|
Slovak Language
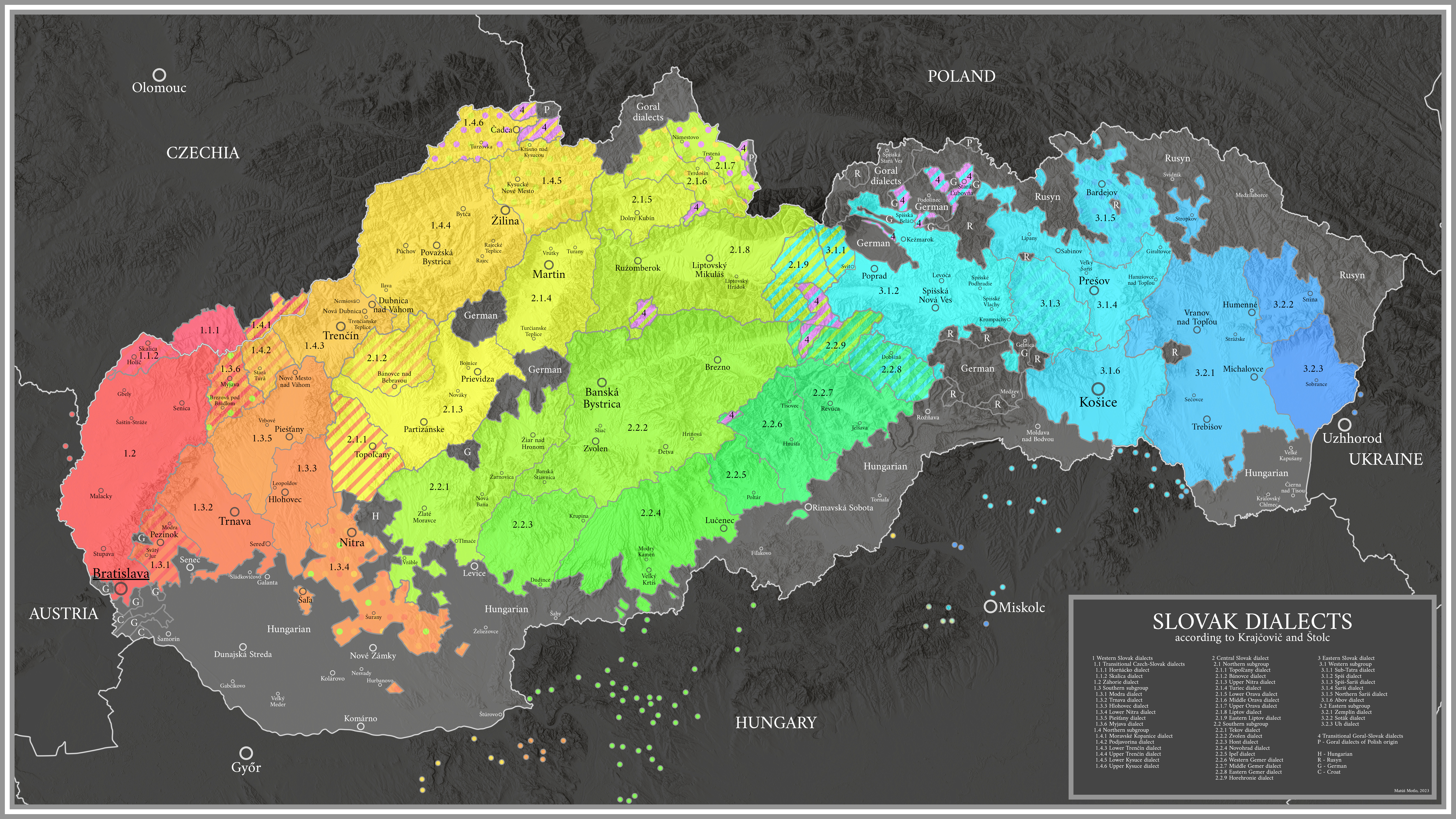
Slovak () , is a West Slavic language of the Czech-Slovak languages, Czech–Slovak group, written in Latin script. It is part of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family, and is one of the Slavic languages, which are part of the larger Balto-Slavic languages, Balto-Slavic branch. Spoken by approximately 5 million people as a native language, primarily ethnic Slovaks, it serves as the official language of Slovakia and one of the 24 official languages of the European Union. Slovak is closely related to Czech language, Czech, to the point of mutual intelligibility to a very high degree, as well as Polish language, Polish. Like other Slavic languages, Slovak is a fusional language with a complex system of morphology (linguistics), morphology and relatively flexible word order. Its vocabulary has been extensively influenced by Latin and German language, German and other Slavic languages. The Czech–Slovak group developed within West Slavic in the high medieval pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slovakia
Slovakia (; sk, Slovensko ), officially the Slovak Republic ( sk, Slovenská republika, links=no ), is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the southwest, and the Czech Republic to the northwest. Slovakia's mostly mountainous territory spans about , with a population of over 5.4 million. The capital and largest city is Bratislava, while the second largest city is Košice. The Slavs arrived in the territory of present-day Slovakia in the fifth and sixth centuries. In the seventh century, they played a significant role in the creation of Samo's Empire. In the ninth century, they established the Principality of Nitra, which was later conquered by the Principality of Moravia to establish Great Moravia. In the 10th century, after the dissolution of Great Moravia, the territory was integrated into the Principality of Hungary, which then became the Kingdom of Hungary in 1000. In 1241 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Official Languages Of The European Union
The European Union (EU) has 24 official languages, of which threeEnglish, French and Germanhave the higher status of "procedural" languages of the European Commission (whereas the European Parliament accepts all official languages as working languages). Irish previously had the lower status of "treaty language" before being upgraded to an official and working language in 2007. However, a temporary derogation was enforced until 1 January 2022. The three procedural languages are those used in the day-to-day workings of the institutions of the EU. The designation of Irish as a "treaty language" meant that only the treaties of the European Union were translated into Irish, whereas Legal Acts of the European Union adopted under the treaties (like Directives and Regulations) did not have to be. Luxembourgish and Turkish, which have official status in Luxembourg and Cyprus, respectively, are the only two official languages of EU member states that are not official languages of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martin Hattala
Martin Hattala (4 November 1821 in Trstená, Kingdom of Hungary (today Slovakia) – 11 December 1903 in Prague) was a Slovak pedagogue, Roman Catholic theologian and linguist. He is best known for his reform of the Štúr's Slovak language, so-called Hodža-Hattala reform, in which he introduced the etymological principle to the Slovak language Slovak () , is a West Slavic language of the Czech–Slovak group, written in Latin script. It is part of the Indo-European language family, and is one of the Slavic languages, which are part of the larger Balto-Slavic branch. Spoken by app .... Linguistic publications * ''Grammatica linguae slovenicae collatae cum proxime cognata bohemica'' (Grammar of the Slovak language compared with the most closely related Czech language) (1850) * ''Krátka mluvnica slovenská'' (A Concise Slovak Grammar) (1852) * ''Zvukosloví jazyka staro- i novo českého a slovenského'' (Phonetics of the old and new Czech and Slovak language) (1854) * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ľudovít Štúr
Ľudovít Velislav Štúr (; hu, Stur Lajos; 28 October 1815 – 12 January 1856), known in his era as Ludevít Štúr, (pen names : B. Dunajský, Bedlivý Ludorob, Boleslav Záhorský, Brat Slovenska, Ein Slave, Ein ungarischer Slave, Karl Wildburn, Pravolub Rokošan, Slovák, Starí, Velislav, and Zpěvomil) was a Slovak revolutionary politician, and writer. As a leader of the Slovak national revival in the 19th century, and the author of the Slovak language standard, he is lauded as one of the most important figures in Slovak history. Štúr was an organizer of the Slovak volunteer campaigns during the Hungarian Revolution of 1848. He was also a politician, poet, journalist, publisher, teacher, philosopher, linguist and member of the Hungarian Parliament. Background Language dispute At the turn of the 18th and 19th centuries, Slovaks were divided concerning the literary language to be used: * Catholics continued to use the standard that had developed in Slovak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Medieval
The High Middle Ages, or High Medieval Period, was the period of European history that lasted from AD 1000 to 1300. The High Middle Ages were preceded by the Early Middle Ages and were followed by the Late Middle Ages, which ended around AD 1500 (by historiographical convention). Key historical trends of the High Middle Ages include the rapidly increasing population of Europe, which brought about great social and political change from the preceding era, and the Renaissance of the 12th century, including the first developments of rural exodus and urbanization. By 1250, the robust population increase had greatly benefited the European economy, which reached levels that would not be seen again in some areas until the 19th century. That trend faltered during the Late Middle Ages because of a series of calamities, most notably the Black Death, but also numerous wars as well as economic stagnation. From around 780, Europe saw the last of the barbarian invasions and became more s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of California, Los Angeles
The University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) is a public land-grant research university in Los Angeles, California. UCLA's academic roots were established in 1881 as a teachers college then known as the southern branch of the California State Normal School (now San José State University). This school was absorbed with the official founding of UCLA as the Southern Branch of the University of California in 1919, making it the second-oldest of the 10-campus University of California system (after UC Berkeley). UCLA offers 337 undergraduate and graduate degree programs in a wide range of disciplines, enrolling about 31,600 undergraduate and 14,300 graduate and professional students. UCLA received 174,914 undergraduate applications for Fall 2022, including transfers, making the school the most applied-to university in the United States. The university is organized into the College of Letters and Science and 12 professional schools. Six of the schools offer undergraduate deg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Language
German ( ) is a West Germanic language mainly spoken in Central Europe. It is the most widely spoken and official or co-official language in Germany, Austria, Switzerland, Liechtenstein, and the Italian province of South Tyrol. It is also a co-official language of Luxembourg and Belgium, as well as a national language in Namibia. Outside Germany, it is also spoken by German communities in France ( Bas-Rhin), Czech Republic ( North Bohemia), Poland (Upper Silesia), Slovakia ( Bratislava Region), and Hungary (Sopron). German is most similar to other languages within the West Germanic language branch, including Afrikaans, Dutch, English, the Frisian languages, Low German, Luxembourgish, Scots, and Yiddish. It also contains close similarities in vocabulary to some languages in the North Germanic group, such as Danish, Norwegian, and Swedish. German is the second most widely spoken Germanic language after English, which is also a West Germanic language. Germ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Oxford
, mottoeng = The Lord is my light , established = , endowment = £6.1 billion (including colleges) (2019) , budget = £2.145 billion (2019–20) , chancellor = The Lord Patten of Barnes , vice_chancellor = Louise Richardson , students = 24,515 (2019) , undergrad = 11,955 , postgrad = 12,010 , other = 541 (2017) , city = Oxford , country = England , coordinates = , campus_type = University town , athletics_affiliations = Blue (university sport) , logo_size = 250px , website = , logo = University of Oxford.svg , colours = Oxford Blue , faculty = 6,995 (2020) , academic_affiliations = , The University of Oxford is a collegiate research university in Oxf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the Roman Republic it became the dominant language in the Italian region and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. Even after the fall of Western Rome, Latin remained the common language of international communication, science, scholarship and academia in Europe until well into the 18th century, when other regional vernaculars (including its own descendants, the Romance languages) supplanted it in common academic and political usage, and it eventually became a dead language in the modern linguistic definition. Latin is a highly inflected language, with three distinct genders (masculine, feminine, and neuter), six or seven noun cases (nominative, accusative, genitive, dative, ablative, and vocative), five declensions, four verb conjug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Word Order
In linguistics, word order (also known as linear order) is the order of the syntactic constituents of a language. Word order typology studies it from a cross-linguistic perspective, and examines how different languages employ different orders. Correlations between orders found in different syntactic sub-domains are also of interest. The primary word orders that are of interest are * the ''constituent order'' of a clause, namely the relative order of subject, object, and verb; * the order of modifiers (adjectives, numerals, demonstratives, possessives, and adjuncts) in a noun phrase; * the order of adverbials. Some languages use relatively fixed word order, often relying on the order of constituents to convey grammatical information. Other languages—often those that convey grammatical information through inflection—allow more flexible word order, which can be used to encode pragmatic information, such as topicalisation or focus. However, even languages with flexible ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morphology (linguistics)
In linguistics, morphology () is the study of words, how they are formed, and their relationship to other words in the same language. It analyzes the structure of words and parts of words such as stems, root words, prefixes, and suffixes. Morphology also looks at parts of speech, intonation and stress, and the ways context can change a word's pronunciation and meaning. Morphology differs from morphological typology, which is the classification of languages based on their use of words, and lexicology, which is the study of words and how they make up a language's vocabulary. While words, along with clitics, are generally accepted as being the smallest units of syntax, in most languages, if not all, many words can be related to other words by rules that collectively describe the grammar for that language. For example, English speakers recognize that the words ''dog'' and ''dogs'' are closely related, differentiated only by the plurality morpheme "-s", only found bound to noun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fusional Language
Fusional languages or inflected languages are a type of synthetic language, distinguished from agglutinative languages by their tendency to use a single inflectional morpheme to denote multiple grammatical, syntactic, or semantic features. For example, the Spanish verb ''comer'' ("to eat") has the first-person singular preterite tense form ''comí'' ("I ate"); the single suffix ''-í'' represents ''both'' the features of first-person singular agreement and preterite tense, instead of having a separate affix for each feature. Another illustration of fusionality is the Latin word ("good"). The ending denotes masculine gender, nominative case, and singular number. Changing any one of these features requires replacing the suffix with a different one. In the form , the ending denotes masculine accusative singular, neuter accusative singular, or neuter nominative singular. Indo-European languages Examples of fusional Indo-European languages include: all Balto-S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)







