|
Soyuz
Soyuz is a transliteration of the Cyrillic text Союз ( Russian and Ukrainian, 'Union'). It can refer to any union, such as a trade union (''profsoyuz'') or the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (Сою́з Сове́тских Социалисти́ческих Респу́блик, ''Soyuz Sovetskikh Sotsialisticheskikh Respublik''). As terminological shorthand "soyuz" by itself was often used interchangeably with each of the slightly longer terms Сове́тский Сою́з (''Sovetskiy Soyuz'', 'Soviet Union'). It was also a shorthand for the citizenry as a whole. Soyuz is also the designated name of various projects the country commissioned during the Space Race. Space program uses * Soyuz programme, a human spaceflight program initiated by the Soviet Union, continued by the Russian Federation * Soyuz (spacecraft), used in that program * Soyuz (rocket), initially used to launch that spacecraft * Soyuz (rocket family), derivatives of that rocket design * Soyuz Launch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
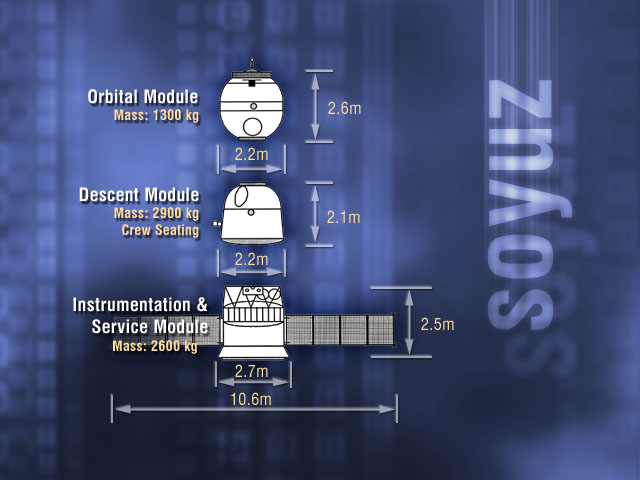
Soyuz (spacecraft)
Soyuz () is a series of spacecraft which has been in service since the 1960s, having made more than 140 flights. It was designed for the Soviet space program by the Korolev Design Bureau (now Energia). The Soyuz succeeded the Voskhod spacecraft and was originally built as part of the Soviet crewed lunar programs. It is launched on a Soyuz rocket from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Between the 2011 retirement of the Space Shuttle and the 2020 demo flight of SpaceX Crew Dragon, the Soyuz served as the only means to ferry crew to or from the International Space Station, for which it remains heavily used. Although China did launch crewed Shenzhou flights during this time, none of them docked with the ISS. History The first Soyuz flight was uncrewed and started on 28 November 1966. The first Soyuz mission with a crew, Soyuz 1, launched on 23 April 1967 but ended with a crash due to a parachute failure, killing cosmonaut Vladimir Komarov. The following flight was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soyuz (rocket Family)
Soyuz (russian: Союз, meaning "union", GRAU index 11A511) is a family of expendable Russian and Soviet carrier rockets developed by OKB-1 and manufactured by Progress Rocket Space Centre in Samara, Russia. With over 1,900 flights since its debut in 1966, the Soyuz is the most frequently used launch vehicle in the world as of 2021. For nearly a decade, between the final flight of the Space Shuttle program in 2011 and the 2020 first crewed mission of SpaceX's Falcon 9 rocket, Soyuz rockets were the only launch vehicles able and approved for transporting astronauts to the International Space Station. The Soyuz vehicles are used as the launcher for the crewed Soyuz spacecraft as part of the Soyuz programme, as well as to launch uncrewed Progress supply spacecraft to the International Space Station and for commercial launches marketed and operated by Starsem and Arianespace. All Soyuz rockets use RP-1 and liquid oxygen (LOX) propellant, with the exception of the Soyuz- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soyuz Programme
The Soyuz programme ( , ; russian: link=no, Союз , meaning "Union") is a human spaceflight programme initiated by the Soviet Union in the early 1960s. The Soyuz spacecraft was originally part of a Moon landing project intended to put a Soviet cosmonaut on the Moon. It was the third Soviet human spaceflight programme after the Vostok (1961–1963) and Voskhod (1964–1965) programmes. The programme consists of the Soyuz capsule and the Soyuz rocket and is now the responsibility of the Russian Roscosmos. After the retirement of the Space Shuttle in 2011, Soyuz was the only way for humans to get to the International Space Station (ISS) until 30 May 2020, when Crew Dragon flew to the ISS for the first time with astronauts. Soyuz rocket The launch vehicles used in the Soyuz expendable launch system are manufactured at the Progress State Research and Production Rocket Space Center (TsSKB-Progress) in Samara, Russia. As well as being used in the Soyuz programme as the lau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soyuz Launch Complex
The Ensemble de Lancement Soyouz (ELS) (in English ''Soyuz Launch Complex'') is a launch complex at the Guiana Space Centre in Kourou/ Sinnamary, French Guiana. It is used by Soyuz-ST rockets: modified versions of the Soyuz-2 optimised for launch from Kourou under Soyuz at the Guiana Space Centre programme. History The first launch to use the complex occurred on 21 October 2011, when a Soyuz ST-B launched the first two Galileo In Orbit Validation spacecraft. The site's equatorial latitude allows a greater payload mass to be delivered into geosynchronous transfer orbit compared to existing Soyuz launch facilities at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. ELS is fifteen kilometres north-west of the launch facilities used by Ariane rockets. It consists of a single launch pad, with a horizontal assembly and processing facility, or MIK, located 700 metres away. As with the Soyuz launch complexes at Baikonur and Plesetsk, the pad is connected to the MIK by means of a wide gaug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Race
The Space Race was a 20th-century competition between two Cold War rivals, the United States and the Soviet Union, to achieve superior spaceflight capability. It had its origins in the ballistic missile-based nuclear arms race between the two nations following World War II. The technological advantage demonstrated by spaceflight achievement was seen as necessary for national security, and became part of the symbolism and ideology of the time. The Space Race brought pioneering launches of artificial satellites, robotic space probes to the Moon, Venus, and Mars, and human spaceflight in low Earth orbit and ultimately to the Moon. Public interest in space travel originated in the 1951 publication of a Soviet youth magazine and was promptly picked up by US magazines. The competition began on July 30, 1955 when the United States announced its intent to launch artificial satellites for the International Geophysical Year. Four days later, the Soviet Union responded by decl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soyuz (rocket)
The Soyuz (russian: Союз, meaning "union", GRAU index 11A511) was a Soviet expendable carrier rocket designed in the 1960s by OKB-1 and manufactured by State Aviation Plant No. 1 in Kuybyshev, Soviet Union. It was commissioned to launch Soyuz spacecraft as part of the Soviet human spaceflight program, first with 8 uncrewed test flights, followed by the first 19 crewed launches. The original Soyuz also propelled four test flights of the improved Soyuz 7K-T capsule between 1972 and 1974. In total it flew 30 successful missions over 10 years and suffered two failures. The Soyuz 11A511 type, a member of the R-7 family of rockets, first flew in 1966. Derived from the Voskhod 11A57 type, It was a two-stage rocket, with four liquid-fuelled strap-on boosters clustered around the first stage, with a Block I second stage. The first four test launches were all failures, but eventually it worked. The new, uprated core stage and strap-ons became standard for all R-7 derived launc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sovetsky Soyuz-class Battleship
The ''Sovetsky Soyuz''-class battleships (Project 23, russian: Советский Союз, "Soviet Union"), also known as "Stalin's Republics", were a class of battleships begun by the Soviet Union in the late 1930s but never brought into service. They were designed in response to the s being built by Germany. Only four hulls of the fifteen originally planned had been laid down by 1940, when the decision was made to cut the program to only three ships to divert resources to an expanded army rearmament program. These ships would have rivaled the Imperial Japanese and America's planned in size if any had been completed, although with significantly weaker firepower: nine guns compared to the nine guns of the Japanese ships and a dozen on the ''Montana''s. The failure of the Soviet armor plate industry to build cemented armor plates thicker than would have negated any advantages from the ''Sovetsky Soyuz'' class's thicker armor in combat. Construction of the first four ship ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a Federation, federal union of Republics of the Soviet Union, fifteen national republics; in practice, both Government of the Soviet Union, its government and Economy of the Soviet Union, its economy were highly Soviet-type economic planning, centralized until its final years. It was a one-party state governed by the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, with the city of Moscow serving as its capital as well as that of its largest and most populous republic: the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, Russian SFSR. Other major cities included Saint Petersburg, Leningrad (Russian SFSR), Kyiv, Kiev (Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic, Ukrainian SSR), Minsk (Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic, Byelorussian SSR), Tas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soyuz (faction)
Soyuz (Russian: Союз, translated as 'Union') was a faction in the Congress of People's Deputies of the USSR. The faction was critical of Perestroika and liberal reforms; it was opposed to de-centralization of the Soviet Union. The group was founded on 14 February 1990, and its leaders included Viktor Alksnis (from Latvian SSR), Yegor Ligachev, Nikolai Petrushenko, Yevgeny Kogan (Estonian SSR), and Anatoly Checkoyev (Georgian SSR, South Ossetian autonomous region). The faction claimed to have 500 members in the USSR Supreme Soviet. The group managed to oust Soviet foreign minister Eduard Shevardnadze for 'giving up' Eastern Europe. In February 1991, it asked for a 'state of emergency' to be introduced in the USSR. The Soyuz faction did not formally support the August Coup of 1991, an event that had devastating consequences for the faction. Many of the group leaders joined Sergei Baburin's movement Russian All-People's Union and the related Rossiya faction in the RSFSR parl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soyuz Station
Soyuz Station is a Russian (formerly Soviet) Antarctic research station, located on the shores of Beaver Lake, 260 km of Prydz Bay on the Lars Christensen Coast of the Mac Robertson Land in East Antarctica. Location and climate The station is located on the eastern shore of Beaver Lake, in the Amery Oasis, about 260 km from the coast of the Prydz Bay. Temperatures in the summer season vary from -25 to 3.5 °C, the wind blows at a speed of 5–9 m/s, reaches a maximum of 20–25 m/s (in gusts up to 30 m/s). The weather is most favorable for work in December and January, when snowstorms are the rarest. History The Soyuz station was opened on December 3, 1982, during the 28th Soviet Antarctic expedition as a support base for prospecting in the Prince Charles Mountains during the summer season. Scientists stationed in it conducted geological and geophysical research. Meteorological research was also regularly conducted there, mainly for the needs of aviation. The more accessi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soyuz (political Party)
The Party "Soyuz" ( uk, Партія "Союз") is a national political party in Ukraine that was mostly based in Crimea until 2014. It was registered in June 1997 under a registration number 867. History The party was founded in 1997 by , one of the richest people of Crimea at the time. The Constituent Party Congress took place on March 15, 1997. Svitlana Savchenko was elected the leader of the party. The congress also adopted the party's program and statute. The party was formed on the basis of the prohibited ''Crimean party''. II Congress (October 4, 1997), city of Simferopol. At the congress was adopted the party's pre-election program. III Congress (November 16, 1997). The congress confirmed the list of deputies for the next elections which was registered with Central Election Commission on December 18, 1997. IV Congress (July 11, 1998). The congress reviewed the election campaign of the party and made some changes to the party's Political council and its statute. The part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SS Albert Ballin
SS ''Albert Ballin'' was an ocean liner of the Hamburg-America Line launched in 1923 and named after Albert Ballin, the visionary director of the Hamburg-America line, who had committed suicide several years earlier. In 1935, the ship was renamed ''Hansa'' on orders from the German government. Towards the end of World War II, she was employed to evacuate civilians during Operation Hannibal, and sank after hitting a mine. She was later raised and refitted by the Soviet Union and was finally scrapped in 1982. History Hamburg America Line ''Albert Ballin'' was built by Blohm & Voss in Hamburg, and served on the Hamburg-New York City route. In 1928, a tourist class was added. Originally built as a 16 knot ship, the engines were replaced in 1929, resulting in a speed of 19 knots. In 1934, she was lengthened by 50 feet, and speed increased again, this time to 21.5 knots. In 1935, the new Nazi government ordered the ship be renamed ''Hansa'' (Ballin having been Jewish). ''Hans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |