|
Stomach
The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the gastrointestinal tract of humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The stomach has a dilated structure and functions as a vital organ in the digestive system. The stomach is involved in the gastric phase of digestion, following chewing. It performs a chemical breakdown by means of enzymes and hydrochloric acid. In humans and many other animals, the stomach is located between the oesophagus and the small intestine. The stomach secretes digestive enzymes and gastric acid to aid in food digestion. The pyloric sphincter controls the passage of partially digested food (chyme) from the stomach into the duodenum, where peristalsis takes over to move this through the rest of intestines. Structure In the human digestive system, the stomach lies between the oesophagus and the duodenum (the first part of the small intestine). It is in the left upper quadrant of the abdominal cavity. The top of the stomach lies ag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyloric Sphincter
The pylorus ( or ), or pyloric part, connects the stomach to the duodenum. The pylorus is considered as having two parts, the ''pyloric antrum'' (opening to the body of the stomach) and the ''pyloric canal'' (opening to the duodenum). The ''pyloric canal'' ends as the ''pyloric orifice'', which marks the junction between the stomach and the duodenum. The orifice is surrounded by a sphincter, a band of muscle, called the ''pyloric sphincter''. The word ''pylorus'' comes from Greek πυλωρός, via Latin. The word ''pylorus'' in Greek means "gatekeeper", related to "gate" ( el, pyle) and is thus linguistically related to the word " pylon". Structure The pylorus is the furthest part of the stomach that connects to the duodenum. It is divided into two parts, the ''antrum'', which connects to the body of the stomach, and the ''pyloric canal'', which connects to the duodenum. Antrum The ''pyloric antrum'' is the initial portion of the pylorus. It is near the bottom of the stomach, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
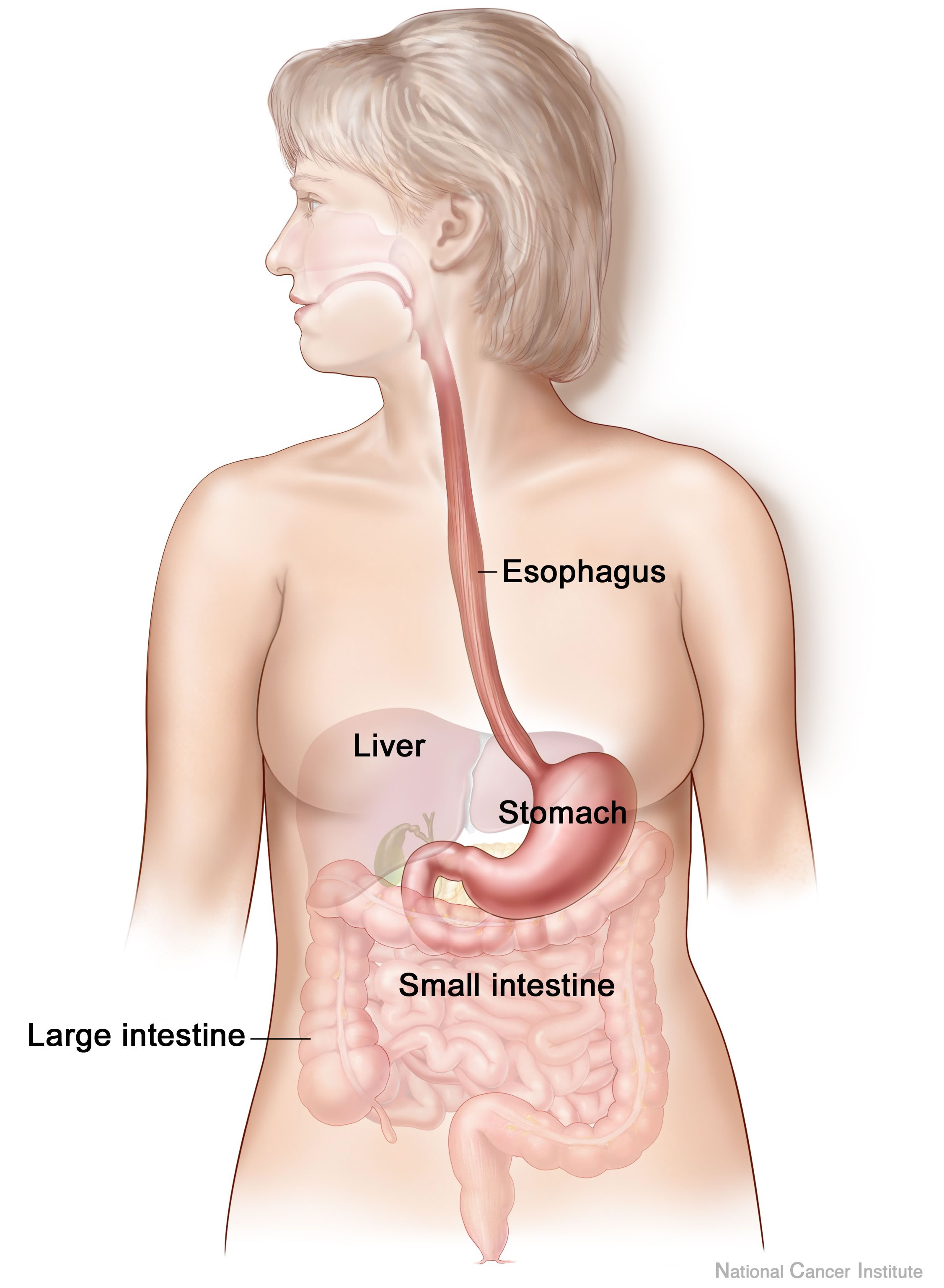
Human Digestive System
The human digestive system consists of the gastrointestinal tract plus the accessory organs of digestion (the tongue, salivary glands, pancreas, liver, and gallbladder). Digestion involves the breakdown of food into smaller and smaller components, until they can be absorbed and assimilated into the body. The process of digestion has three stages: the cephalic phase, the gastric phase, and the intestinal phase. The first stage, the cephalic phase of digestion, begins with secretions from gastric glands in response to the sight and smell of food. This stage includes the mechanical breakdown of food by chewing, and the chemical breakdown by digestive enzymes, that takes place in the mouth. Saliva contains the digestive enzymes amylase, and lingual lipase, secreted by the salivary and serous glands on the tongue. Chewing, in which the food is mixed with saliva, begins the mechanical process of digestion. This produces a bolus which is swallowed down the esophagus to ent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Digestive System
The human digestive system consists of the gastrointestinal tract plus the accessory organs of digestion (the tongue, salivary glands, pancreas, liver, and gallbladder). Digestion involves the breakdown of food into smaller and smaller components, until they can be absorbed and assimilated into the body. The process of digestion has three stages: the cephalic phase, the gastric phase, and the intestinal phase. The first stage, the cephalic phase of digestion, begins with secretions from gastric glands in response to the sight and smell of food. This stage includes the mechanical breakdown of food by chewing, and the chemical breakdown by digestive enzymes, that takes place in the mouth. Saliva contains the digestive enzymes amylase, and lingual lipase, secreted by the salivary and serous glands on the tongue. Chewing, in which the food is mixed with saliva, begins the mechanical process of digestion. This produces a bolus which is swallowed down the esophagus to ent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Right Gastric Artery
The right gastric artery arises, in most cases (53% of cases), from the proper hepatic artery, descends to the pyloric end of the stomach, and passes from right to left along its lesser curvature, supplying it with branches, and anastomosing with the left gastric artery. It can also arise from the region of division of the common hepatic artery The common hepatic artery is a short blood vessel that supplies oxygenated blood to the liver, pylorus of the stomach, duodenum, pancreas, and gallbladder. It arises from the celiac artery and has the following branches: Additional images ... (20% of cases), the left branch of the hepatic artery (15% of cases), the gastroduodenal artery (8% of cases), and most rarely, the common hepatic artery itself (4% of cases). Additional images File:Gray532.png, The celiac artery and its branches; the liver has been raised, and the lesser omentum and anterior layer of the greater omentum removed. File:Slide14fff.JPG, Right gastric arter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Left Gastric Artery
In human anatomy, the left gastric artery arises from the celiac artery and runs along the superior portion of the lesser curvature of the stomach. Branches also supply the lower esophagus. The left gastric artery anastomoses with the right gastric artery, which runs right to left. Important to note is that the esophageal branch of the left gastric artery ascends and passes through the esophageal hiatus. Clinical significance In terms of disease, the left gastric artery may be involved in peptic ulcer disease: if an ulcer erodes through the stomach mucosa into a branch of the artery, this can cause massive blood loss into the stomach, which may result in such symptoms as hematemesis or melaena. Additional images File:Stomach blood supply.svg, Blood supply to the stomach: left and right gastric artery, left and right gastro-omental artery and short gastric artery The short gastric arteries consist of from five to seven small branches, which arise from the end of the sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Right Gastro-omental Artery
The right gastroepiploic artery (or right gastro-omental artery) is one of the two terminal branches of the gastroduodenal artery. It runs from right to left along the greater curvature of the stomach, between the layers of the greater omentum, anastomosing with the left gastroepiploic artery, a branch of the splenic artery. Except at the pylorus where it is in contact with the stomach, it lies about a finger's breadth from the greater curvature. Branches This vessel gives off numerous branches: * "gastric branches": ascend to supply both surfaces of the stomach. * "omental branches": descend to supply the greater omentum and anastomose with branches of the middle colic. Use in coronary artery surgery The right gastroepiploic artery was first used as a coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) in 1984 by John Pym and colleagues at Queen's University. It has become an accepted alternative conduit, and is particularly useful in patients who do not have suitable saphenous veins to ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Left Gastro-omental Artery
The left gastroepiploic artery (or left gastro-omental artery), the largest branch of the splenic artery, runs from left to right about a finger's breadth or more from the greater curvature of the stomach, between the layers of the greater omentum, and anastomoses with the right gastroepiploic (a branch of the right gastro-duodenal artery originating from the hepatic branch of the coeliac trunk). In its course it distributes: * "Gastric branches": several ascending branches to both surfaces of the stomach; * "Omental branches": descend to supply the greater omentum The greater omentum (also the great omentum, omentum majus, gastrocolic omentum, epiploon, or, especially in animals, caul) is a large apron-like fold of visceral peritoneum that hangs down from the stomach. It extends from the greater curvature ... and anastomose with branches of the middle colic. Additional images File:Gray533.png, Branches of the celiac artery. References External links * - "Stomach ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Short Gastric Arteries
The short gastric arteries consist of from five to seven small branches, which arise from the end of the splenic artery, and from its terminal divisions. They pass from left to right, between the layers of the gastrolienal ligament, and are distributed to the greater curvature of the stomach, anastomosing with branches of the left gastric and left gastroepiploic artery, left gastroepiploic arteries. Unlike the gastroepiploics and the left and right gastric arteries, the short gastric arteries have poor anastomoses if the splenic artery is blocked. Structure The short gastric arteries arise from the splenic artery. They run along part of the Curvatures of the stomach, greater curvature of the stomach. Function The short gastric arteries supply the Stomach, fundus of the stomach on the side of the Curvatures of the stomach, greater curvature of the stomach. References External links * {{Authority control Arteries of the abdomen Stomach ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastric Acid
Gastric acid, gastric juice, or stomach acid is a digestive fluid formed within the stomach lining. With a pH between 1 and 3, gastric acid plays a key role in digestion of proteins by activating digestive enzymes, which together break down the long chains of amino acids of proteins. Gastric acid is regulated in feedback systems to increase production when needed, such as after a meal. Other cells in the stomach produce bicarbonate, a base, to buffer the fluid, ensuring a regulated pH. These cells also produce mucus – a viscous barrier to prevent gastric acid from damaging the stomach. The pancreas further produces large amounts of bicarbonate and secretes bicarbonate through the pancreatic duct to the duodenum to neutralize gastric acid passing into the digestive tract. The active components of gastric acid are protons and chloride. Often simplistically described as hydrochloric acid, these species are produced by parietal cells in the gastric glands in the stomach. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastrointestinal Tract
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organs of the digestive system, in humans and other animals, including the esophagus, stomach, and intestines. Food taken in through the mouth is digested to extract nutrients and absorb energy, and the waste expelled at the anus as feces. ''Gastrointestinal'' is an adjective meaning of or pertaining to the stomach and intestines. Most animals have a "through-gut" or complete digestive tract. Exceptions are more primitive ones: sponges have small pores ( ostia) throughout their body for digestion and a larger dorsal pore ( osculum) for excretion, comb jellies have both a ventral mouth and dorsal anal pores, while cnidarians and acoels have a single pore for both digestion and excretion. The human gastrointestinal tract consists of the esophagus, stomach, and intestines, and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastrointestinal Tract
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organs of the digestive system, in humans and other animals, including the esophagus, stomach, and intestines. Food taken in through the mouth is digested to extract nutrients and absorb energy, and the waste expelled at the anus as feces. ''Gastrointestinal'' is an adjective meaning of or pertaining to the stomach and intestines. Most animals have a "through-gut" or complete digestive tract. Exceptions are more primitive ones: sponges have small pores ( ostia) throughout their body for digestion and a larger dorsal pore ( osculum) for excretion, comb jellies have both a ventral mouth and dorsal anal pores, while cnidarians and acoels have a single pore for both digestion and excretion. The human gastrointestinal tract consists of the esophagus, stomach, and intestines, and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Right Gastroepiploic Vein
The right gastroepiploic vein (right gastroomental vein) is a blood vessel that drains blood from the greater curvature and left part of the body of the stomach into the superior mesenteric vein. It runs from left to right along the greater curvature of the stomach between the two layers of the greater omentum, along with the right gastroepiploic artery. As a tributary of the superior mesenteric vein, it is a part of the hepatic portal system In human anatomy, the hepatic portal system is the system of veins comprising the hepatic portal vein and its tributaries. It is also called the portal venous system (although it is not the only example of a portal venous system) and splanchnic .... References Veins of the torso Stomach {{cardiovascular-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |