|
Types Of Karma
According to Jain karma theory, there are eight main types of karma (''Prikriti'') which are categorized as either ‘harming’ or ‘non-harming’, with each category further divided into four types. The harming karmas (''ghātiyā karmas'') directly affect the soul powers by impeding its perception, knowledge and energy, and also bring about delusion. These harming karmas are: ''darśanāvaraṇa'' (perception obscuring karma), ''gnanavarniya'' (knowledge obscuring karma), ''antarāya'' (obstacles creating karma) and ''mohanīya'' (deluding karma). The non-harming category (''aghātiyā karmas'') is responsible for the reborn soul's physical and mental circumstances (nāma), longevity (āyuś), spiritual potential (gotra) and experience of pleasant and unpleasant sensations (vedanīya). In other terms these non-harming karmas are: ''nāma'' (body determining karma), ''āyu'' (life span determining karma), ''gotra'' (status determining karma) and ''vedanīya'' (feeling prod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Types Of Karma
According to Jain karma theory, there are eight main types of karma (''Prikriti'') which are categorized as either ‘harming’ or ‘non-harming’, with each category further divided into four types. The harming karmas (''ghātiyā karmas'') directly affect the soul powers by impeding its perception, knowledge and energy, and also bring about delusion. These harming karmas are: ''darśanāvaraṇa'' (perception obscuring karma), ''gnanavarniya'' (knowledge obscuring karma), ''antarāya'' (obstacles creating karma) and ''mohanīya'' (deluding karma). The non-harming category (''aghātiyā karmas'') is responsible for the reborn soul's physical and mental circumstances (nāma), longevity (āyuś), spiritual potential (gotra) and experience of pleasant and unpleasant sensations (vedanīya). In other terms these non-harming karmas are: ''nāma'' (body determining karma), ''āyu'' (life span determining karma), ''gotra'' (status determining karma) and ''vedanīya'' (feeling prod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
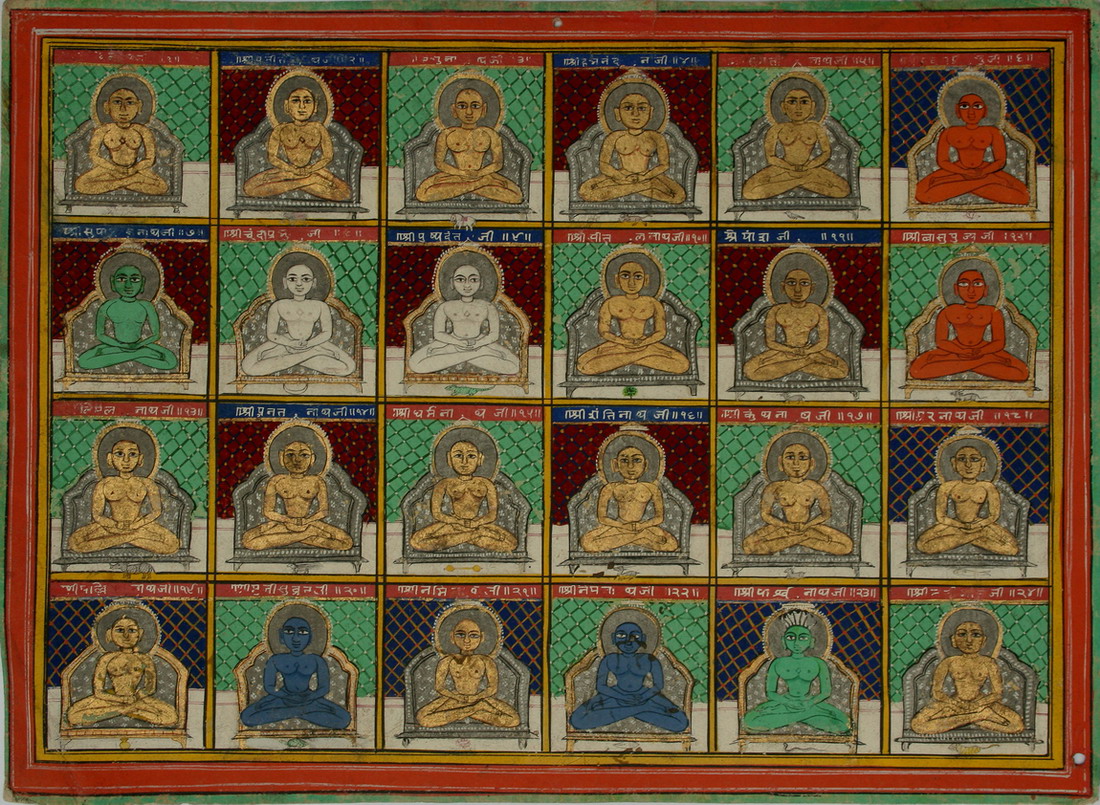
Tirthankara
In Jainism, a ''Tirthankara'' (Sanskrit: '; English: literally a ' ford-maker') is a saviour and spiritual teacher of the '' dharma'' (righteous path). The word ''tirthankara'' signifies the founder of a '' tirtha'', which is a fordable passage across the sea of interminable births and deaths, the '' saṃsāra''. According to Jains, a ''Tirthankara'' is an individual who has conquered the ''saṃsāra'', the cycle of death and rebirth, on their own, and made a path for others to follow. After understanding the true nature of the self or soul, the ''Tīrthaṅkara'' attains '' Kevala Jnana'' (omniscience). Tirthankara provides a bridge for others to follow the new teacher from ''saṃsāra'' to ''moksha'' (liberation). In Jain cosmology, the wheel of time is divided in two halves, Utsarpiṇī' or ascending time cycle and ''avasarpiṇī'', the descending time cycle (said to be current now). In each half of the cosmic time cycle, exactly twenty-four ''tirthankaras'' grace t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motilal Banarsidass
Motilal Banarsidass Publishing House (MLBD) is an Indian academic publishing house, founded in Delhi, India in 1903. It publishes and distributes serials, monographs, and scholarly publications on Asian religions, Buddhology, Indology, Eastern philosophy, history, culture, arts, architecture, archaeology, language, literature, linguistics, musicology, mysticism, yoga, tantra, occult, medicine, astronomy, and astrology. Amongst its publications are the 100 volumes of the Mahapuranas; the 50 volumes of the '' Sacred Books of the East'', edited by Max Müller; ''Bibliotheca Buddhica'' (30 volumes in 32 pts); Ramcharitmanas with Hindi and English translations; the Manusmriti in 10 volumes and the Sanskrit lexicon; and the 7 volumes of ''Encyclopedia of Indian Philosophies''. It also brings out books based on research and study conducted at organizations such as the Indian Council of Historical Research (ICHR), Indira Gandhi National Centre for the Arts (IGNCA), and India ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Causes Of Karma
The karmic process in Jainism is based on seven truths or fundamental principles (''tattva'') of Jainism which explain the human predicament. Out of those, four—influx ( āsrava), bondage (''bandha''), stoppage ('' saṃvara'') and release ('' nirjarā'')—pertain to the karmic process. Karma gets bound to the soul on account of two processes: *'' āsrava'' – Influx of karmas, and *'' bandha'' – bondage or sticking of karmas to consciousness Influx of Karma The ''āsrava'', that is, the influx of karma occurs when the karmic particles are attracted to the soul on account of vibrations created by activities of mind, speech and body. p.112 '' Tattvārthasūtra'', 6:1–2 states: "The activities of body, speech and mind is called ''yoga''. This three-fold action results in ''āsrava'' or influx of karma." The karmic inflow on account of ''yoga'' driven by passions and emotions cause a long term inflow of karma prolonging the cycle of reincarnations. On the other hand, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
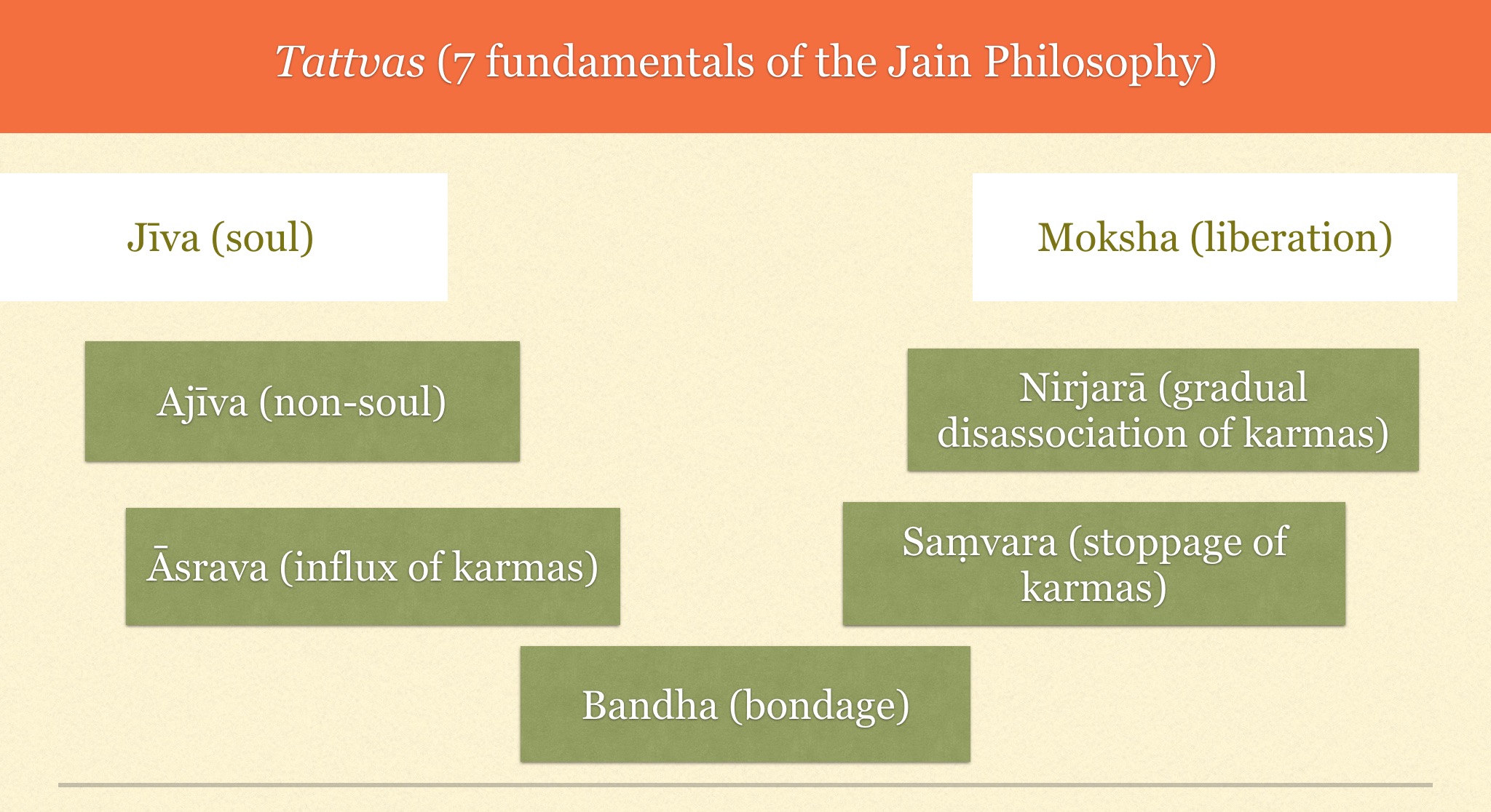
Tattva (Jainism)
Jain philosophy explains that seven ''tattva'' (truths or fundamental principles) constitute reality. These are:— #'' jīva''- the soul which is characterized by consciousness #''ajīva''- the non-soul #''āsrava'' (influx)- inflow of auspicious and evil karmic matter into the soul. #''bandha'' (bondage)- mutual intermingling of the soul and ''karmas''. #''samvara'' (stoppage)- obstruction of the inflow of karmic matter into the soul. #''nirjara'' (gradual dissociation)- separation or falling-off of part of karmic matter from the soul. #''mokṣha'' (liberation)- complete annihilation of all karmic matter (bound with any particular soul). The knowledge of these reals is said to be essential for the liberation of the soul. However, as per one sect of Jain i.e. Shwetamber (Sthanakwasi), there are total nine tattva (truths or fundamental principles). Seven tattva are same as above but 2 more tattva are there namely: Overview The first two are the two ontological catego ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dharma (Jainism)
Jain texts assign a wide range of meaning to the Sanskrit ''dharma'' or Prakrit ''dhamma''. It is often translated as “religion” and as such, Jainism is called ''Jain Dharma'' by its adherents. In Jainism, the word ''Dharma'' is used to refer the following: #Religion #Dharmastikaay (the principle of motion) as a dravya (substance or a reality) #The true nature of a thing #Ten virtues like forgiveness, etc. also called ten forms of Dharma Religion Usage of the word ''dharma'' in reference to the religion. Ahimsa as Dharma According to Jain texts, Ahimsa is the greatest Dharma (अहिंसा परमॊ धर्मः hiṃsā paramo dharmaḥ "non-violence is the highest religion") and there is no religion equal to the religion of non-violence. Dharma bhāvanā Jain texts prescribe meditation on twelve forms of reflection (''bhāvanā'') for those who wish to stop the influx of ''karmas'' that extend transmigration. One such reflection is ''Dharma bhāvan� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ahimsa In Jainism
''Ahimsā'' (', alternatively spelled 'ahinsā', Sanskrit: अहिंसा IAST: ', Pāli: ') in Jainism is a fundamental principle forming the cornerstone of its ethics and doctrine. The term '' ahinsa'' means nonviolence, non-injury and absence of desire to harm any life forms. Vegetarianism and other nonviolent practices and rituals of Jains flow from the principle of ahimsa. There are five specific transgressions of Ahinsa principle in Jain scriptures - Binding of animals, beating, mutilating limbs, overloading, withholding food and drink. Any other interpretation is subject to individual choices and not authorized by scriptures. The Jain concept of ''ahimsa'' is very different from the concept of nonviolence found in other philosophies. Violence is usually associated with causing harm to others. But according to the Jain philosophy, violence refers primarily to injuring one's own self – behaviour which inhibits the soul's own ability to attain ''moksha'' (libera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deshna
In Jainism, a ''Tirthankara'' (Sanskrit: '; English: literally a 'ford-maker') is a saviour and spiritual teacher of the ''dharma'' (righteous path). The word ''tirthankara'' signifies the founder of a '' tirtha'', which is a fordable passage across the sea of interminable births and deaths, the ''saṃsāra''. According to Jains, a ''Tirthankara'' is an individual who has conquered the ''saṃsāra'', the cycle of death and rebirth, on their own, and made a path for others to follow. After understanding the true nature of the self or soul, the ''Tīrthaṅkara'' attains '' Kevala Jnana'' (omniscience). Tirthankara provides a bridge for others to follow the new teacher from ''saṃsāra'' to ''moksha'' (liberation). In Jain cosmology, the wheel of time is divided in two halves, Utsarpiṇī' or ascending time cycle and ''avasarpiṇī'', the descending time cycle (said to be current now). In each half of the cosmic time cycle, exactly twenty-four ''tirthankaras'' grace this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jainism
Jainism ( ), also known as Jain Dharma, is an Indian religion. Jainism traces its spiritual ideas and history through the succession of twenty-four tirthankaras (supreme preachers of ''Dharma''), with the first in the current time cycle being Rishabhadeva, whom the tradition holds to have lived millions of years ago, the twenty-third ''tirthankara'' Parshvanatha, whom historians date to the 9th century BCE, and the twenty-fourth ''tirthankara'' Mahavira, around 600 BCE. Jainism is considered to be an eternal '' dharma'' with the ''tirthankaras'' guiding every time cycle of the cosmology. The three main pillars of Jainism are ''ahiṃsā'' (non-violence), ''anekāntavāda'' (non-absolutism), and '' aparigraha'' (asceticism). Jain monks, after positioning themselves in the sublime state of soul consciousness, take five main vows: ''ahiṃsā'' (non-violence), '' satya'' (truth), '' asteya'' (not stealing), '' brahmacharya'' (chastity), and '' aparigraha'' (non-possessiveness) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |