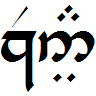|
Valinor
Valinor ( Quenya'': Land of the Valar'') or the Blessed Realms is a fictional location in J. R. R. Tolkien's legendarium, the home of the immortal Valar on the continent of Aman, far to the west of Middle-earth; he used the name Aman mainly to mean Valinor. It included Eldamar, the land of the Elves, who as immortals were permitted to live in Valinor. Aman was known somewhat misleadingly as "the Undying Lands", but the land itself does not cause mortals to live forever., #156 to Father R. Murray, SJ, November 1954 However, only immortal beings were generally allowed to reside there. Exceptions were made for the surviving bearers of the One Ring: Bilbo and Frodo Baggins and Sam Gamgee, who dwelt there for a time, and the dwarf Gimli., "The Grey Havens", and Appendix B, entry for S.R. 1482 and 1541., #249 to Michael George Tolkien, October 1963 Scholars have described the similarity of Tolkien's myth of the attempt of Númenor to capture Aman to the biblical Tower of Babel and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valinor
Valinor ( Quenya'': Land of the Valar'') or the Blessed Realms is a fictional location in J. R. R. Tolkien's legendarium, the home of the immortal Valar on the continent of Aman, far to the west of Middle-earth; he used the name Aman mainly to mean Valinor. It included Eldamar, the land of the Elves, who as immortals were permitted to live in Valinor. Aman was known somewhat misleadingly as "the Undying Lands", but the land itself does not cause mortals to live forever., #156 to Father R. Murray, SJ, November 1954 However, only immortal beings were generally allowed to reside there. Exceptions were made for the surviving bearers of the One Ring: Bilbo and Frodo Baggins and Sam Gamgee, who dwelt there for a time, and the dwarf Gimli., "The Grey Havens", and Appendix B, entry for S.R. 1482 and 1541., #249 to Michael George Tolkien, October 1963 Scholars have described the similarity of Tolkien's myth of the attempt of Númenor to capture Aman to the biblical Tower of Babel and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elves (Middle-Earth)
In J. R. R. Tolkien's writings, Elves are the first fictional race to appear in Middle-earth. Unlike Men and Dwarves, Elves are immortal. They feature in '' The Hobbit'' and ''The Lord of the Rings''. Their history is described in detail in ''The Silmarillion''. Tolkien derived his Elves from mentions in the ancient poetry and languages of Northern Europe, especially Old English. These suggested to him that Elves were large, dangerous, beautiful, lived in wild natural places, and practised archery. He invented languages for the Elves, including Sindarin and Quenya. Tolkien-style Elves have become a staple of fantasy literature. They have appeared, too, in film and role-playing game adaptations of Tolkien's works. Origins Germanic word The modern English word '' elf'' derives from the Old English word '' ælf'' (which has cognates in all other Germanic languages). Numerous types of elves appear in Germanic mythology; the West Germanic concept appears to have come to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manwë (Middle-earth)
The Valar (; singular Vala) are characters in J. R. R. Tolkien's legendarium. They are "angelic powers" or "gods", #154 to Naomi Mitchison, September 1954 subordinate to the one God ( Eru Ilúvatar). The Ainulindalë describes how those of the Ainur who chose to enter the World (Arda) to complete its material development after its form was determined by the Music of the Ainur are called the Valar, or "the Powers of the World". The Valaquenta indicates that the Elves generally reserved the term "Valar" for the mightiest of these, calling the others the Maiar. The Valar are mentioned briefly in ''The Lord of the Rings'' but were developed earlier in material published posthumously in ''The Silmarillion'', ''The History of Middle-earth'', and ''Unfinished Tales''. Scholars have noted that the Valar resemble angels in Christianity but that Tolkien presented them rather more like pagan gods. Their role in providing what the characters on Middle-earth experience as luck or providen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vala (Middle-earth)
The Valar (; singular Vala) are characters in J. R. R. Tolkien's legendarium. They are "angelic powers" or "gods", #154 to Naomi Mitchison, September 1954 subordinate to the one God ( Eru Ilúvatar). The Ainulindalë describes how those of the Ainur who chose to enter the World (Arda) to complete its material development after its form was determined by the Music of the Ainur are called the Valar, or "the Powers of the World". The Valaquenta indicates that the Elves generally reserved the term "Valar" for the mightiest of these, calling the others the Maiar. The Valar are mentioned briefly in ''The Lord of the Rings'' but were developed earlier in material published posthumously in ''The Silmarillion'', ''The History of Middle-earth'', and ''Unfinished Tales''. Scholars have noted that the Valar resemble angels in Christianity but that Tolkien presented them rather more like pagan gods. Their role in providing what the characters on Middle-earth experience as luck or provi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ekkaia
The cosmology of J. R. R. Tolkien's legendarium combines aspects of Christian theology and metaphysics with pre-modern cosmological concepts in the flat Earth paradigm, along with the modern spherical Earth view of the Solar System. The created world, ''Eä'', includes the planet Arda, corresponding to the Earth. It is created flat, with the dwelling of the godlike Valar at its centre. When this is marred by the evil Vala Melkor, the world is reshaped, losing its perfect symmetry, and the Valar move to Valinor, but the Elves can still sail there from Middle-earth. When Men try to go there, hoping for immortality, Valinor and its continent of Aman are removed from Arda, which is reshaped as a round world. Scholars have compared the implied cosmology with that of Tolkien's religion, Roman Catholicism, and of Medieval poetry such as ''Pearl'' or Dante's '' Paradiso'', where there are three parts, Earth, Purgatory or the Earthly Paradise, and Heaven or the Celestial Paradise. Schol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belegaer
The cosmology of J. R. R. Tolkien's legendarium combines aspects of Christian theology and metaphysics with pre-modern cosmological concepts in the flat Earth paradigm, along with the modern spherical Earth view of the Solar System. The created world, ''Eä'', includes the planet Arda, corresponding to the Earth. It is created flat, with the dwelling of the godlike Valar at its centre. When this is marred by the evil Vala Melkor, the world is reshaped, losing its perfect symmetry, and the Valar move to Valinor, but the Elves can still sail there from Middle-earth. When Men try to go there, hoping for immortality, Valinor and its continent of Aman are removed from Arda, which is reshaped as a round world. Scholars have compared the implied cosmology with that of Tolkien's religion, Roman Catholicism, and of Medieval poetry such as ''Pearl'' or Dante's '' Paradiso'', where there are three parts, Earth, Purgatory or the Earthly Paradise, and Heaven or the Celestial Paradise. Schol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sundering Of The Elves
In J. R. R. Tolkien's legendarium, the Elves or Quendi are a sundered (divided) people. They awoke at Cuiviénen on the continent of Middle-earth, where they were divided into three tribes: Minyar (the Firsts), Tatyar (the Seconds) and Nelyar (the Thirds). After some time, they were summoned by Oromë to live with the Valar in Valinor, on Aman. That summoning and the Great Journey that followed split the Elves into two main groups (and many minor ones), which were never fully reunited. Tolkien stated that the stories were made to create a world for his elvish languages, not the reverse. The Tolkien scholar Tom Shippey writes that ''The Silmarillion'' derived from the linguistic relationship between the two languages, Quenya and Sindarin, of the divided Elves. The Tolkien scholar Verlyn Flieger states that Tolkien used the Indo-European type of proto-language as his model. In her view, the sundering of the Elves reflects the progressive decline and fall in Middle-earth from i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quenya
Quenya ()Tolkien wrote in his "Outline of Phonology" (in '' Parma Eldalamberon'' 19, p. 74) dedicated to the phonology of Quenya: is "a sound as in English ''new''". In Quenya is a combination of consonants, ibidem., p. 81. is a constructed language, one of those devised by J. R. R. Tolkien for the Elves in his Middle-earth fiction. Tolkien began devising the language around 1910, and restructured its grammar several times until it reached its final state. The vocabulary remained relatively stable throughout the creation process. He successively changed the language's name from ''Elfin'' and ''Qenya'' to the eventual ''Quenya''. Finnish had been a major source of inspiration, but Tolkien was also fluent in Latin and Old English, and was familiar with Greek, Welsh (the latter being the primary inspiration for Sindarin, Tolkien's other major Elvish language), and other ancient Germanic languages, particularly Gothic, during his development of Quenya. A notable feature of To ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frodo Baggins
Frodo Baggins is a fictional character in J. R. R. Tolkien's writings, and one of the protagonists in '' The Lord of the Rings''. Frodo is a hobbit of the Shire who inherits the One Ring from his cousin Bilbo Baggins, described familiarly as "uncle", and undertakes the quest to destroy it in the fires of Mount Doom in Mordor. He is mentioned in Tolkien's posthumously published works, '' The Silmarillion'' and ''Unfinished Tales''. Frodo is repeatedly wounded during the quest, and becomes increasingly burdened by the Ring as it nears Mordor. He changes, too, growing in understanding and compassion, and avoiding violence. On his return to the Shire, he is unable to settle back into ordinary life; two years after the Ring's destruction, he is allowed to take ship to the earthly paradise of Valinor. Frodo's name comes from the Old English name '' Fróda'', meaning "wise by experience". Commentators have written that he combines courage, selflessness, and fidelity, and that a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle-earth
Middle-earth is the fictional setting of much of the English writer J. R. R. Tolkien's fantasy. The term is equivalent to the '' Miðgarðr'' of Norse mythology and ''Middangeard'' in Old English works, including ''Beowulf''. Middle-earth is the human-inhabited world, that is, the central continent of the Earth, in Tolkien's imagined mythological past. Tolkien's most widely read works, '' The Hobbit'' and ''The Lord of the Rings'', are set entirely in Middle-earth. "Middle-earth" has also become a short-hand term for Tolkien's legendarium, his large body of fantasy writings, and for the entirety of his fictional world. Middle-earth is the main continent of Earth (Arda) in an imaginary period of the Earth's past, ending with Tolkien's Third Age, about 6,000 years ago. Tolkien's tales of Middle-earth mostly focus on the north-west of the continent. This part of Middle-earth is suggestive of Europe, the north-west of the Old World, with the environs of the Shire reminiscen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Númenor
Númenor, also called Elenna-nórë or Westernesse, is a fictional place in J. R. R. Tolkien's writings. It was the kingdom occupying a large island to the west of Middle-earth, the main setting of Tolkien's writings, and was the greatest civilization of Men. However, after centuries of prosperity many of the inhabitants ceased to worship the One God, Eru Ilúvatar, and rebelled against the Valar, resulting in the destruction of the island and the death of most of its people. Tolkien intended Númenor to allude to the legendary Atlantis., ##131, 154, 156, 227. Commentators have noted that the destruction of Númenor echoes the Biblical stories of the fall of man and the destruction of Sodom and Gomorrah, and John Milton's '' Paradise Lost''. Fictional geography Physical geography ''A Description of the Island of Númenor'', published in '' Unfinished Tales'', was supposedly derived from the archives of Gondor. The island of Númenor was in the Great Sea, closer t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tolkien's Legendarium
Tolkien's legendarium is the body of J. R. R. Tolkien's Mythopoeia, mythopoeic writing, unpublished in his lifetime, that forms the background to his ''The Lord of the Rings'', and which his son Christopher Tolkien, Christopher summarized in his compilation of ''The Silmarillion'' and documented in his 12-volume series ''The History of Middle-earth''. The legendarium's origins reach back to 1914, when Tolkien began Poetry in The Lord of the Rings, writing poems and story sketches, Tolkien's maps, drawing maps, and Languages constructed by J. R. R. Tolkien, inventing languages and names as a private project to create a unique English mythology. The earliest story drafts (of ''The Book of Lost Tales'') are from 1916; he revised and rewrote these for most of his adult life. ''The Hobbit'' (1937), Tolkien's first published novel, was not originally part of the larger mythology but became linked to it. Both ''The Hobbit'' and ''The Lord of the Rings'' (1954 and 1955) took place in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |