|
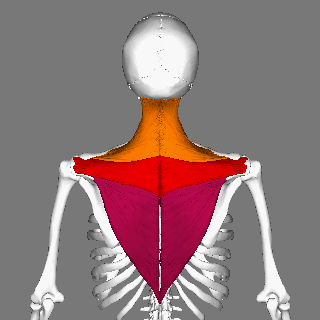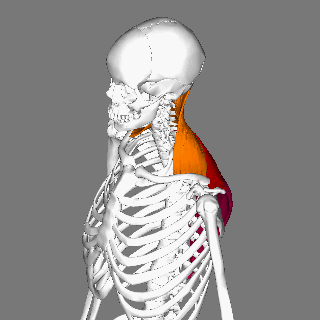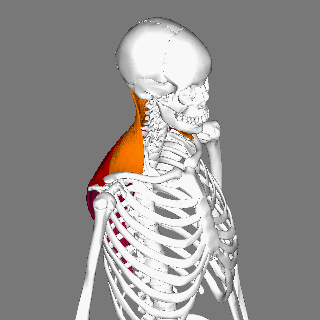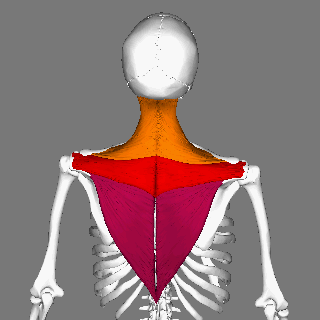
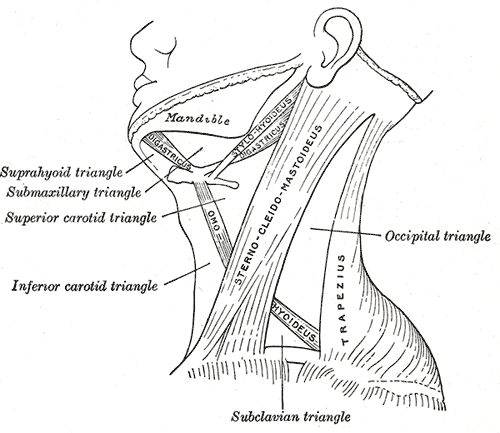
Trapezius
The trapezius is a large paired trapezoid-shaped surface muscle that extends longitudinally from the occipital bone to the lower thoracic vertebrae of the spine and laterally to the spine of the scapula. It moves the scapula and supports the arm. The trapezius has three functional parts: an upper (descending) part which supports the weight of the arm; a middle region (transverse), which retracts the scapula; and a lower (ascending) part which medially rotates and depresses the scapula. Name and history The trapezius muscle resembles a trapezium, also known as a trapezoid, or diamond-shaped quadrilateral. The word "spinotrapezius" refers to the human trapezius, although it is not commonly used in modern texts. In other mammals, it refers to a portion of the analogous muscle. Similarly, the term "tri-axle back plate" was historically used to describe the trapezius muscle. Structure The ''superior'' or ''upper'' (or descending) fibers of the trapezius originate from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trapezius Animation Small2
The trapezius is a large paired trapezoid-shaped surface muscle that extends longitudinally from the occipital bone to the lower thoracic vertebrae of the spine and laterally to the spine of the scapula. It moves the scapula and supports the arm. The trapezius has three functional parts: an upper (descending) part which supports the weight of the arm; a middle region (transverse), which retracts the scapula; and a lower (ascending) part which medially rotates and depresses the scapula. Name and history The trapezius muscle resembles a trapezium, also known as a trapezoid, or diamond-shaped quadrilateral. The word "spinotrapezius" refers to the human trapezius, although it is not commonly used in modern texts. In other mammals, it refers to a portion of the analogous muscle. Similarly, the term "tri-axle back plate" was historically used to describe the trapezius muscle. Structure The ''superior'' or ''upper'' (or descending) fibers of the trapezius originate from the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accessory Nerve
The accessory nerve, also known as the eleventh cranial nerve, cranial nerve XI, or simply CN XI, is a cranial nerve that supplies the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles. It is classified as the eleventh of twelve pairs of cranial nerves because part of it was formerly believed to originate in the brain. The sternocleidomastoid muscle tilts and rotates the head, whereas the trapezius muscle, connecting to the scapula, acts to shrug the shoulder. Traditional descriptions of the accessory nerve divide it into a spinal part and a cranial part. The cranial component rapidly joins the vagus nerve, and there is ongoing debate about whether the cranial part should be considered part of the accessory nerve proper. Consequently, the term "accessory nerve" usually refers only to nerve supplying the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles, also called the spinal accessory nerve. Strength testing of these muscles can be measured during a neurological examination to assess fu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superficial Branch Of Transverse Cervical Artery
The transverse cervical artery (transverse artery of neck or transversa colli artery) is an artery in the neck and a branch of the thyrocervical trunk, running at a higher level than the suprascapular artery. Structure It passes transversely below the inferior belly of the omohyoid muscle to the anterior margin of the trapezius, beneath which it divides into a superficial and a deep branch. It crosses in front of the phrenic nerve and the scalene muscles, and in front of or between the divisions of the brachial plexus, and is covered by the platysma and sternocleidomastoid muscles, and crossed by the omohyoid and trapezius. The transverse cervical artery originates from the thyrocervical trunk, it passes through the posterior triangle of the neck to the anterior border of the levator scapulae muscle, where it divides into deep and superficial branches. * Superficial branch ** Ascending branch ** Descending branch (also known as superficial cervical artery, which supplies t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superficial Cervical Artery
The transverse cervical artery (transverse artery of neck or transversa colli artery) is an artery in the neck and a branch of the thyrocervical trunk, running at a higher level than the suprascapular artery. Structure It passes transversely below the inferior belly of the omohyoid muscle to the anterior margin of the trapezius, beneath which it divides into a superficial and a deep branch. It crosses in front of the phrenic nerve and the scalene muscles, and in front of or between the divisions of the brachial plexus, and is covered by the platysma and sternocleidomastoid muscles, and crossed by the omohyoid and trapezius. The transverse cervical artery originates from the thyrocervical trunk, it passes through the posterior triangle of the neck to the anterior border of the levator scapulae muscle, where it divides into deep and superficial branches. * Superficial branch ** Ascending branch ** Descending branch (also known as superficial cervical artery, which supplies t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scapula
The scapula (plural scapulae or scapulas), also known as the shoulder blade, is the bone that connects the humerus (upper arm bone) with the clavicle (collar bone). Like their connected bones, the scapulae are paired, with each scapula on either side of the body being roughly a mirror image of the other. The name derives from the Classical Latin word for trowel or small shovel, which it was thought to resemble. In compound terms, the prefix omo- is used for the shoulder blade in medical terminology. This prefix is derived from ὦμος (ōmos), the Ancient Greek word for shoulder, and is cognate with the Latin , which in Latin signifies either the shoulder or the upper arm bone. The scapula forms the back of the shoulder girdle. In humans, it is a flat bone, roughly triangular in shape, placed on a posterolateral aspect of the thoracic cage. Structure The scapula is a thick, flat bone lying on the thoracic wall that provides an attachment for three groups of muscles: i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latissimus Dorsi
The latissimus dorsi () is a large, flat muscle on the back that stretches to the sides, behind the arm, and is partly covered by the trapezius on the back near the midline. The word latissimus dorsi (plural: ''latissimi dorsorum'') comes from Latin and means "broadest uscleof the back", from "latissimus" ( la, broadest)' and "dorsum" ( la, back). The pair of muscles are commonly known as "lats", especially among bodybuilders. The latissimus dorsi is the largest muscle in the upper body. The latissimus dorsi is responsible for extension, adduction, transverse extension also known as horizontal abduction (or horizontal extension), flexion from an extended position, and (medial) internal rotation of the shoulder joint. It also has a synergistic role in extension and lateral flexion of the lumbar spine. Due to bypassing the scapulothoracic joints and attaching directly to the spine, the actions the latissimi dorsi have on moving the arms can also influence the movement of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serratus Anterior Muscle
The serratus anterior is a muscle that originates on the surface of the 1st to 8th ribs at the side of the chest and inserts along the entire anterior length of the medial border of the scapula. The serratus anterior acts to pull the scapula forward around the thorax. The muscle is named from Latin: ''serrare'' = to saw, referring to the shape, ''anterior'' = on the front side of the body. Structure Serratus anterior normally originates by nine or ten muscle slips – branches from either the first to ninth ribs or the first to eighth ribs. Because two slips usually arise from the second rib, the number of slips is greater than the number of ribs from which they originate. The muscle is inserted along the medial border of the scapula between the superior and inferior angles along with being inserted along the thoracic vertebrae. The muscle is divided into three named parts depending on their points of insertions: #the serratus anterior superior is inserted near the superior ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sternocleidomastoid
The sternocleidomastoid muscle is one of the largest and most superficial cervical muscles. The primary actions of the muscle are rotation of the head to the opposite side and flexion of the neck. The sternocleidomastoid is innervated by the accessory nerve. Etymology and location It is given the name ''sternocleidomastoid'' because it originates at the manubrium of the sternum (''sterno-'') and the clavicle (''cleido-'') and has an insertion at the mastoid process of the temporal bone of the skull. Structure The sternocleidomastoid muscle originates from two locations: the manubrium of the sternum and the clavicle. It travels obliquely across the side of the neck and inserts at the mastoid process of the temporal bone of the skull by a thin aponeurosis. The sternocleidomastoid is thick and narrow at its centre, and broader and thinner at either end. The sternal head is a round fasciculus, tendinous in front, fleshy behind, arising from the upper part of the front of the ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Back
The human back, also called the dorsum, is the large posterior area of the human body, rising from the top of the buttocks to the back of the neck. It is the surface of the body opposite from the chest and the abdomen. The vertebral column runs the length of the back and creates a central area of recession. The breadth of the back is created by the shoulders at the top and the pelvis at the bottom. Back pain is a common medical condition, generally benign in origin. Structure The central feature of the human back is the vertebral column, specifically the length from the top of the thoracic vertebrae to the bottom of the lumbar vertebrae, which houses the spinal cord in its spinal canal, and which generally has some curvature that gives shape to the back. The ribcage extends from the spine at the top of the back (with the top of the ribcage corresponding to the T1 vertebra), more than halfway down the length of the back, leaving an area with less protection between the bot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ligamentum Nuchae
The nuchal ligament is a ligament at the back of the neck that is continuous with the supraspinous ligament. Structure The nuchal ligament extends from the external occipital protuberance on the skull and median nuchal line to the spinous process of the seventh cervical vertebra in the lower part of the neck. From the anterior border of the nuchal ligament, a fibrous lamina is given off. This is attached to the posterior tubercle of the atlas, and to the spinous processes of the cervical vertebrae, and forms a septum between the muscles on either side of the neck. The trapezius and splenius capitis muscle attach to the nuchal ligament. Function It is a tendon-like structure that has developed independently in humans and other animals well adapted for running. In some four-legged animals, particularly ungulates, the nuchal ligament serves to sustain the weight of the head. Clinical significance In Chiari malformation treatment, decompression and duraplasty with a harvest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acromion
In human anatomy, the acromion (from Greek: ''akros'', "highest", ''ōmos'', "shoulder", plural: acromia) is a bony process on the scapula (shoulder blade). Together with the coracoid process it extends laterally over the shoulder joint. The acromion is a continuation of the scapular spine, and hooks over anteriorly. It articulates with the clavicle (collar bone) to form the acromioclavicular joint. Structure The acromion forms the summit of the shoulder, and is a large, somewhat triangular or oblong process, flattened from behind forward, projecting at first lateralward, and then curving forward and upward, so as to overhang the glenoid fossa.'' Gray's Anatomy'' 1918, see infobox It starts from the base of acromion which marks its projecting point emerging from the spine of scapula. Surfaces Its superior surface, directed upward, backward, and lateralward, is convex, rough, and gives attachment to some fibers of the deltoideus, and in the rest of its extent is subcutaneo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscle
Skeletal muscles (commonly referred to as muscles) are organs of the vertebrate muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The muscle cells of skeletal muscles are much longer than in the other types of muscle tissue, and are often known as muscle fibers. The muscle tissue of a skeletal muscle is striated – having a striped appearance due to the arrangement of the sarcomeres. Skeletal muscles are voluntary muscles under the control of the somatic nervous system. The other types of muscle are cardiac muscle which is also striated and smooth muscle which is non-striated; both of these types of muscle tissue are classified as involuntary, or, under the control of the autonomic nervous system. A skeletal muscle contains multiple fascicles – bundles of muscle fibers. Each individual fiber, and each muscle is surrounded by a type of connective tissue layer of fascia. Muscle fibers are formed from the fusion of developmental myoblasts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |