|
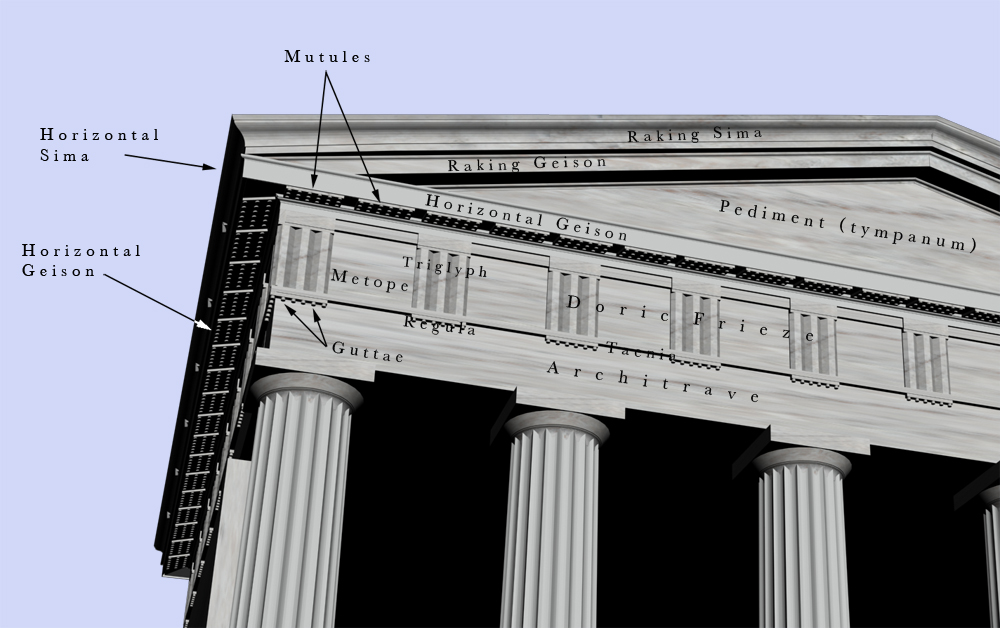
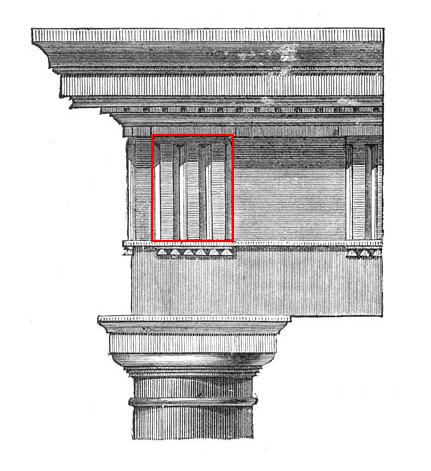
Triglyph
Triglyph is an architectural term for the vertically channeled tablets of the Doric frieze in classical architecture, so called because of the angular channels in them. The rectangular recessed spaces between the triglyphs on a Doric frieze are called metopes. The raised spaces between the channels themselves (within a triglyph) are called ''femur'' in Latin or ''meros'' in Greek. In the strict tradition of classical architecture, a set of guttae, the six triangular "pegs" below, always go with a triglyph above (and vice versa), and the pair of features are only found in entablatures of buildings using the Doric order. The absence of the pair effectively converts a building from being in the Doric order to being in the Tuscan order. The triglyph is largely thought to be a tectonic and skeuomorphic representation in stone of the wooden beam ends of the typical primitive hut, as described by Vitruvius and Renaissance writers. The wooden beams were notched in three separate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doric Order
The Doric order was one of the three orders of ancient Greek and later Roman architecture; the other two canonical orders were the Ionic and the Corinthian. The Doric is most easily recognized by the simple circular capitals at the top of columns. Originating in the western Doric region of Greece, it is the earliest and, in its essence, the simplest of the orders, though still with complex details in the entablature above. The Greek Doric column was fluted or smooth-surfaced, and had no base, dropping straight into the stylobate or platform on which the temple or other building stood. The capital was a simple circular form, with some mouldings, under a square cushion that is very wide in early versions, but later more restrained. Above a plain architrave, the complexity comes in the frieze, where the two features originally unique to the Doric, the triglyph and gutta, are skeuomorphic memories of the beams and retaining pegs of the wooden constructions that preceded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metope (architecture)
In classical architecture, a metope (μετόπη) is a rectangular architectural element that fills the space between two triglyphs in a Doric frieze, which is a decorative band of alternating triglyphs and metopes above the architrave of a building of the Doric order. Metopes often had painted or sculptural decoration; the most famous example are the 92 metopes of the Parthenon marbles some of which depict the battle between the Centaurs and the Lapiths. The painting on most metopes has been lost, but sufficient traces remain to allow a close idea of their original appearance. In terms of structure, metopes may be carved from a single block with a triglyph (or triglyphs), or they may be cut separately and slide into slots in the triglyph blocks as at the Temple of Aphaea. Sometimes the metopes and friezes were cut from different stone, so as to provide color contrast. Although they tend to be close to square in shape, some metopes are noticeably larger in height or in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greek Architecture
Ancient Greek architecture came from the Greek-speaking people (''Hellenic'' people) whose culture flourished on the Greek mainland, the Peloponnese, the Aegean Islands, and in colonies in Anatolia and Italy for a period from about 900 BC until the 1st century AD, with the earliest remaining architectural works dating from around 600 BC. Ancient Greek architecture is best known from its temples, many of which are found throughout the region, with the Parthenon regarded, now as in ancient times, as the prime example. Most remains are very incomplete ruins, but a number survive substantially intact, mostly outside modern Greece. The second important type of building that survives all over the Hellenic world is the open-air theatre, with the earliest dating from around 525–480 BC. Other architectural forms that are still in evidence are the processional gateway (''propylon''), the public square (''agora'') surrounded by storied colonnade (''stoa''), the town council building ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gutta
A gutta (Latin pl. guttae, "drops") is a small water-repelling, cone-shaped projection used near the top of the architrave of the Doric order in classical architecture. At the top of the architrave blocks, a row of six ''guttae'' below the narrow projection of the taenia (fillet) formed an element called a regula. A ''regula'' was aligned under each triglyph of the Doric frieze. In addition, the underside of the projecting geison above the frieze had rectangular protrusions termed ''mutules'' that each had three rows of six ''guttae''. These mutules were aligned above each triglyph and each metope. It is thought that the guttae were a skeuomorphic representation of the pegs used in the construction of the wooden structures that preceded the familiar Greek architecture in stone. However, they have some functionality, as water drips over the edges, away from the edge of the building. Outside the Doric In the strict tradition of classical architecture, a set of guttae alway ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skeuomorph
A skeuomorph (also spelled skiamorph, ) is a derivative object that retains ornamental design cues (attributes) from structures that were necessary in the original. Skeuomorphs are typically used to make something new feel familiar in an effort to speed understanding and acclimation. They employ elements that, while essential to the original object, serve no pragmatic purpose in the new system. Examples include pottery embellished with imitation rivets reminiscent of similar pots made of metal and a software calendar that imitates the appearance of binding on a paper desk calendar. Definition and purpose The term ''skeuomorph'' is compounded from ''skeuos'' (σκεῦος), meaning "container or tool", and ''morphḗ'' (μορφή), meaning "shape". It has been applied to material objects since 1890. With the advent of computer systems in the 1980s, skeuomorph is used to characterize the many "old fashioned" icons utilized in graphic user interfaces. A similar alternative defi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fascia (architecture)
Fascia () is an architectural term for a vertical frieze or band under a roof edge, or which forms the outer surface of a cornice, visible to an observer. Typically consisting of a wooden board, unplasticized PVC (uPVC), or non-corrosive sheet metal, many of the non-domestic fascias made of stone form an ornately carved or pieced together cornice, in which case the term fascia is rarely used. The word fascia derives from Latin ''fascia'' meaning "band, bandage, ribbon, swathe". The term is also used, although less commonly, for other such band-like surfaces like a wide, flat trim strip around a doorway, different and separate from the wall surface. The horizontal "fascia board" which caps the end of rafters outside a building may be used to hold the rain gutter. The finished surface below the fascia and rafters is called the soffit or eave. In classical architecture, the fascia is the plain, wide band (or bands) that make up the architrave section of the entablature, dir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temple Of Hephaestus
The Temple of Hephaestus or ''Hephaisteion'' (also "Hephesteum" or "Hephaesteum"; grc, Ἡφαιστεῖον, ell, Ναός Ηφαίστου, and formerly called in error the Theseion or "Theseum"; grc, Θησεῖον, ell, Θησείο), is a well-preserved Greek temple dedicated to Hephaestus; it remains standing largely intact today. It is a Doric peripteral temple, and is located at the north-west side of the Agora of Athens, on top of the Agoraios Kolonos hill. From the 7th century until 1834, it served as the Greek Orthodox church of Saint George Akamates. The building's condition has been maintained due to its history of varied use. Name Hephaestus was the patron god of metal working, craftsmanship, and fire. There were numerous potters' workshops and metal-working shops in the vicinity of the temple, as befits the temple's honoree. Archaeological evidence suggests that there was no earlier building on the site except for a small sanctuary that was burned during ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temple Of Concordia, Agrigento
The Temple of Concordia ( it, Tempio della Concordia) is an ancient Greek temple in the Valle dei Templi (Valley of the Temples) in Agrigento (Greek: Akragas) on the south coast of Sicily, Italy. It is the largest and best-preserved Doric temple in Sicily and one of the best-preserved Greek temples in general, especially of the Doric order. It is located a kilometer east to the Temple of Heracles. Description The temple was built BC. The well-preserved peristasis of six by thirteen columns stands on a crepidoma of four steps (measuring , and high) The cella measures . The columns are high and carved with twenty flutes and harmonious entasis (tapering at the tops of the columns and swelling around the middles). It is constructed, like the nearby Temple of Juno, on a solid base designed to overcome the unevenness of the rocky terrain. It has been conventionally named after Concordia, the Roman goddess of harmony, for the Roman-era Latin inscription found nearby, which i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
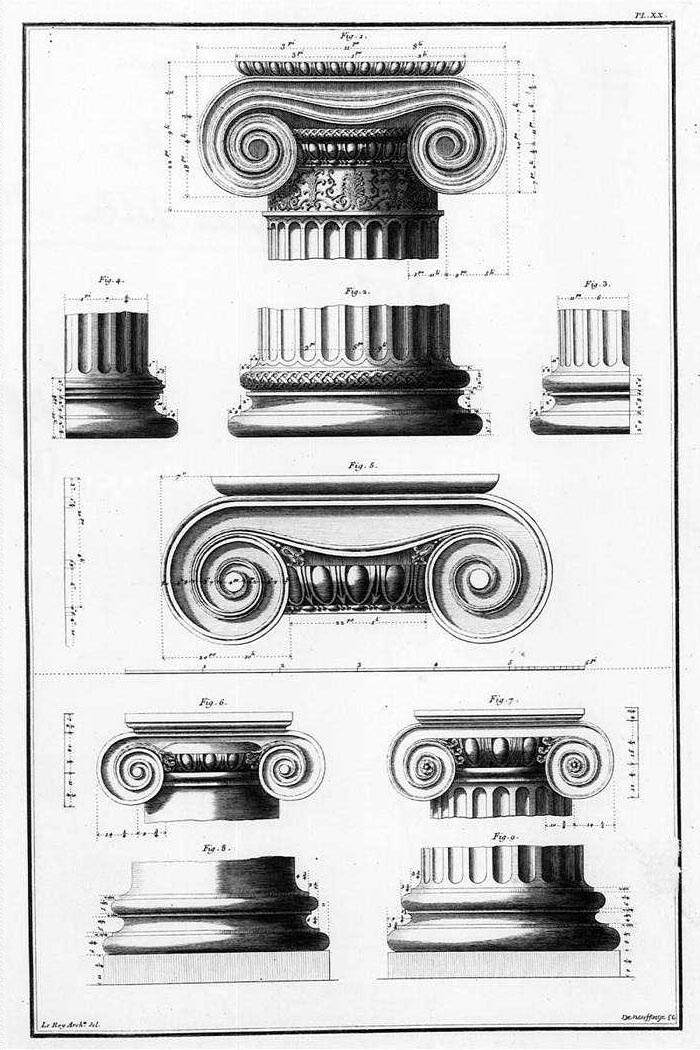
Ionic Order
The Ionic order is one of the three canonic orders of classical architecture, the other two being the Doric and the Corinthian. There are two lesser orders: the Tuscan (a plainer Doric), and the rich variant of Corinthian called the composite order. Of the three classical canonic orders, the Corinthian order has the narrowest columns, followed by the Ionic order, with the Doric order having the widest columns. The Ionic capital is characterized by the use of volutes. The Ionic columns normally stand on a base which separates the shaft of the column from the stylobate or platform while the cap is usually enriched with egg-and-dart. The ancient architect and architectural historian Vitruvius associates the Ionic with feminine proportions (the Doric representing the masculine). Description Capital The major features of the Ionic order are the volutes of its capital, which have been the subject of much theoretical and practical discourse, based on a brief and obscure pas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prague
Prague ( ; cs, Praha ; german: Prag, ; la, Praga) is the capital and List of cities in the Czech Republic, largest city in the Czech Republic, and the historical capital of Bohemia. On the Vltava river, Prague is home to about 1.3 million people. The city has a temperate climate, temperate oceanic climate, with relatively warm summers and chilly winters. Prague is a political, cultural, and economic hub of central Europe, with a rich history and Romanesque architecture, Romanesque, Czech Gothic architecture, Gothic, Czech Renaissance architecture, Renaissance and Czech Baroque architecture, Baroque architectures. It was the capital of the Kingdom of Bohemia and residence of several Holy Roman Emperors, most notably Charles IV, Holy Roman Emperor, Charles IV (r. 1346–1378). It was an important city to the Habsburg monarchy and Austro-Hungarian Empire. The city played major roles in the Bohemian Reformation, Bohemian and the Protestant Reformations, the Thirty Year ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Černín Palace
The Czernin Palace ( cs, Černínský palác) is the largest of the baroque palaces of Prague, which has served as the offices of the Czechoslovak and later Czech foreign ministry since the 1930s. It was commissioned by the diplomat Humprecht Jan Czernin, the Habsburg imperial ambassador to Venice and Rome, in the 1660s. The palace features stuccos by Italian artists.Mojmír Horyna, Pavel Zahradník, Pavel Preiss ''Czernin Palace in Prague'' 2001 Page 23 "... working so hard it could be hoped that they would finish before the Count's arrival in Prague. This was the first time the two stucco makers working at the palace were actually named - Giovanni Bartolommeo Cometa and Giovanni Maderna." History In 1666, Humprecht Jan Czernin purchased a part of the debt loaded property of the House of Lobkowicz, including a building plot with gardens located in the centre of Prague. In 1668, he commissioned Francesco Caratti, a Swiss-Italian architect, and assigned him to develop th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


%2C_Athens_-_20070711.jpg)