|
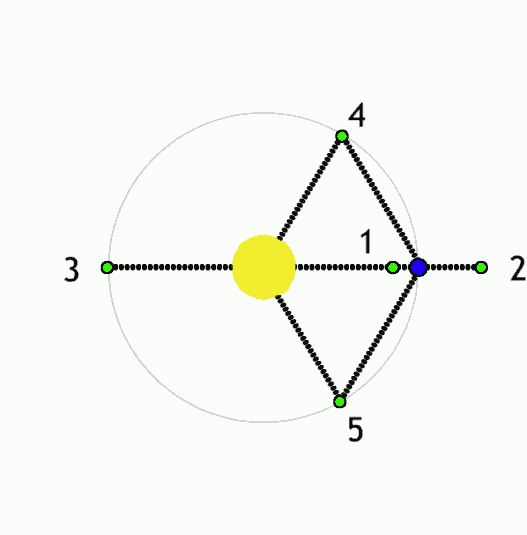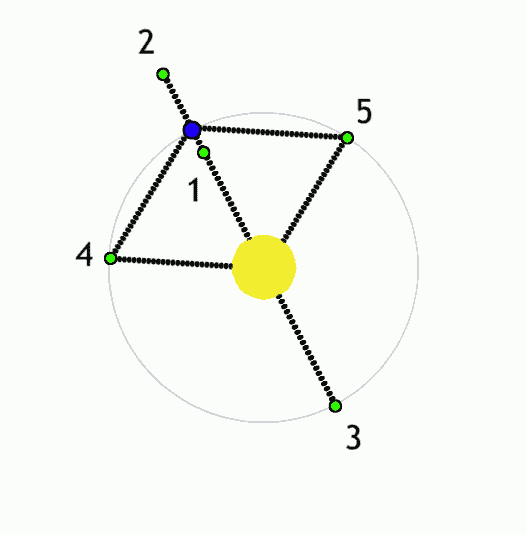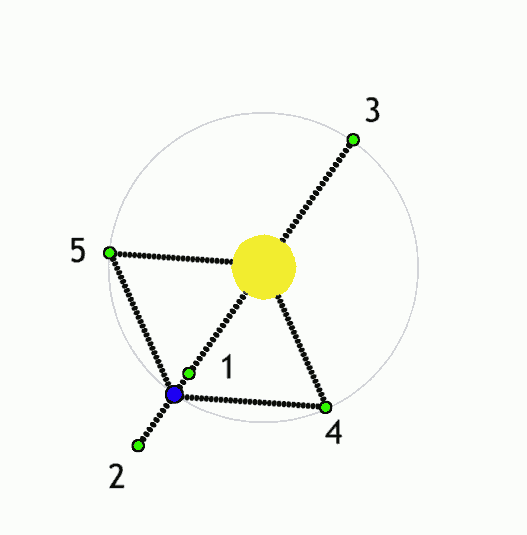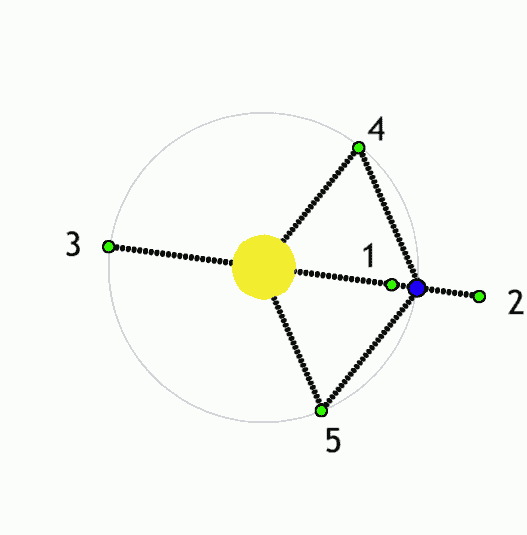
Tianlian I-03
Tianlian (Simplified Chinese: 天链, Traditional Chinese: 天鏈, English: ''Sky Link'') also known as CTDRS, is a Chinese data relay communication satellite constellation. The constellation serves to relay data from ground stations to spacecraft and rockets, most significantly China's crewed spaceflight program. The system currently consists of seven satellites in two generations, with the first satellite being launched in 2008. Mission Tianlian is used to provide real-time communications between orbiting satellites and ground control stations. The Chinese tracking and data relay satellites were developed by the China Academy of Space Technology (CAST) and it is similar to the American Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System (TDRSS) in concept. The system is designed to support near-real-time communications between orbiting spacecraft and ground control, as well as complement the ground-based space tracking and telemetry stations and ships in tracking spacecraft. This is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dongfanghong Program
Dongfanghong () was a satellite program of the People's Republic of China. The program started in August 1965 as Project 651—a less ambitious successor to the earlier Project 581—with the goal of launching a satellite heavier than both Sputnik 1 and Explorer 1 into space, and developing all the necessary technologies to do so. History In 1958, the Chinese Academy of Science proposed Project 581 which included a plan to launch a satellite into space before 1 October 1959. The project was troubled due to the country's lack of expertise in the field of rocketry. On 21 January 1959, Zhang Jingfu, who was in charge in the satellite research program, postponed the project to allow effort to be put into developing more basic technologies, such as sounding rocketry. In December 1964, during the 3rd National People's Congress, Zhao Jiuzhang suggested that the work on satellites be resumed. In August 1968, the Central Special Committee approved Chinese Academy of Science's plan, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satellite Bus
A satellite bus (or spacecraft bus) is the main body and structural component of a satellite or spacecraft, in which the payload and all scientific instruments are held. Bus-derived satellites are opposed to specially produced satellites. Bus-derived satellites are usually customized to customer requirements, for example with specialized sensors or transponders, in order to achieve a specific mission. They are commonly used for geosynchronous satellites, particularly communications satellites, but are also used in spacecraft which occupy lower orbits, occasionally including low Earth orbit missions. Examples Some satellite bus examples include: * Boeing DS&S 702 * Lockheed Martin Space Systems A2100 * Alphabus * INVAP ARSAT-3K * Airbus D&S Eurostar * ISRO's I-1K, I-2K, I-3K, I-4K, I-6K, and Indian Mini Satellite bus * NASA Ames MCSB * SSL 1300 * Orbital ATK GEOStar * Mitsubishi Electric DS2000 * Spacecraft bus of the James Webb Space Telescope * SPUTNIX ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inter-satellite Service
Inter-satellite service (also: inter-satellite radiocommunication service) is – according to ''Article 1.22'' of the International Telecommunication Union's (ITU) Radio Regulations (RR)ITU Radio Regulations, Section IV. Radio Stations and Systems – Article 1.22, definition: ''inter-satellite service / inter-satellite radiocommunication service'' – defined as ''«A radiocommunication service providing links between artificial satellites.'' Classification In accordance with ''ITU Radio Regulations'' (article 1) variations of this ''radiocommunication service'' are classified as follows: * Fixed service (article 1.20) ** Fixed-satellite service (article 1.21) ** (article 1.22) ** Earth exploration-satellite service (article 1.51) *** Meteorological-satellite service (article 1.52) Satellites Inter-satellite radiocommunications satellites * U.S. Tracking and Data Relay Satellite * Artemis (satellite) * European Data Relay System * Indian Data Relay Satellite System * Luc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Data Relay System
The European Data Relay System (EDRS) system is a European constellation of GEO satellites that relay information and data between satellites, spacecraft, UAVs, and ground stations. The first components (a payload and dedicated GEO satellite) were launched in 2016 and 2019. Purpose and context The designers intend the system to provide almost full-time communication, even with satellites in low Earth orbit that often have reduced visibility from ground stations. It makes on-demand data available to, for example, rescue workers who want near-real-time satellite data of a crisis region. There are a number of key services that will benefit from this system's infrastructure: * Earth Observation applications in support of time-critical and/or data-intensive services; e.g., change detection, environmental monitoring. * Government and security services that need images from key European space systems such as Global Monitoring for Environment and Security. * Emergency response and crisi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Data Relay Satellite System
Indian Data Relay Satellite System or IDRSS is a planned Indian constellation of Inter-satellite communications satellites. It is planned to initially comprise two satellites, CMS-04 (formerly IDRSS-1) & IDRSS-2 in geostationary orbit. It will facilitate relay of information between various Indian spacecraft, in-flight launch vehicle monitoring and assist Indian Human Spaceflight Programme. Objectives A Data Relay Satellite System (DRSS) facilitates continuous real-time communication between Low Earth orbit bound spacecraft to the ground station as well as inter-satellite communication. Such a satellite in geostationary orbit can track a low altitude spacecraft up to almost half of its orbit. India operates one of world's largest remote sensing satellites systems. Visibility of these satellites is not more than 10-15 minutes in a day and sometimes even lower. The IDRSS satellites, one opposite to each half of earth in GEO, can see about 80 per cent of the area where Indian remo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luch (satellite)
The ''Luch'' (russian: Луч; lit. ''Ray'') Satellite Data Relay Network (SDRN), also referred to as ''Altair'' and ''Gelios'', is a series of geosynchronous Russian relay satellites, used to transmit live TV images, communications and other telemetry from the Soviet/Russian space station '' Mir'', the Russian Orbital Segment (ROS) of the International Space Station and other orbital spacecraft to the Earth, in a manner similar to that of the US Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System. First generation The first generation of satellites was created by NPO-PM using the satellite platform KAUR-4 (its first use) and had the code name "Altair" (index GUKOS - 11F669). The system was conceived as part of the second generation of the Global Satellite Data Relay Network (Глобальная Космическая Командно-Ретрансляционная система (GKKRS)) and was developed by decree of the Soviet Council of Ministers of February 17, 1976 ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Deep Space Network
The Chinese Deep Space Network (CDSN) is a network of large antennas and communication facilities that are used for the interplanetary spacecraft missions of China. It is managed by the China Satellite Launch and Tracking Control Center General (CLTC), which reports to the People's Liberation Army Strategic Support Force Space Systems Department. They also deal with radio-astronomical and radar observations. The network was first needed for the lunar mission Chang'e 1, and since has been used to support subsequent missions to the Moon and Mars such as Chang'e 5, and Tianwen-1 missions. Similar deep space networks are run by the United States, Russia, European countries, Japan, and India. Introduction In principle, a Chinese deep space network has existed since 1993 with the commissioning of the Nanshan 25-meter telescope in the mountains south of Ürümqi. The 25-meter antenna of the Shanghai Astronomical Observatory was then not only able to participate in the Southern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Queqiao Relay Satellite
''Queqiao'' relay satellite (), also known as the Chang'e 4 Relay, is a communications relay and radio astronomy satellite for the Chang'e 4 lunar farside mission. As part of the Chinese Lunar Exploration Program, the China National Space Administration (CNSA) launched the Queqiao relay satellite on 20 May 2018 to a halo orbit around the Earth–Moon L2 Lagrangian point Queqiao is the first ever communication relay and radio astronomy satellite at this location. The name ''Queqiao'' ("Magpie Bridge") was inspired by and came from the Chinese tale ''The Cowherd and the Weaver Girl''. Design and development Queqiao was designed to function as a communication relay for the Chang'e 4 mission to the far side of the Moon, as well as a deep space radio astronomy observatory for the Chinese space program. Direct communication with Earth is impossible on the far side of the Moon, since transmissions are blocked by the Moon. Communications must go through a communications relay satel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long March 3B
The Long March 3B (, ''Chang Zheng 3B''), also known as the CZ-3B and LM-3B, is a Chinese orbital launch vehicle. Introduced in 1996, it is launched from Launch Area 2 and 3 at the Xichang Satellite Launch Center in Sichuan. A three-stage rocket with four strap-on liquid rocket boosters, it is currently the second most powerful member of the Long March rocket family after the Long March 5 and the heaviest of the Long March 3 rocket family, and is mainly used to place communications satellites into geosynchronous orbits. An enhanced version, the Long March 3B/E or G2, was introduced in 2007 to increase the rocket's geostationary transfer orbit (GTO) cargo capacity and lift heavier geosynchronous orbit (GEO) communications satellites. The Long March 3B also served as the basis for the medium-capacity Long March 3C, which was first launched in 2008. , the Long March 3B, 3B/E and 3B/G5 have conducted 82 successful launches, plus 2 failures and 2 partial failures, accumulati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DFH-3
Dongfanghong () was a satellite program of the People's Republic of China. The program started in August 1965 as Project 651—a less ambitious successor to the earlier Project 581—with the goal of launching a satellite heavier than both Sputnik 1 and Explorer 1 into space, and developing all the necessary technologies to do so. History In 1958, the Chinese Academy of Science proposed Project 581 which included a plan to launch a satellite into space before 1 October 1959. The project was troubled due to the country's lack of expertise in the field of rocketry. On 21 January 1959, Zhang Jingfu, who was in charge in the satellite research program, postponed the project to allow effort to be put into developing more basic technologies, such as sounding rocketry. In December 1964, during the 3rd National People's Congress, Zhao Jiuzhang suggested that the work on satellites be resumed. In August 1968, the Central Special Committee approved Chinese Academy of Science's plan, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satellite Catalog Number
The Satellite Catalog Number (SATCAT, also known as NORAD (North American Aerospace Defense) Catalog Number, NORAD ID, USSPACECOM object number or simply catalog number, among similar variants) is a sequential nine-digit number assigned by the United States Space Command (USSPACECOM) in the order of launch or discovery to all artificial objects in the orbits of Earth and those that left Earth's orbit. The first catalogued object, catalog number 1, is the Sputnik 1 launch vehicle, with the Sputnik 1 satellite having been assigned catalog number 2. __NOTOC__ Objects that fail to orbit or orbit for a short time are not catalogued. The minimum object size in the catalog is in diameter. , the catalog listed 54,200 objects, including 14,102 satellites that had been launched into orbit since 1957 of which 7,043 were still active. 24,146 of the objects were well tracked while 1,850 were lost. In addition USSPACECOM was also tracking 20,900 analyst objects. Analyst objects are variably tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Designator
The International Designator, also known as COSPAR ID, is an international identifier assigned to artificial objects in space. It consists of the launch year, a three-digit incrementing launch number of that year and up to a three-letter code representing the sequential identifier of a piece in a launch. In TLE format the first two digits of the year and the dash are dropped. For example1990-037Ais the Space Shuttle ''Discovery'' on mission STS-31, which carried the Hubble Space Telescope1990-037B into space. This launch was the 37th known successful launch worldwide in 1990. The designation system has been generally known as the COSPAR system, named for the Committee on Space Research (COSPAR) of the International Council for Science. COSPAR subsumed the first designation system, devised at Harvard University. That system used letters of the Greek alphabet to designate artificial satellites. This was based on the scientific naming convention for natural satellites. For exampl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |