|
Upper Lip
The lips are the visible body part at the mouth of many animals, including humans. Lips are soft, movable, and serve as the opening for food intake and in the articulation of sound and speech. Human lips are a tactile sensory organ, and can be an erogenous zone when used in kissing and other acts of intimacy. Structure The upper and lower lips are referred to as the "Labium superius oris" and "Labium inferius oris", respectively. The juncture where the lips meet the surrounding skin of the mouth area is the vermilion border, and the typically reddish area within the borders is called the vermilion zone. The vermilion border of the upper lip is known as the cupid's bow. The fleshy protuberance located in the center of the upper lip is a tubercle known by various terms including the procheilon (also spelled ''prochilon''), the "tuberculum labii superioris", and the "labial tubercle". The vertical groove extending from the procheilon to the nasal septum is called the philt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inferior Labial Artery
The inferior labial artery (inferior labial branch of facial artery) arises near the angle of the mouth as a branch of the facial artery; it passes upward and forward beneath the triangularis and, penetrating the orbicularis oris, runs in a tortuous course along the edge of the lower lip between this muscle and the mucous membrane. It supplies the labial glands, the mucous membrane, and the muscles of the lower lip The lips are the visible body part at the mouth of many animals, including humans. Lips are soft, movable, and serve as the opening for food intake and in the articulation of sound and speech. Human lips are a tactile sensory organ, and can be ...; and anastomoses with the artery of the opposite side, and with the mental branch of the inferior alveolar artery. Additional images File:Lateral head anatomy detail.jpg, Lateral head anatomy detail File:Head ap anatomy.jpg, Head anatomy anterior view File:Slide2bbb.JPG, Inferior labial artery References Exte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pigment
A pigment is a colored material that is completely or nearly insoluble in water. In contrast, dyes are typically soluble, at least at some stage in their use. Generally dyes are often organic compounds whereas pigments are often inorganic compounds. Pigments of prehistoric and historic value include ochre, charcoal, and lapis lazuli. Economic impact In 2006, around 7.4 million tons of inorganic, organic, and special pigments were marketed worldwide. Estimated at around US$14.86 billion in 2018 and will rise at over 4.9% CAGR from 2019 to 2026. The global demand for pigments was roughly US$20.5 billion in 2009. According to an April 2018 report by ''Bloomberg Businessweek'', the estimated value of the pigment industry globally is $30 billion. The value of titanium dioxide – used to enhance the white brightness of many products – was placed at $13.2 billion per year, while the color Ferrari red is valued at $300 million each year. Physical principles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Lip
The lips are the visible body part at the mouth of many animals, including humans. Lips are soft, movable, and serve as the opening for food intake and in the articulation of sound and speech. Human lips are a tactile sensory organ, and can be an erogenous zone when used in kissing and other acts of intimacy. Structure The upper and lower lips are referred to as the "Labium superius oris" and "Labium inferius oris", respectively. The juncture where the lips meet the surrounding skin of the mouth area is the vermilion border, and the typically reddish area within the borders is called the vermilion zone. The vermilion border of the upper lip is known as the cupid's bow. The fleshy protuberance located in the center of the upper lip is a tubercle known by various terms including the procheilon (also spelled ''prochilon''), the "tuberculum labii superioris", and the "labial tubercle". The vertical groove extending from the procheilon to the nasal septum is called the phi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Levator Labii Superioris
The levator labii superioris (pl. ''levatores labii superioris'', also called quadratus labii superioris, pl. ''quadrati labii superioris'') is a muscle of the human body used in facial expression. It is a broad sheet, the origin of which extends from the side of the nose to the zygomatic bone. Structure Its medial fibers form the ''angular head'' (also known as the levator labii superioris alaeque nasi muscle,) which arises by a pointed extremity from the upper part of the frontal process of the maxilla and passing obliquely downward and lateralward divides into two slips. One of these is inserted into the greater alar cartilage and skin of the nose; the other is prolonged into the lateral part of the upper lip, blending with the infraorbital head and with the orbicularis oris. The intermediate portion or ''infraorbital head'' arises from the lower margin of the orbit immediately above the infraorbital foramen, some of its fibers being attached to the maxilla The ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anterior Surface Of The Body Of The Maxilla
The maxilla (plural: ''maxillae'' ) in vertebrates is the upper fixed (not fixed in Neopterygii) bone of the jaw formed from the fusion of two maxillary bones. In humans, the upper jaw includes the hard palate in the front of the mouth. The two maxillary bones are fused at the intermaxillary suture, forming the anterior nasal spine. This is similar to the mandible (lower jaw), which is also a fusion of two mandibular bones at the mandibular symphysis. The mandible is the movable part of the jaw. Structure In humans, the maxilla consists of: * The body of the maxilla * Four processes ** the zygomatic process ** the frontal process of maxilla ** the alveolar process ** the palatine process * three surfaces – anterior, posterior, medial * the Infraorbital foramen * the maxillary sinus * the incisive foramen Articulations Each maxilla articulates with nine bones: * two of the cranium: the frontal and ethmoid * seven of the face: the nasal, zygomatic, lacrimal, inferior nas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbicularis Oris
In human anatomy, the orbicularis oris muscle is a complex of muscles in the lips that encircles the mouth. It is a sphincter, or circular muscle, but it is actually composed of four independent quadrants that interlace and give only an appearance of circularity.Saladin, "Anatomy & Physiology: The Unity of Form and Function". 5th edition. McGraw Hill. Page 330 It is also one of the muscles used in the playing of all brass instruments and some woodwind instruments. This muscle closes the mouth and puckers the lips when it contracts. Structure The orbicularis oris is not a simple sphincter muscle like the orbicularis oculi; it consists of numerous strata of muscular fibers surrounding the orifice of the mouth, but having different direction. It consists partly of fibers derived from the other facial muscles which are inserted into the lips, and partly of fibers proper to the lips. Of the former, a considerable number are derived from the buccinator and form the deeper stratum of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Depressor Labii Inferioris Muscle
The depressor labii inferioris (or quadratus labii inferioris) is a facial muscle. It helps to lower the bottom lip. Structure The depressor labii inferioris muscle arises from the lateral surface of the mandible. This is below the mental foramen, and the origin may be around 3 cm wide. It inserts on the skin of the lower lip, blending in with the orbicularis oris muscle around 2 cm wide. At its origin, depressor labii is continuous with the fibers of the platysma muscle. Some yellow fat is intermingled with the fibers. Nerve supply The depressor labii inferioris muscle is supplied by the marginal mandibular branch of the facial nerve. Function The depressor labii inferioris muscle helps to depress and everts the lower lip. It is the most important of the muscles of the lower lip for this function. It is an antagonist of the orbicularis oris muscle. It is needed to expose the mandibular (lower) teeth during smiling. Clinical significance Resection The depressor labi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Body Of The Mandible
In anatomy, the mandible, lower jaw or jawbone is the largest, strongest and lowest bone in the human facial skeleton. It forms the lower jaw and holds the lower teeth in place. The mandible sits beneath the maxilla. It is the only movable bone of the skull (discounting the ossicles of the middle ear). It is connected to the temporal bones by the temporomandibular joints. The bone is formed in the fetus from a fusion of the left and right mandibular prominences, and the point where these sides join, the mandibular symphysis, is still visible as a faint ridge in the midline. Like other symphyses in the body, this is a midline articulation where the bones are joined by fibrocartilage, but this articulation fuses together in early childhood.Illustrated Anatomy of the Head and Neck, Fehrenbach and Herring, Elsevier, 2012, p. 59 The word "mandible" derives from the Latin word ''mandibula'', "jawbone" (literally "one used for chewing"), from '' mandere'' "to chew" and ''-bula'' (ins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Pharyngeal Arch
The pharyngeal arches, also known as visceral arches'','' are structures seen in the embryonic development of vertebrates that are recognisable precursors for many structures. In fish, the arches are known as the branchial arches, or gill arches. In the human embryo, the arches are first seen during the fourth week of development. They appear as a series of outpouchings of mesoderm on both sides of the developing pharynx. The vasculature of the pharyngeal arches is known as the aortic arches. In fish, the branchial arches support the gills. Structure In vertebrates, the pharyngeal arches are derived from all three germ layers (the primary layers of cells that form during embryogenesis). Neural crest cells enter these arches where they contribute to features of the skull and facial skeleton such as bone and cartilage. However, the existence of pharyngeal structures before neural crest cells evolved is indicated by the existence of neural crest-independent mechanisms of pharyn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandibular Prominence
The mandibular prominence is an embryological structure which gives rise to the lower portion of the face. The mandible and lower lip derive from it. The mesenchymal cells within the mandibular prominence condense to form Meckel's cartilage. It is innervated by the mandibular nerve In neuroanatomy, the mandibular nerve (V) is the largest of the three divisions of the trigeminal nerve, the fifth cranial nerve (CN V). Unlike the other divisions of the trigeminal nerve ( ophthalmic nerve, maxillary nerve) which contain only .... References External links * Embryology {{musculoskeletal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
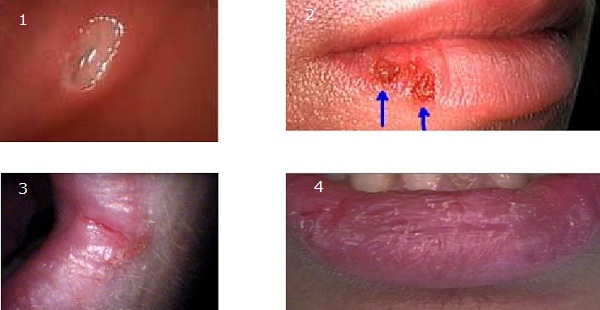
Chapped
Cheilitis is a medical condition characterized by inflammation of the lips. The inflammation may include the perioral skin (the skin around the mouth), the vermilion border, or the labial mucosa. The skin and the vermilion border are more commonly involved, as the mucosa is less affected by inflammatory and allergic reactions. ''Cheilitis'' is a general term, and there are many recognized types and different causes. According to its onset and course, cheilitis can be either acute or chronic. Most cheilitis is caused by exogenous factors such as dryness (chapping) and acute sun exposure. Allergic tests may identify allergens that cause cheilitis. Chapped lips Chapped lips (also known as cheilitis simplex or common cheilitis) is characterized by the cracking, fissuring, and peeling of the skin of the lips, and is one of the most common types of cheilitis. While both lips may be affected, the lower lip is the most common site. There may also be burning or the formation of large ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |