|
Subcontinent
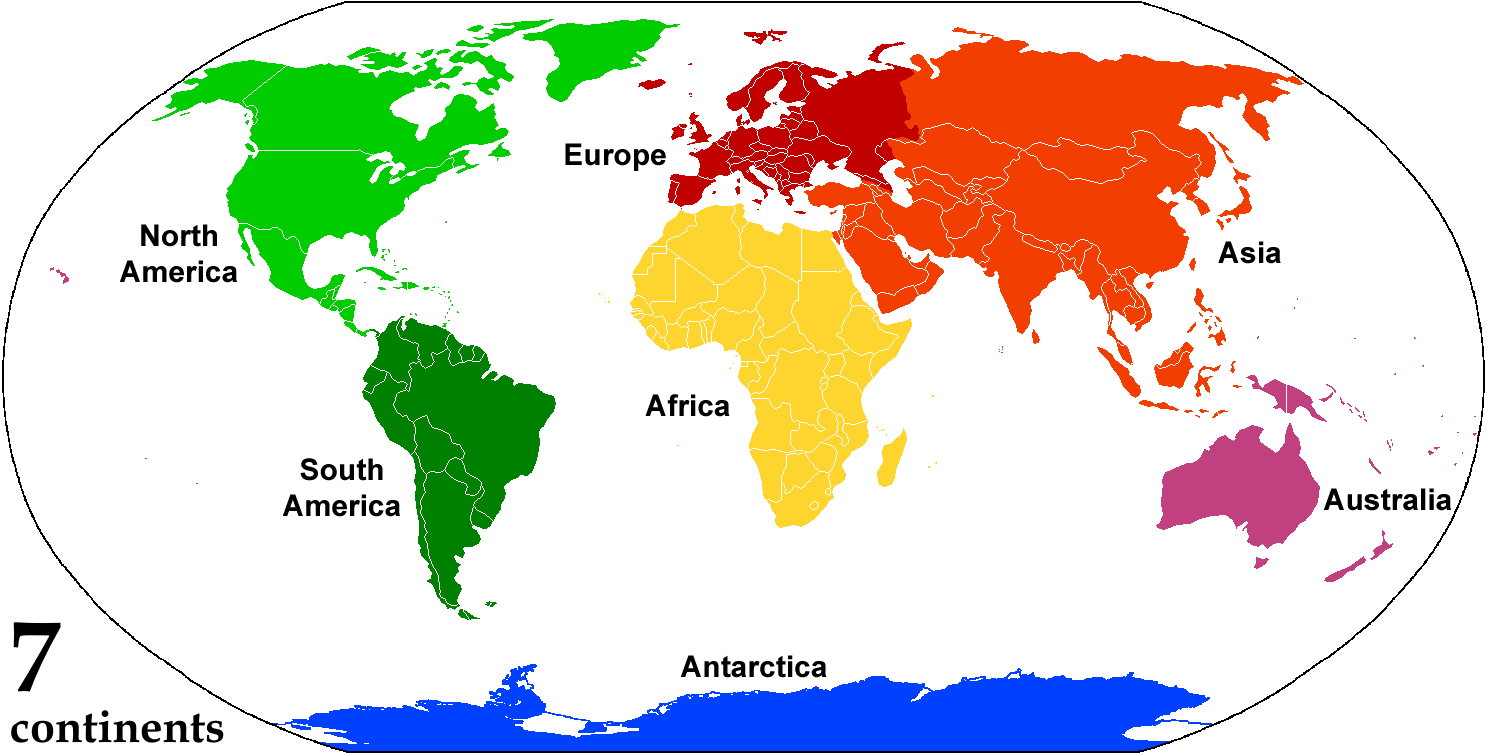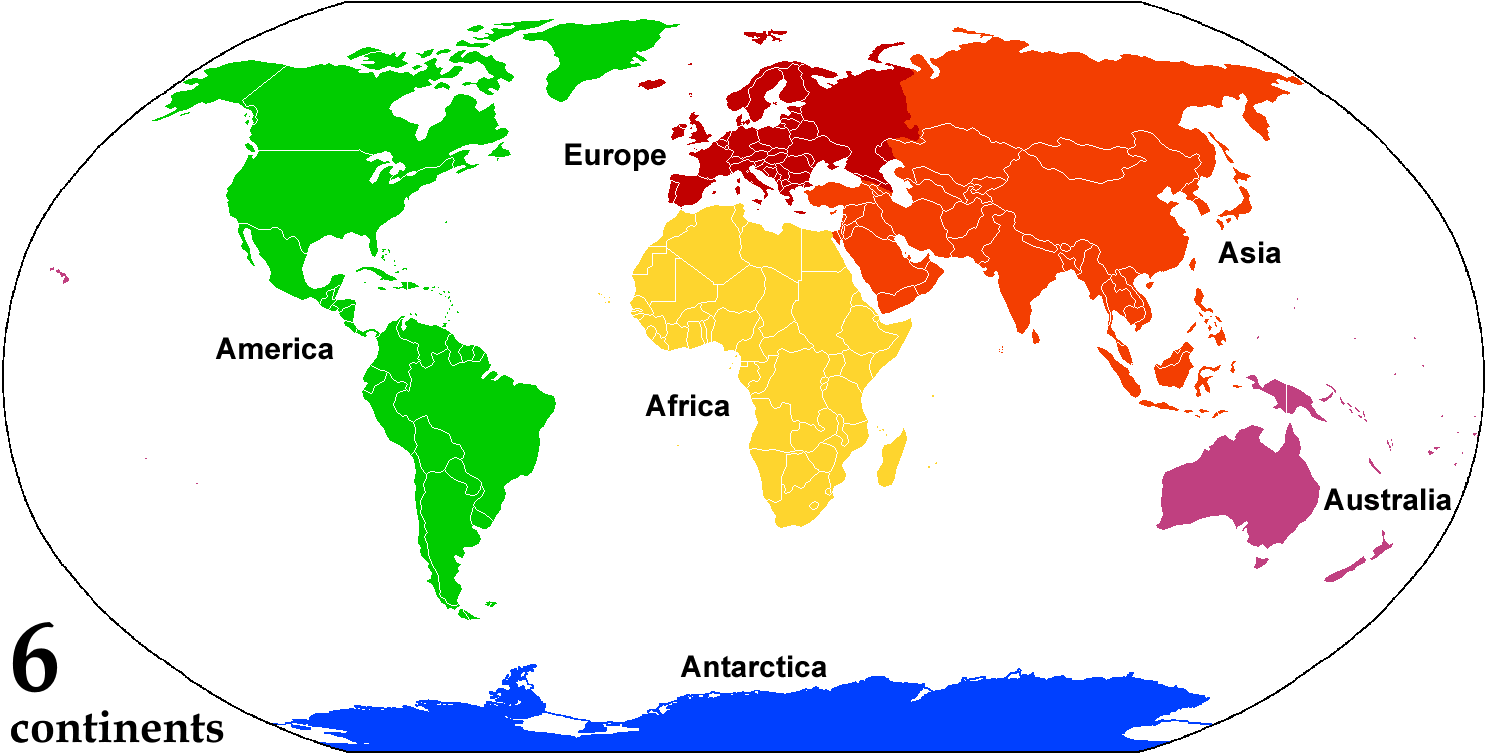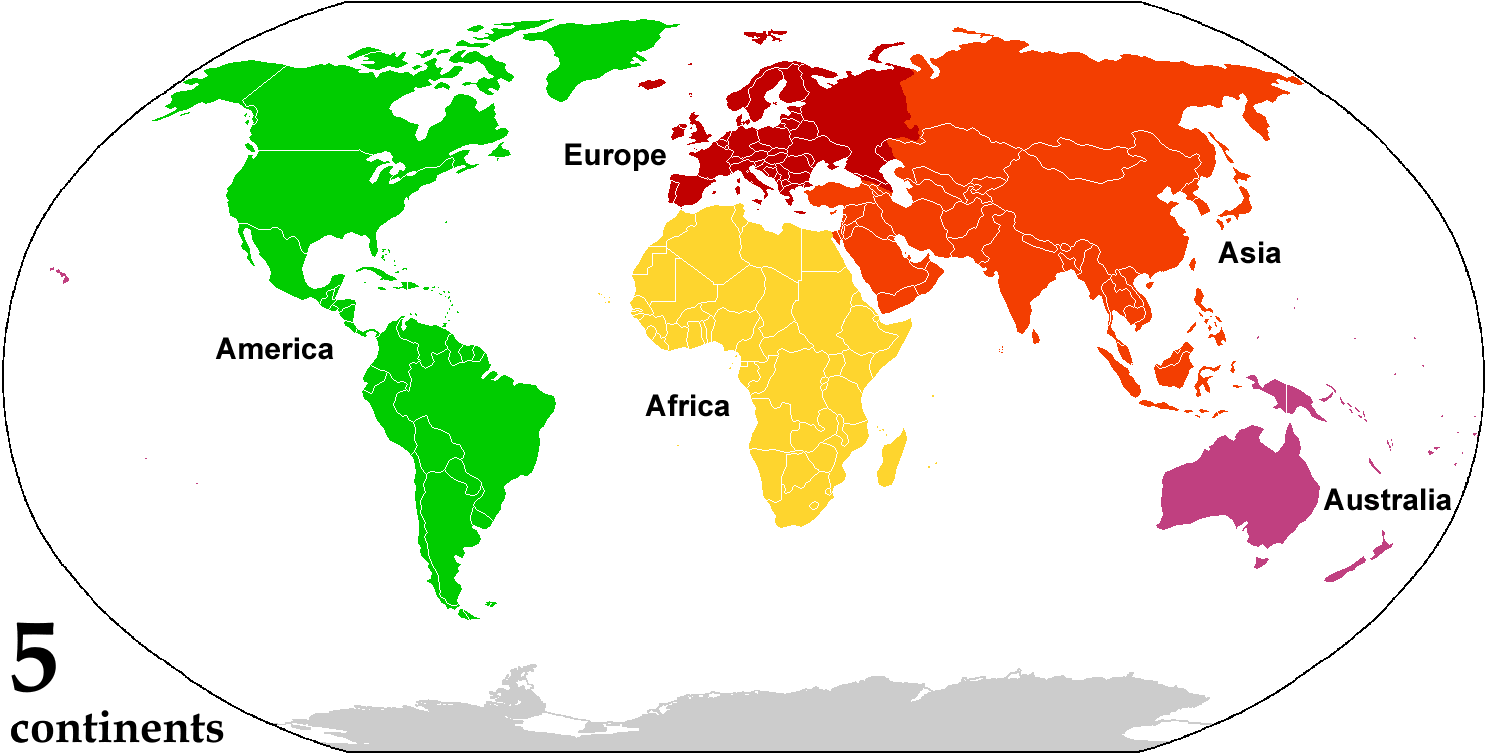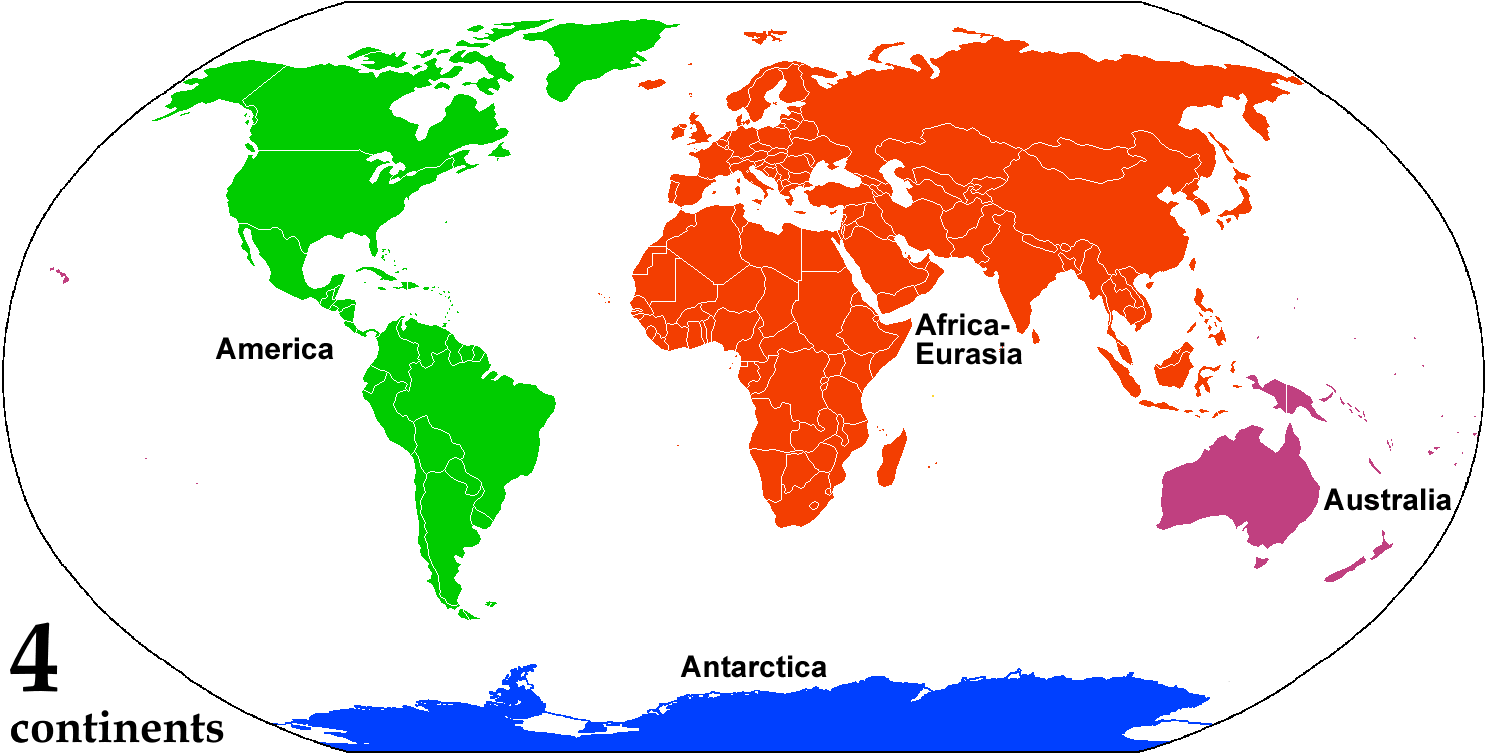
A continent is any of several large landmasses. Generally identified by convention rather than any strict criteria, up to seven geographical regions are commonly regarded as continents. Ordered from largest in area to smallest, these seven regions are: Asia, Africa, North America, South America, Antarctica, Europe, and Australia. "Most people recognize seven continents—Asia, Africa, North America, South America, Antarctica, Europe, and Australia, from largest to smallest—although sometimes Asia and Europe are considered a single continent, Eurasia." Variations with fewer continents may merge some of these, for example America, Eurasia, or Afro-Eurasia are sometimes treated as single continents, which can bring the total number as low as four. Zealandia, a largely submerged mass of continental crust, has also been described as a continent. Oceanic islands are frequently grouped with a nearby continent to divide all the world's land into geographical regions. Under this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. Comprising the westernmost peninsulas of Eurasia, it shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with both Africa and Asia. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south and Asia to the east. Europe is commonly considered to be separated from Asia by the watershed of the Ural Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian Sea, the Greater Caucasus, the Black Sea and the waterways of the Turkish Straits. "Europe" (pp. 68–69); "Asia" (pp. 90–91): "A commonly accepted division between Asia and Europe ... is formed by the Ural Mountains, Ural River, Caspian Sea, Caucasus Mountains, and the Black Sea wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regions
In geography, regions, otherwise referred to as zones, lands or territories, are areas that are broadly divided by physical characteristics (physical geography), human impact characteristics (human geography), and the interaction of humanity and the environment ( environmental geography). Geographic regions and sub-regions are mostly described by their imprecisely defined, and sometimes transitory boundaries, except in human geography, where jurisdiction areas such as national borders are defined in law. Apart from the global continental regions, there are also hydrospheric and atmospheric regions that cover the oceans, and discrete climates above the land and water masses of the planet. The land and water global regions are divided into subregions geographically bounded by large geological features that influence large-scale ecologies, such as plains and features. As a way of describing spatial areas, the concept of regions is important and widely used among the many branches ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an area of , about 30% of Earth's total land area and 8.7% of Earth's total surface area. The continent, which has long been home to the majority of the human population, was the site of many of the first civilizations. Its 4.7 billion people constitute roughly 60% of the world's population. In general terms, Asia is bounded on the east by the Pacific Ocean, on the south by the Indian Ocean, and on the north by the Arctic Ocean. The border of Asia with Europe is a historical and cultural construct, as there is no clear physical and geographical separation between them. It is somewhat arbitrary and has moved since its first conception in classical antiquity. The division of Eurasia into two continents reflects East–West cultural, linguistic, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Caribbean Sea, and to the west and south by the Pacific Ocean. Because it is on the North American Plate, North American Tectonic Plate, Greenland is included as a part of North America geographically. North America covers an area of about , about 16.5% of Earth's land area and about 4.8% of its total surface. North America is the third-largest continent by area, following Asia and Africa, and the list of continents and continental subregions by population, fourth by population after Asia, Africa, and Europe. In 2013, its population was estimated at nearly 579 million people in List of sovereign states and dependent territories in North America, 23 independent states, or about 7.5% of the world's population. In Americas (terminology)#Human ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the southern subregion of a single continent called America. South America is bordered on the west by the Pacific Ocean and on the north and east by the Atlantic Ocean; North America and the Caribbean Sea lie to the northwest. The continent generally includes twelve sovereign states: Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Chile, Colombia, Ecuador, Guyana, Paraguay, Peru, Suriname, Uruguay, and Venezuela; two dependent territories: the Falkland Islands and South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands; and one internal territory: French Guiana. In addition, the ABC islands of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, Ascension Island (dependency of Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha, a British Overseas Territory), Bouvet Island ( dependency ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Tectonic Plates
This is a list of tectonic plates on Earth's surface. Tectonic plates are pieces of Earth's crust and uppermost mantle, together referred to as the lithosphere. The plates are around thick and consist of two principal types of material: oceanic crust (also called '' sima'' from silicon and magnesium) and continental crust (''sial'' from silicon and aluminium). The composition of the two types of crust differs markedly, with mafic basaltic rocks dominating oceanic crust, while continental crust consists principally of lower-density felsic granitic rocks. Current plates Geologists generally agree that the following tectonic plates currently exist on Earth's surface with roughly definable boundaries. Tectonic plates are sometimes subdivided into three fairly arbitrary categories: ''major'' (or ''primary'') ''plates'', ''minor'' (or ''secondary'') ''plates'', and ''microplates'' (or ''tertiary plates''). Major plates These plates comprise the bulk of the continents an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surface is made up of the ocean, dwarfing Earth's polar ice, lakes, and rivers. The remaining 29% of Earth's surface is land, consisting of continents and islands. Earth's surface layer is formed of several slowly moving tectonic plates, which interact to produce mountain ranges, volcanoes, and earthquakes. Earth's liquid outer core generates the magnetic field that shapes the magnetosphere of the Earth, deflecting destructive solar winds. The atmosphere of the Earth consists mostly of nitrogen and oxygen. Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere like carbon dioxide (CO2) trap a part of the energy from the Sun close to the surface. Water vapor is widely present in the atmosphere and forms clouds that cover most of the planet. More solar e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Land
Land, also known as dry land, ground, or earth, is the solid terrestrial surface of the planet Earth that is not submerged by the ocean or other bodies of water. It makes up 29% of Earth's surface and includes the continents and various islands. Earth's land surface is almost entirely covered by regolith, a layer of rock, soil, and minerals that forms the outer part of the crust. Land plays important roles in Earth's climate system and is involved in the carbon cycle, nitrogen cycle, and water cycle. One-third of land is covered in trees, 15% is used for crops, and 10% is covered in permanent snow and glaciers. Land terrain varies greatly and consists of mountains, deserts, plains, plateaus, glaciers, and other landforms. In physical geology, the land is divided into two major categories: mountain ranges and relatively flat interiors called cratons. Both are formed over millions of years through plate tectonics. A major part of Earth's water cycle, streams shape the lands ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continental Shelf
A continental shelf is a portion of a continent that is submerged under an area of relatively shallow water, known as a shelf sea. Much of these shelves were exposed by drops in sea level during glacial periods. The shelf surrounding an island is known as an ''insular shelf''. The continental margin, between the continental shelf and the abyssal plain, comprises a steep continental slope, surrounded by the flatter continental rise, in which sediment from the continent above cascades down the slope and accumulates as a pile of sediment at the base of the slope. Extending as far as 500 km (310 mi) from the slope, it consists of thick sediments deposited by turbidity currents from the shelf and slope. The continental rise's gradient is intermediate between the gradients of the slope and the shelf. Under the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea, the name continental shelf was given a legal definition as the stretch of the seabed adjacent to the shores of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
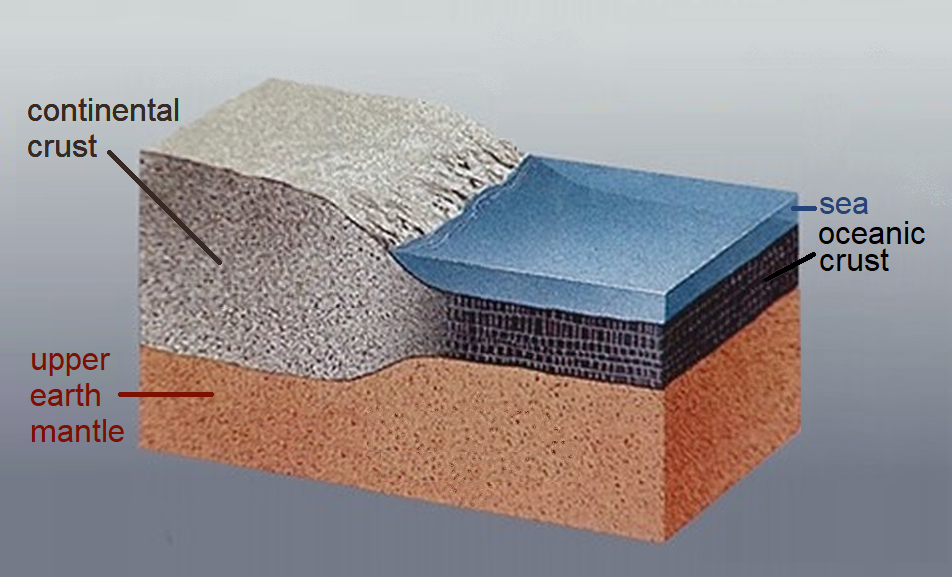
Continental Crust
Continental crust is the layer of igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks that forms the geological continents and the areas of shallow seabed close to their shores, known as continental shelves. This layer is sometimes called '' sial'' because its bulk composition is richer in aluminium silicates (Al-Si) and has a lower density compared to the oceanic crust, called ''sima'' which is richer in magnesium silicate (Mg-Si) minerals. Changes in seismic wave velocities have shown that at a certain depth (the Conrad discontinuity), there is a reasonably sharp contrast between the more felsic upper continental crust and the lower continental crust, which is more mafic in character. The continental crust consists of various layers, with a bulk composition that is intermediate (SiO2 wt% = 60.6). The average density of continental crust is about , less dense than the ultramafic material that makes up the mantle, which has a density of around . Continental crust is also less dense ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continental Models-Australia
Continental may refer to: Places * Continent, the major landmasses of Earth * Continental, Arizona, a small community in Pima County, Arizona, US * Continental, Ohio, a small town in Putnam County, US Arts and entertainment * Continental (album), ''Continental'' (album), an album by Saint Etienne * Continental (card game), a rummy-style card game * Continental (film), ''Continental'' (film), a 2013 film * Continental Singers, a Christian music organization Companies * Continental AG, a German automotive parts and technologies manufacturer * Continental Airlines, a former American airline * Continental Electronics, an American radio transmitter manufacturer * Continental Films, a German-controlled French film company during the Nazi occupation of France * Continental Illinois, a defunct large bank * Continental Mortgage and Loan Company (later known as Continental, Inc.), the former name of HomeStreet Bank * Continental Motors, Inc., a Chinese manufacturer of aircraft engines * Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continental Fragment
Continental crustal fragments, partly synonymous with microcontinents, are pieces of continents that have broken off from main continental masses to form distinct islands that are often several hundred kilometers from their place of origin. Causes Continental fragments and microcontinent crustal compositions are very similar to those of regular continental crust. The rifting process that caused the continental fragments to form most likely impacts their layers and overall thickness along with the addition of mafic intrusions to the crust. Studies have determined that the average crustal thickness of continental fragments is approximately . The sedimentary layer of continental fragments can be up to thick and can overlay two to three crustal layers. Continental fragments have an average crustal density of which is very similar to that of typical continental crust. Strike-slip fault zones cause the fragmentation of microcontinents. The zones link the extensional zones where ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)




.jpg)