture"). Historical context Sources differ on dating, some saying use of the culture distinguishes itself from the Amratian and begins circa 3500 BC lasting through circa 3200 BC. Accordingly, some authorities place the onset of the Gerzeh coincident with the Amratian or Badari cultures, i.e. c.3800 BC to 3650 BC even though ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Standards
Roman or Romans most often refers to: *Rome, the capital city of Italy *Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD *Roman people, the people of ancient Rome *'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a letter in the New Testament of the Christian Bible Roman or Romans may also refer to: Arts and entertainment Music * Romans (band), a Japanese pop group * ''Roman'' (album), by Sound Horizon, 2006 * ''Roman'' (EP), by Teen Top, 2011 *" Roman (My Dear Boy)", a 2004 single by Morning Musume Film and television * Film Roman, an American animation studio * ''Roman'' (film), a 2006 American suspense-horror film * ''Romans'' (2013 film), an Indian Malayalam comedy film * ''Romans'' (2017 film), a British drama film * ''The Romans'' (''Doctor Who''), a serial in British TV series People * Roman (given name), a given name, including a list of people and fictional characters * Roman (surname), including a list of people named Roman or Romans *Ῥω� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Units
Military organization or military organisation is the structuring of the armed forces of a state so as to offer such military capability as a national defense policy may require. In some countries paramilitary forces are included in a nation's armed forces, though not considered military. Armed forces that are not a part of military or paramilitary organizations, such as insurgent forces, often mimic military organizations, or use ''ad hoc'' structures, while formal military organization tends to use hierarchical forms. History The use of formalized ranks in a hierarchical structure came into widespread use with the Roman Army. In modern times, executive control, management and administration of military organization is typically undertaken by governments through a government department within the structure of public administration, often known as a ministry of defence or department of defense. These in turn manage military branches that themselves command formations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victory Stele Of Naram-Sin
The Victory Stele of Naram-Sin is a stele that dates to approximately 2254–2218 BC, in the time of the Akkadian Empire, and is now at the Louvre in Paris. The relief measures 200cm in height (6' 7") and was carved in pink limestone, with cuneiform writings in Akkadian and Elamite. It depicts the King Naram-Sin of Akkad leading the Akkadian army to victory over the Lullubi, a mountain people from the Zagros Mountains. The stele shows a narrative scene of the king crossing the steep slopes into enemy territory; on the left are the ordered imperial forces keeping in rank while marching over the disordered defenders that lie broken and defeated. Naram-Sin is shown as by far the most important figure, towering over his enemy and troops and all eyes gaze up toward him. The weak and chaotic opposing forces are shown being thrown from atop the mountainside, impaled by spears, fleeing and begging Naram-Sin for mercy as well as being trampled underfoot by Naram-Sin himself. This is sup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |