|
Tupolev Tu-144
The Tupolev Tu-144 (russian: Tyполев Ту-144; NATO reporting name: Charger) is a Soviet supersonic passenger airliner designed by Tupolev in operation from 1968 to 1999. The Tu-144 was the world's first commercial supersonic transport aircraft with its prototype's maiden flight from Zhukovsky Airport on 31 December 1968, two months before the British-French Concorde. The Tu-144 was a product of the Tupolev Design Bureau, an OKB headed by aeronautics pioneer Aleksey Tupolev, and 16 aircraft were manufactured by the Voronezh Aircraft Production Association in Voronezh. The Tu-144 conducted 102 commercial flights, of which only 55 carried passengers, at an average service altitude of and cruised at a speed of around ( Mach 2). The Tu-144 first went supersonic on 5 June 1969, four months before Concorde, and on 26 May 1970 became the world's first commercial transport to exceed Mach 2. Reliability and developmental issues, together with repercussions of the 1973 Paris ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supersonic Airliner
A supersonic transport (SST) or a supersonic airliner is a civilian supersonic aircraft designed to transport passengers at speeds greater than the speed of sound. To date, the only SSTs to see regular service have been Concorde and the Tupolev Tu-144. The last passenger flight of the Tu-144 was in June 1978 and it was last flown in 1999 by NASA. Concorde's last commercial flight was in October 2003, with a November 26, 2003 ferry flight being its last airborne operation. Following the permanent cessation of flying by Concorde, there are no remaining SSTs in commercial service. Several companies have each proposed a supersonic business jet, which may bring supersonic transport back again. Supersonic airliners have been the objects of numerous recent and ongoing design studies. Drawbacks and design challenges are excessive noise generation (at takeoff and due to sonic booms during flight), high development costs, expensive construction materials, high fuel consumption, extr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commercial Flight
Commercial aviation is the part of civil aviation that involves operating aircraft for remuneration or hire, as opposed to private aviation. Definition Commercial aviation is not a rigorously defined category. All commercial air transport and aerial work operations are regarded as commercial aviation, as well as some general aviation flights. Commercial air transport is defined as an aircraft operation involving the transport of passengers, cargo or mail for remuneration or hire. It includes scheduled and non-scheduled air transport operations. Aerial work is defined as an aircraft operation in which an aircraft is used for specialized services such as agriculture, construction, photography, surveying, observation and patrol, search and rescue, advertisement, etc. General aviation includes commercial activities such as corporate and business aviation, as well as non-commercial activities such as recreational flying. Most commercial aviation activities require at minimum a commerc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Council Of Ministers Of The Soviet Union
The Council of Ministers of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics ( rus, Совет министров СССР, r=Sovet Ministrov SSSR, p=sɐˈvʲet mʲɪˈnʲistrəf ɛsɛsɛˈsɛr; sometimes abbreviated to ''Sovmin'' or referred to as the ''Soviet of Ministers''), was the ''de jure'' government of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR), comprising the main executive and administrative agency of the USSR from 1946 until 1991. During 1946 the Council of People's Commissars was reorganized as the Council of Ministers. Accordingly, the People's Commissariats were renamed as Ministries. The council issued declarations and instructions based on and in accordance with applicable laws, which had obligatory jurisdictional power in all republics of the Union. However, the most important decisions were made by joint declarations with the Central Committee of the Communist Party of Soviet Union (CPSU), which was ''de facto'' more powerful than the Council of Ministers. Durin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Government Of The Soviet Union
The Government of the Soviet Union ( rus, Прави́тельство СССР, p=prɐˈvʲitʲɪlʲstvə ɛs ɛs ɛs ˈɛr, r=Pravítelstvo SSSR, lang=no), formally the All-Union Government of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics, commonly abbreviated to Soviet Government, was the executive and administrative organ of state in the former Soviet Union. It had four different names throughout its existence; Council of People's Commissars (1923–1946), Council of Ministers (1946–1991), Cabinet of Ministers (January – August 1991) and Committee on the Operational Management of the National Economy (August–December 1991). It also was known as Workers-Peasants Government of the Soviet Union. The government was led by a chairman, most commonly referred to as " premier" by outside observers. The chairman was nominated by the Central Committee of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union (CPSU) and elected by delegates at the first plenary session of a newly elected Supreme Sovi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aeroflot Tupolev Tu-144 1977 Volpati-1
PJSC AeroflotRussian Airlines (russian: ПАО "Аэрофло́т — Росси́йские авиали́нии", ), commonly known as Aeroflot ( or ; russian: Аэрофлот, , ), is the flag carrier and the largest airline of Russia. The airline was founded in 1923, making Aeroflot one of the oldest active airlines in the world. Aeroflot is headquartered in the Central Administrative Okrug, Moscow, with its hub being Sheremetyevo International Airport. Before the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine, the airline flew to 146 destinations in 52 countries, excluding codeshared services. The number of destinations was significantly reduced after many countries banned Russian aircraft; as of 8 March 2022, Aeroflot flies only to destinations in Russia and Belarus. From its inception to the early 1990s, Aeroflot was the flag carrier and a state-owned enterprise of the Soviet Union (USSR). During this time, Aeroflot grew its fleet to over five thousand domestically made aircraft a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aircraft Mig-21I Under The Wing Of The Plane Tu-144 (9678535680)
An aircraft is a vehicle that is able to fly by gaining support from the air. It counters the force of gravity by using either static lift or by using the dynamic lift of an airfoil, or in a few cases the downward thrust from jet engines. Common examples of aircraft include airplanes, helicopters, airships (including blimps), gliders, paramotors, and hot air balloons. The human activity that surrounds aircraft is called ''aviation''. The science of aviation, including designing and building aircraft, is called ''aeronautics.'' Crewed aircraft are flown by an onboard pilot, but unmanned aerial vehicles may be remotely controlled or self-controlled by onboard computers. Aircraft may be classified by different criteria, such as lift type, aircraft propulsion, usage and others. History Flying model craft and stories of manned flight go back many centuries; however, the first manned ascent — and safe descent — in modern times took place by larger hot-air b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
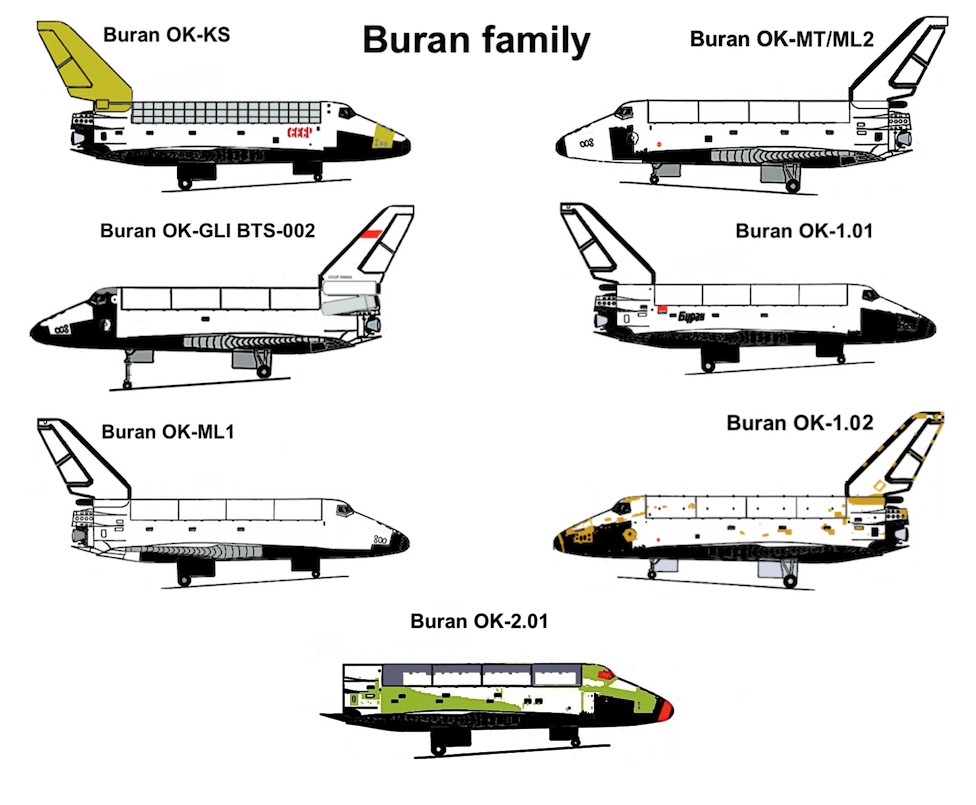
Buran (spacecraft)
''Buran'' (russian: Буран, , meaning "Snowstorm" or "Blizzard"; GRAU index serial number: 11F35 1K, construction number: 1.01) was the first spaceplane to be produced as part of the Soviet/Russian Buran program. Besides describing the first operational Soviet/Russian shuttle orbiter, "Buran" was also the designation for the entire Soviet/Russian spaceplane project and its orbiters, which were known as "Buran-class orbiters". Buran completed one uncrewed spaceflight in 1988, and was destroyed in the 2002 collapse of its storage hangar. The Buran-class orbiters used the expendable Energia rocket, a class of super heavy-lift launch vehicle. It is named after the Asian wind. Construction The construction of the Buran spacecraft began in 1980, and by 1984 the first full-scale orbiter was rolled out. Over 1000 companies all over the Soviet Union were involved in construction and development. The Buran spacecraft was made to be launched on the Soviet Union's super-heavy li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Space Program
The Soviet space program (russian: Космическая программа СССР, Kosmicheskaya programma SSSR) was the national space program of the former Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR), active from 1955 until the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991. Soviet investigations in rocketry began with the formation of a research laboratory in 1921, but these efforts were hampered by the devastating war with Germany. Competing in the Space Race with the United States and later with the European Union and China, the Soviet program was notable in setting many records in space exploration, including the first intercontinental missile that launched the first satellite and sent the first animal into Earth orbit in 1957, and placed the first human in space in 1961. In addition, the Soviet program also saw the first woman in space in 1963 and a cosmonaut performing the first spacewalk in 1965. Other milestones included computerized robotic missions exploring t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cargo Aircraft
A cargo aircraft (also known as freight aircraft, freighter, airlifter or cargo jet) is a fixed-wing aircraft that is designed or converted for the carriage of cargo rather than passengers. Such aircraft usually do not incorporate passenger amenities and generally feature one or more large doors for loading cargo. Freighters may be operated by civil passenger or cargo airlines, by private individuals or by the armed forces of individual countries. Aircraft designed for cargo flight usually have features that distinguish them from conventional passenger aircraft: a wide/tall fuselage cross-section, a high-wing to allow the cargo area to sit near the ground, numerous wheels to allow it to land at unprepared locations, and a high-mounted tail to allow cargo to be driven directly into and off the aircraft. By 2015, dedicated freighters represent 43% of the 700 billion ATK (available tonne-kilometer) capacity, while 57% is carried in airliner's cargo holds. Also in 2015, Boein ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1978 Yegoryevsk Tu-144 Crash
The 1978 Yegoryevsk Tu-144 crash occurred during a test flight of a Tupolev Tu-144 on 23 May 1978. The aircraft suffered a fuel leak, which led to an in-flight fire in the right wing, forcing the shutdown of two of the aircraft's four engines. One of the two remaining engines subsequently failed, forcing the crew to make a belly landing in a field near Yegoryevsk, Moscow Oblast. Two flight engineers were killed in the ensuing crash, but the remaining six crew members survived. The accident prompted a ban on passenger flights of the Tu-144, which had already been beset by numerous problems, leading to a lack of interest that ultimately resulted in the Tu-144 program's cancellation. Aircraft and crew The aircraft was a supersonic Tupolev Tu-144D, registered СССР-77111, built at the Voronezh Aircraft Production Association facility and destined for Soviet flag carrier Aeroflot. It had first flown on 27 April 1978 and completed test flights on 12 May, 16 May, and 18 May, as well ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alma-Ata
Almaty (; kk, Алматы; ), formerly known as Alma-Ata ( kk, Алма-Ата), is the largest city in Kazakhstan, with a population of about 2 million. It was the capital of Kazakhstan from 1929 to 1936 as an autonomous republic as part of the Soviet Union, then from 1936 to 1991 as a union republic and finally from 1991 as an independent state to 1997 when the government relocated the capital to Akmola (renamed Astana in 1998, Nur-Sultan in 2019, and back to Astana in 2022). Almaty is still the major commercial, financial, and cultural centre of Kazakhstan, as well as its most populous and most cosmopolitan city. The city is located in the mountainous area of southern Kazakhstan near the border with Kyrgyzstan in the foothills of the Trans-Ili Alatau at an elevation of 700–900 m (2,300–3,000 feet), where the Large and Small Almatinka rivers run into the plain. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)