|
Top
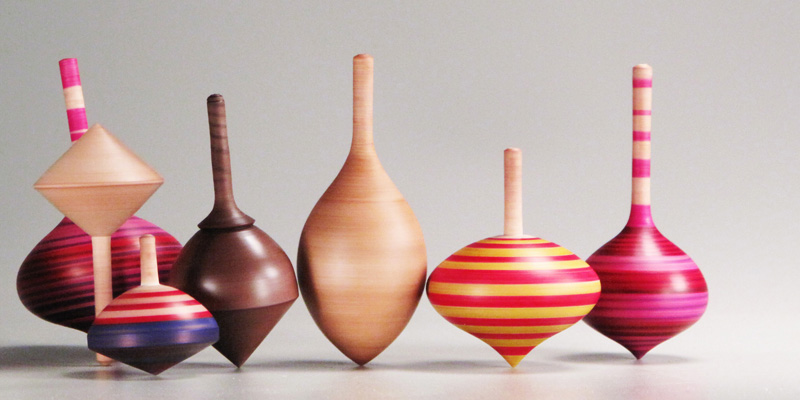
A spinning top, or simply a top, is a toy with a squat body and a sharp point at the bottom, designed to be spun on its vertical axis, balancing on the tip due to the gyroscopic effect. Once set in motion, a top will usually wobble for a few seconds, spin upright for a while, then start to wobble again with increasing amplitude as it loses energy, and finally tip over and roll on its side. Tops exist in many variations and materials, chiefly wood, metal, and plastic, often with a metal tip. They may be set in motion by twirling a handle with the fingers, by pulling a rope coiled around the body, or by means of a built-in auger (spiral plunger). Such toys have been used since antiquity in solitary or competitive games, where each player tries to keep one's top spinning for as long as possible, or achieve some other goal. Some tops have faceted bodies with symbols or inscriptions, and are used like dice to inject randomness into games, or for divination and ritual purposes. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
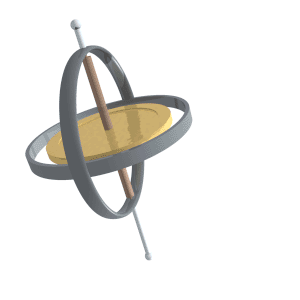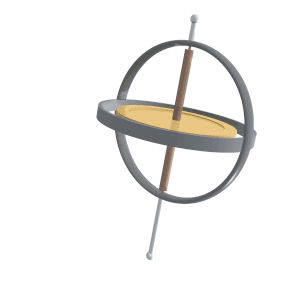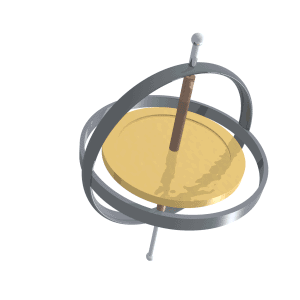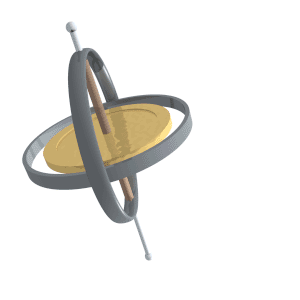
Gyroscopic Effect
A gyroscope (from Ancient Greek γῦρος ''gŷros'', "round" and σκοπέω ''skopéō'', "to look") is a device used for measuring or maintaining orientation and angular velocity. It is a spinning wheel or disc in which the axis of rotation (spin axis) is free to assume any orientation by itself. When rotating, the orientation of this axis is unaffected by tilting or rotation of the mounting, according to the conservation of angular momentum. Gyroscopes based on other operating principles also exist, such as the microchip-packaged MEMS gyroscopes found in electronic devices (sometimes called gyrometers), solid-state ring lasers, fibre optic gyroscopes, and the extremely sensitive quantum gyroscope. Applications of gyroscopes include inertial navigation systems, such as in the Hubble Space Telescope, or inside the steel hull of a submerged submarine. Due to their precision, gyroscopes are also used in gyrotheodolites to maintain direction in tunnel mining. Gyroscopes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Clerk Maxwell
James Clerk Maxwell (13 June 1831 – 5 November 1879) was a Scottish mathematician and scientist responsible for the classical theory of electromagnetic radiation, which was the first theory to describe electricity, magnetism and light as different manifestations of the same phenomenon. Maxwell's equations for electromagnetism have been called the " second great unification in physics" where the first one had been realised by Isaac Newton. With the publication of "A Dynamical Theory of the Electromagnetic Field" in 1865, Maxwell demonstrated that electric and magnetic fields travel through space as waves moving at the speed of light. He proposed that light is an undulation in the same medium that is the cause of electric and magnetic phenomena. (This article accompanied an 8 December 1864 presentation by Maxwell to the Royal Society. His statement that "light and magnetism are affections of the same substance" is at page 499.) The unification of light and elec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rope
A rope is a group of yarns, plies, fibres, or strands that are twisted or braided together into a larger and stronger form. Ropes have tensile strength and so can be used for dragging and lifting. Rope is thicker and stronger than similarly constructed cord, string, and twine. Construction Rope may be constructed of any long, stringy, fibrous material, but generally is constructed of certain natural or synthetic fibres. Synthetic fibre ropes are significantly stronger than their natural fibre counterparts, they have a higher tensile strength, they are more resistant to rotting than ropes created from natural fibres, and they can be made to float on water. But synthetic ropes also possess certain disadvantages, including slipperiness, and some can be damaged more easily by UV light. Common natural fibres for rope are Manila hemp, hemp, linen, cotton, coir, jute, straw, and sisal. Synthetic fibres in use for rope-making include polypropylene, nylon, polyes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gambling
Gambling (also known as betting or gaming) is the wagering of something of value ("the stakes") on a random event with the intent of winning something else of value, where instances of strategy are discounted. Gambling thus requires three elements to be present: consideration (an amount wagered), risk (chance), and a prize. The outcome of the wager is often immediate, such as a single roll of dice, a spin of a roulette wheel, or a horse crossing the finish line, but longer time frames are also common, allowing wagers on the outcome of a future sports contest or even an entire sports season. The term "gaming" in this context typically refers to instances in which the activity has been specifically permitted by law. The two words are not mutually exclusive; ''i.e.'', a "gaming" company offers (legal) "gambling" activities to the public and may be regulated by one of many gaming control boards, for example, the Nevada Gaming Control Board. However, this distinction is not u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclosa Turbinata
''Cyclosa turbinata'' is a species of orb weaver belonging to the family of spiders known as Araneidae. It is found in a range from the United States to Panama, West Indies, Galapagos Islands, and has been introduced into Hawaii. Geographic Location The spider is native to the continental United States, and Mexico, but has been introduced and found in places across Hawaii, the Caribbean, Middle, and South America, the Galapagos Islands, and even Oceania. Its large geographic range is likely due to its ability to travel through the wind using its silk to catch the current. Five species of ''Cyclosa ''Cyclosa'', also called trashline orbweavers, is a genus of orb-weaver spiders first described by Anton Menge in 1866. Widely distributed worldwide, spiders of the genus ''Cyclosa'' build relatively small orb webs with a web decoration. The w ...'' occur in the continental United States. Etymology The specific name is derived from the Latin word ''turbo'', meaning spinning t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axis Of Rotation
Rotation around a fixed axis is a special case of rotational motion. The fixed- axis hypothesis excludes the possibility of an axis changing its orientation and cannot describe such phenomena as wobbling or precession. According to Euler's rotation theorem, simultaneous rotation along a number of stationary axes at the same time is impossible; if two rotations are forced at the same time, a new axis of rotation will appear. This article assumes that the rotation is also stable, such that no torque is required to keep it going. The kinematics and dynamics of rotation around a fixed axis of a rigid body are mathematically much simpler than those for free rotation of a rigid body; they are entirely analogous to those of linear motion along a single fixed direction, which is not true for ''free rotation of a rigid body''. The expressions for the kinetic energy of the object, and for the forces on the parts of the object, are also simpler for rotation around a fixed axis, than ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Precession
Precession is a change in the orientation of the rotational axis of a rotating body. In an appropriate reference frame it can be defined as a change in the first Euler angle, whereas the third Euler angle defines the rotation itself. In other words, if the axis of rotation of a body is itself rotating about a second axis, that body is said to be precessing about the second axis. A motion in which the second Euler angle changes is called '' nutation''. In physics, there are two types of precession: torque-free and torque-induced. In astronomy, ''precession'' refers to any of several slow changes in an astronomical body's rotational or orbital parameters. An important example is the steady change in the orientation of the axis of rotation of the Earth, known as the precession of the equinoxes. Torque-free Torque-free precession implies that no external moment (torque) is applied to the body. In torque-free precession, the angular momentum is a constant, but the angular veloci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plastic
Plastics are a wide range of synthetic or semi-synthetic materials that use polymers as a main ingredient. Their plasticity makes it possible for plastics to be moulded, extruded or pressed into solid objects of various shapes. This adaptability, plus a wide range of other properties, such as being lightweight, durable, flexible, and inexpensive to produce, has led to its widespread use. Plastics typically are made through human industrial systems. Most modern plastics are derived from fossil fuel-based chemicals like natural gas or petroleum; however, recent industrial methods use variants made from renewable materials, such as corn or cotton derivatives. 9.2 billion tonnes of plastic are estimated to have been made between 1950 and 2017. More than half this plastic has been produced since 2004. In 2020, 400 million tonnes of plastic were produced. If global trends on plastic demand continue, it is estimated that by 2050 annual global plastic production will reach over 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prophecy
In religion, a prophecy is a message that has been communicated to a person (typically called a '' prophet'') by a supernatural entity. Prophecies are a feature of many cultures and belief systems and usually contain divine will or law, or preternatural knowledge, for example of future events. They can be revealed to the prophet in various ways depending on the religion and the story, such as visions, divination, or direct interaction with divine beings in physical form. Stories of prophetic deeds sometimes receive considerable attention and some have been known to survive for centuries through oral tradition or as religious texts. Etymology The English noun "prophecy", in the sense of "function of a prophet" appeared from about 1225, from Old French ''profecie'' (12th century), and from ''prophetia'', Greek ''propheteia'' "gift of interpreting the will of God", from Greek ''prophetes'' (see prophet). The related meaning, "thing spoken or written by a prophet", dates from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dice
Dice (singular die or dice) are small, throwable objects with marked sides that can rest in multiple positions. They are used for generating random values, commonly as part of tabletop games, including dice games, board games, role-playing games, and games of chance. A traditional die is a cube with each of its six faces marked with a different number of dots ( pips) from one to six. When thrown or rolled, the die comes to rest showing a random integer from one to six on its upper surface, with each value being equally likely. Dice may also have polyhedral or irregular shapes, may have faces marked with numerals or symbols instead of pips and may have their numbers carved out from the material of the dice instead of marked on it. Loaded dice are designed to favor some results over others for cheating or entertainment. History Dice have been used since before recorded history, and it is uncertain where they originated. It is theorized that dice developed from the pract ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotation
Rotation, or spin, is the circular movement of an object around a '' central axis''. A two-dimensional rotating object has only one possible central axis and can rotate in either a clockwise or counterclockwise direction. A three-dimensional object has an infinite number of possible central axes and rotational directions. If the rotation axis passes internally through the body's own center of mass, then the body is said to be ''autorotating'' or '' spinning'', and the surface intersection of the axis can be called a '' pole''. A rotation around a completely external axis, e.g. the planet Earth around the Sun, is called ''revolving'' or ''orbiting'', typically when it is produced by gravity, and the ends of the rotation axis can be called the '' orbital poles''. Mathematics Mathematically, a rotation is a rigid body movement which, unlike a translation, keeps a point fixed. This definition applies to rotations within both two and three dimensions (in a plane and in spa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rattleback
A rattleback is a semi-ellipsoidal top which will rotate on its axis in a preferred direction. If spun in the opposite direction, it becomes unstable, "rattles" to a stop and reverses its spin to the preferred direction. This spin-reversal appears to violate the law of the conservation of angular momentum. Moreover, for most rattlebacks the motion will happen when the rattleback is spun in one direction, but not when spun in the other. Some exceptional rattlebacks will reverse when spun in either direction. This makes the rattleback a physical curiosity that has excited human imagination since prehistoric times. A rattleback may also be known as a "anagyre", "(rebellious) celt", "Celtic stone", "druid stone", "rattlerock", "Robinson Reverser", "spin bar", "wobble stone" (or "wobblestone") and by product names including "ARK", "Bizzaro Swirl", "Space Pet" and "Space Toy". History Archeologists who investigated ancient Celtic and Egyptian sites in the 19th century found celts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)



.jpg)
_-_Emmanuel_Peluchon.jpg)