|
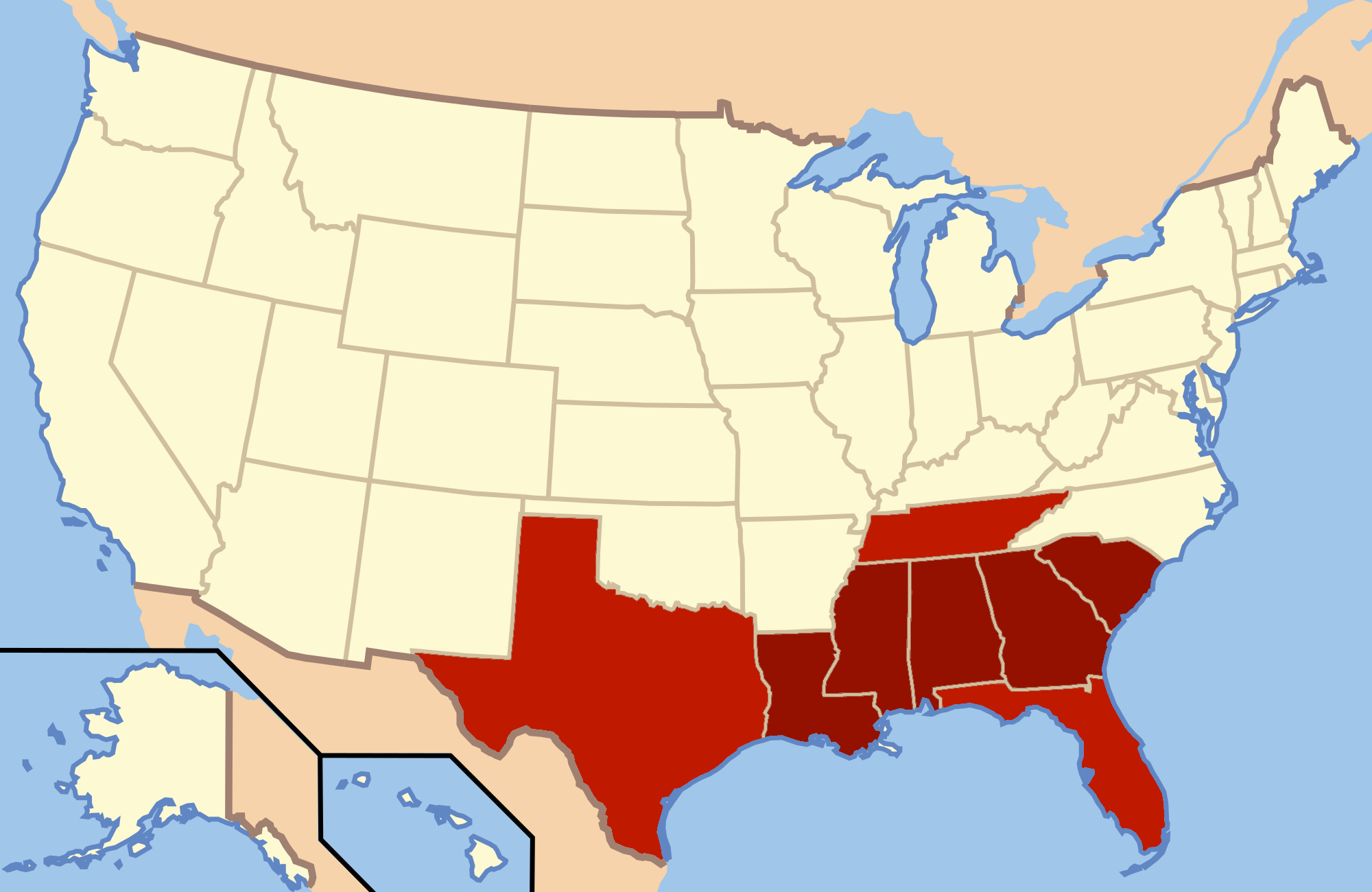
Southern Democrats
Southern Democrats, historically sometimes known colloquially as Dixiecrats, are members of the U.S. Democratic Party who reside in the Southern United States. Southern Democrats were generally much more conservative than Northern Democrats with most of them voting against the Civil Rights Act of 1964 by holding the longest filibuster in the American Senate history while Democrats in non-Southern states supported the Civil Rights Act of 1964. After 1994 the Republicans typically won most elections in the South. In the 19th century, Southern Democrats were people in the South who believed in Jacksonian democracy. In the 19th century, they defended slavery in the United States, and promoted its expansion into the West against northern Free Soil opposition. The United States presidential election of 1860 formalized the split in the Democratic Party and brought about the American Civil War. Stephen Douglas was the candidate for the Northern Democratic Party, and John C. Breck ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Redeemers
The Redeemers were a political coalition in the Southern United States during the Reconstruction Era that followed the Civil War. Redeemers were the Southern wing of the Democratic Party. They sought to regain their political power and enforce white supremacy. Their policy of Redemption was intended to oust the Radical Republicans, a coalition of freedmen, "carpetbaggers", and "scalawags". They generally were led by the White yeomanry and they dominated Southern politics in most areas from the 1870s to 1910. During Reconstruction, the South was under occupation by federal forces, and Southern state governments were dominated by Republicans, elected largely by freedmen and allies. Republicans nationally pressed for the granting of political rights to the newly-freed slaves as the key to their becoming full citizens and the votes they would cast for the party. The Thirteenth Amendment (banning slavery), Fourteenth Amendment (guaranteeing the civil rights of former slaves and en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Democratic Party (United States)
The Democratic Party is one of the two major contemporary political parties in the United States. Founded in 1828, it was predominantly built by Martin Van Buren, who assembled a wide cadre of politicians in every state behind war hero Andrew Jackson, making it the world's oldest active political party.M. Philip Lucas, "Martin Van Buren as Party Leader and at Andrew Jackson's Right Hand." in ''A Companion to the Antebellum Presidents 1837–1861'' (2014): 107–129."The Democratic Party, founded in 1828, is the world's oldest political party" states Its main political rival has been the Republican Party since the 1850s. The party is a big tent, and though it is often described as liberal, it is less ideologically uniform than the Republican Party (with major individuals within it frequently holding widely different political views) due to the broader list of unique voting blocs that compose it. The historical predecessor of the Democratic Party is considered to be th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German-American
German Americans (german: Deutschamerikaner, ) are Americans who have full or partial German ancestry. With an estimated size of approximately 43 million in 2019, German Americans are the largest of the self-reported ancestry groups by the United States Census Bureau in its American Community Survey. German Americans account for about one third of the total population of people of German ancestry in the world. Very few of the German states had colonies in the new world. In the 1670s, the first significant groups of German immigrants arrived in the British colonies, settling primarily in Pennsylvania, New York and Virginia. The Mississippi Company of France moved thousands of Germans from Europe to Louisiana and to the German Coast, Orleans Territory between 1718 and 1750. Immigration ramped up sharply during the 19th century. There is a "German belt" that extends all the way across the United States, from eastern Pennsylvania to the Oregon coast. Pennsylvania, with 3.5 mill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elliott County, Kentucky
Elliott County is a county located in the U.S. state of Kentucky. Its county seat is Sandy Hook. The county was formed in 1869 from parts of Morgan, Lawrence, and Carter counties, and is named for John Lyle Elliott, U.S. Congressman, Confederate Justice of the Kentucky Court of Appeals. In regard to alcohol sales, Elliott County is a dry county, meaning the sale of alcoholic beverages is prohibited everywhere in the county. History Elliott County was established in 1869 from land given by Carter, Lawrence, and Morgan counties. A fire at the courthouse in 1957 resulted in the destruction of many county records. Geography According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has a total area of , of which is land and (0.4%) is water. Adjacent counties * Carter County (north) * Lawrence County (east) * Morgan County (south) * Rowan County (west) Demographics As of the census of 2000, there were 6,748 people, 2,638 households, and 1,925 families residing in the county. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Donald Trump
Donald John Trump (born June 14, 1946) is an American politician, media personality, and businessman who served as the 45th president of the United States from 2017 to 2021. Trump graduated from the Wharton School of the University of Pennsylvania with a bachelor's degree in 1968. He became president of his father's real estate business in 1971 and renamed it The Trump Organization. He expanded the company's operations to building and renovating skyscrapers, hotels, casinos, and golf courses. He later started side ventures, mostly by licensing his name. From 2004 to 2015, he co-produced and hosted the reality television series '' The Apprentice''. Trump and his businesses have been involved in more than 4,000 state and federal legal actions, including six bankruptcies. Trump's political positions have been described as populist, protectionist, isolationist, and nationalist. He won the 2016 United States presidential election as the Republican nominee against Democratic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2016 United States Presidential Election
The 2016 United States presidential election was the 58th quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 8, 2016. The Republican ticket of businessman Donald Trump and Indiana governor Mike Pence defeated the Democratic ticket of former secretary of state and First Lady of the United States Hillary Clinton and the United States senator from Virginia Tim Kaine, in what was considered a large upset. Trump took office as the 45th president, and Pence as the 48th vice president, on January 20, 2017. It was the fifth and most recent presidential election in which the winning candidate lost the popular vote. It was also the sixth presidential election, and the first since 1944, in which both major party candidates were registered in the same home state. Per the Twenty-second Amendment to the United States Constitution, then-incumbent president Barack Obama was ineligible to seek a third term. Clinton defeated self-described democratic socialist Senator Ber ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Republican Revolution
The "Republican Revolution", "Revolution of '94", or "Gingrich Revolution" are political slogans that refer to the Republican Party (GOP) success in the 1994 U.S. mid-term elections, which resulted in a net gain of 54 seats in the House of Representatives, and a pick-up of eight seats in the Senate. On November 9, 1994, the day after the election, Senator Richard Shelby of Alabama, a conservative Democrat, changed parties, becoming a Republican; on March 3, 1995, Colorado Senator Ben Nighthorse Campbell switched to the Republican side as well, increasing the GOP Senate majority. Rather than campaigning independently in each district, Republican candidates chose to rally behind a single national program and message fronted by Georgia congressman and House Republican whip Newt Gingrich. They alleged that President Bill Clinton was not the " New Democrat" he claimed to be during his 1992 campaign, but was a " tax and spend" liberal. The Republicans offered an alternative t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voting Rights Act Of 1965
The Voting Rights Act of 1965 is a landmark piece of federal legislation in the United States that prohibits racial discrimination in voting. It was signed into law by President Lyndon B. Johnson during the height of the civil rights movement on August 6, 1965, and Congress later amended the Act five times to expand its protections. Designed to enforce the voting rights guaranteed by the Fourteenth and Fifteenth Amendments to the United States Constitution, the Act sought to secure the right to vote for racial minorities throughout the country, especially in the South. According to the U.S. Department of Justice, the Act is considered to be the most effective piece of federal civil rights legislation ever enacted in the country. It is also "one of the most far-reaching pieces of civil rights legislation in U.S. history." The act contains numerous provisions that regulate elections. The act's "general provisions" provide nationwide protections for voting rights. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lyndon B
Lyndon may refer to: Places * Lyndon, Alberta, Canada * Lyndon, Rutland, East Midlands, England * Lyndon, Solihull, West Midlands, England United States * Lyndon, Illinois * Lyndon, Kansas * Lyndon, Kentucky * Lyndon, New York * Lyndon, Ohio * Lyndon, Pennsylvania * Lyndon, Vermont * Lyndon, Sheboygan County, Wisconsin, a town * Lyndon, Juneau County, Wisconsin, a town Other uses * Lyndon State College, a public college located in Lyndonville, Vermont People * Lyndon (name), given name and surname See also * Lyndon School (other) * Lyndon Township (other) * * Lydon (other) * Lynden (other) * Lindon (other) Lindon may refer to: Places ; Real *Lindon, Colorado * Lindon, Utah * Lindon, South Australia ; Fictional * Lindon (Middle-earth), a region of the extreme west of J.R.R. Tolkien's fictional Middle-earth Other uses *Lindon (name) See also *Linden ... * Linden (other) {{disambig, geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strom Thurmond
James Strom Thurmond Sr. (December 5, 1902June 26, 2003) was an American politician who represented South Carolina in the United States Senate from 1954 to 2003. Prior to his 48 years as a senator, he served as the 103rd governor of South Carolina from 1947 to 1951. Thurmond was a member of the Democratic Party until 1964, when he joined the Republican Party for the remainder of his legislative career. He also ran for president in 1948 as the Dixiecrat candidate, receiving over a million votes and winning four states. A staunch opponent of civil rights legislation in the 1950s and 1960s, Thurmond conducted the longest speaking filibuster ever by a lone senator, at 24 hours and 18 minutes in length, in opposition to the Civil Rights Act of 1957. In the 1960s, he voted against the 1964 Civil Rights Act and the Voting Rights Act of 1965. Despite his support for racial segregation, Thurmond denied the accusation that he was a racist by insisting he was a supporter of states ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dixiecrats
The States' Rights Democratic Party (whose members are often called the Dixiecrats) was a short-lived segregationist political party in the United States, active primarily in the South. It arose due to a Southern regional split in opposition to the Democratic Party. After President Harry S. Truman, a member of the Democratic Party, ordered integration of the military in 1948 and other actions to address civil rights of African Americans, many Southern conservative white politicians who objected to this course organized themselves as a breakaway faction. The Dixiecrats wished to protect Southern states' rights to maintain racial segregation. Supporters assumed control of the state Democratic parties in part or in full in several Southern states. The Party opposed racial integration and wanted to retain Jim Crow laws and white supremacy in the face of possible federal intervention. Its members were referred to as "Dixiecrats", a portmanteau of "Dixie", referring to the Southe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |