|
SkyLab
Skylab was the first United States space station, launched by NASA, occupied for about 24 weeks between May 1973 and February 1974. It was operated by three separate three-astronaut crews: Skylab 2, Skylab 3, and Skylab 4. Major operations included an orbital workshop, a solar observatory, Earth observation, and hundreds of experiments. Unable to be re-boosted by the Space Shuttle, which was not ready until 1981, Skylab's orbit eventually decayed, and it disintegrated in the atmosphere on July 11, 1979, scattering debris across the Indian Ocean and Western Australia. Overview Skylab was the only space station operated exclusively by the United States. A permanent station was planned starting in 1988, but funding for this was canceled and replaced with United States participation in an International Space Station in 1993. Skylab had a mass of with a Apollo command and service module (CSM) attached and included a workshop, a solar observatory, and several hundred lif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
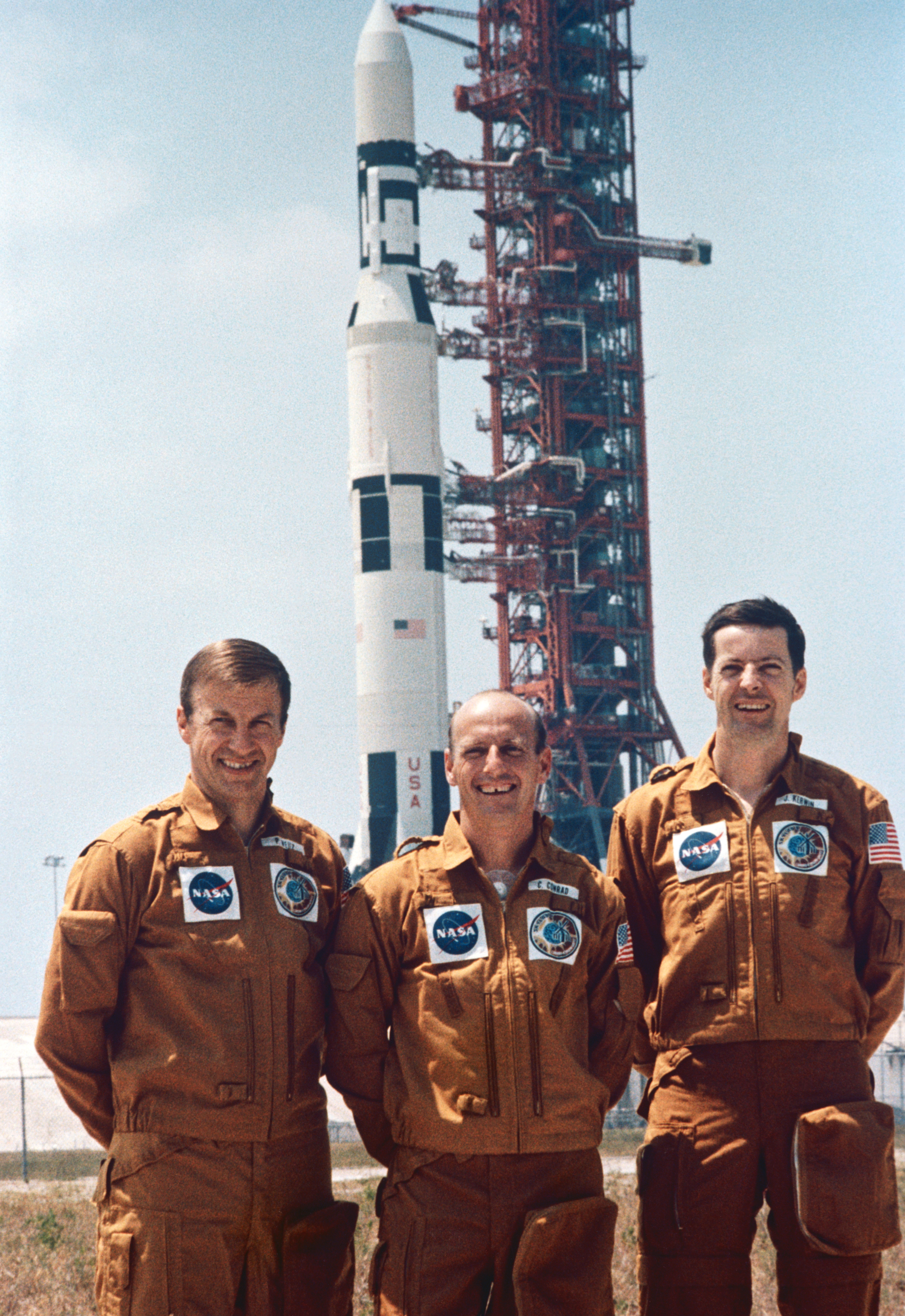
Skylab 4
Skylab 4 (also SL-4 and SLM-3) was the third crewed Skylab mission and placed the third and final crew aboard the first American space station. The mission began on November 16, 1973, with the launch of Gerald P. Carr, Edward Gibson, and William R. Pogue in an Apollo command and service module on a Saturn IB rocket from the Kennedy Space Center, Florida, and lasted 84 days, one hour and 16 minutes. A total of 6,051 astronaut-utilization hours were tallied by the Skylab 4 astronauts performing scientific experiments in the areas of medical activities, solar observations, Earth resources, observation of the Comet Kohoutek and other experiments. The crewed Skylab missions were officially designated Skylab 2, 3, and 4. Miscommunication about the numbering resulted in the mission emblems reading "Skylab I", "Skylab II", and "Skylab 3" respectively. Launch NASA's launch center was located in an area called Cape Kennedy since May 15, 1964. Cape Kennedy was renamed Cape Canavera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skylab 3
Skylab 3 (also SL-3 and SLM-2) was the second crewed mission to the first American space station, Skylab. The mission began on July 28, 1973, with the launch of NASA astronauts Alan Bean, Owen Garriott, and Jack Lousma in the Apollo command and service module on the Saturn IB rocket, and lasted 59 days, 11 hours and 9 minutes. A total of 1,084.7 astronaut-utilization hours were tallied by the Skylab 3 crew performing scientific experiments in the areas of medical activities, solar observations, Earth resources, and other experiments. The crewed Skylab missions were officially designated Skylab 2, 3, and 4. Miscommunication about the numbering resulted in the mission emblems reading "Skylab I", "Skylab II", and "Skylab 3" respectively. Crew Backup crew Support crew *Robert L. Crippen * Henry W. Hartsfield, Jr * Karl G. Henize * F. Story Musgrave *William E. Thornton * Richard H. Truly Mission parameters *Mass: about *Maximum Altitude: 440 km *Distance: 24.5 m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
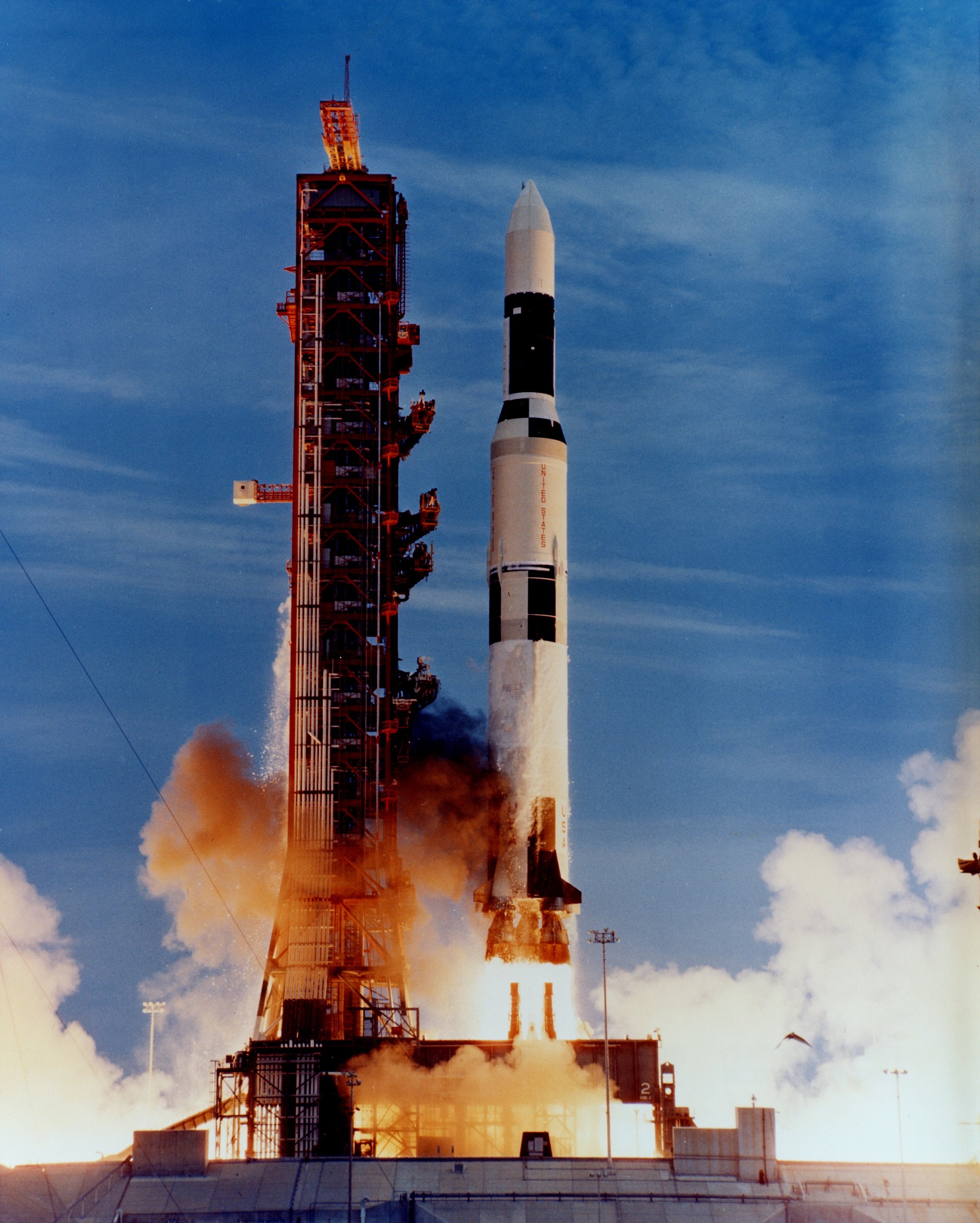
Skylab 2
Skylab 2 (also SL-2 and SLM-1) was the first crewed mission to Skylab, the first American orbital space station. The mission was launched on an Apollo command and service module by a Saturn IB rocket on May 25, 1973, and carried NASA astronauts Pete Conrad, Joseph P. Kerwin, Paul J. Weitz to the station. The name Skylab 2 also refers to the vehicle used for that mission. The Skylab 2 mission established a twenty-eight-day record for human spaceflight duration. Furthermore, its crew were the first space station occupants ever to return safely to Earth – the only previous space station occupants, the crew of the 1971 Soyuz 11 mission that had crewed the Salyut 1 station for twenty-four days, died upon reentry due to unexpected cabin depressurization. The crewed Skylab missions were officially designated Skylab 2, 3, and 4. Miscommunication about the numbering resulted in the mission emblems reading "Skylab I", "Skylab II", and "Skylab 3" respectively. Crew Backup crew S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skylab B
Skylab B was a proposed second US space station similar to Skylab that was planned to be launched by NASA for different purposes, mostly involving the Apollo–Soyuz Test Project, but was canceled due to lack of funding. Two Skylab modules were built in 1970 by McDonnell Douglas for the Skylab program, originally the Apollo Applications Program. The first was launched in 1973 and the other put in storage, while NASA considered how to use the remaining assets from Apollo. One considered option was to use Saturn V SA-515 to launch the backup Skylab station into orbit sometime between January 1975 and April 1976. That way, it could expand the Apollo–Soyuz mission by 56–90 days. Further proposals were made for an International Skylab, launched using Saturn V SA-514. This station would have been serviced by Apollo, Soyuz and later by the Space Shuttle. The vision of a international space station would not be realized until two decades later. Potential uses Some uses consi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apollo Telescope Mount
The Apollo Telescope Mount, or ATM, was a crewed solar observatory that was a part of Skylab, the first American space station. It could observe the Sun in wavelengths ranging from soft X-rays, ultra-violet, and visible light. The ATM was manually operated by the astronauts aboard Skylab from 1973–74, yielding data principally as exposed photographic film that was returned to Earth with the crew. The film magazines had to be changed out by the crew during spacewalks, although some instruments had a live video feed that could be observed from inside the space station. Some of the first Polaroid photos (an instant film-to-hard copy camera) in space were taken of a Skylab CRT video screen displaying the Sun as recorded by an ATM instrument. Although the ATM was integrated with the Skylab station, it started as a separate project related to use of the Apollo spacecraft, which is why it has the name Apollo in it rather than Skylab; the Skylab station was visited by astronau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saturn V
Saturn V is a retired American super heavy-lift launch vehicle developed by NASA under the Apollo program for human exploration of the Moon. The rocket was human-rated, with three stages, and powered with liquid fuel. It was flown from 1967 to 1973. It was used for nine crewed flights to the Moon, and to launch Skylab, the first American space station. the Saturn V remains the only launch vehicle to carry humans beyond low Earth orbit (LEO). Saturn V holds records for the heaviest payload launched and largest payload capacity to low Earth orbit: , which included the third stage and unburned propellant needed to send the Apollo command and service module and Lunar Module to the Moon. The largest production model of the Saturn family of rockets, the Saturn V was designed under the direction of Wernher von Braun at the Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama; the lead contractors were Boeing, North American Aviation, Douglas Aircraft Company, and IBM. A total ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saturn IB
The Saturn IB (also known as the uprated Saturn I) was an American launch vehicle commissioned by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) for the Apollo program. It uprated the Saturn I by replacing the S-IV second stage (, 43,380,000 lb-sec total impulse), with the S-IVB (, 96,000,000 lb-sec total impulse). The S-IB first stage also increased the S-I baseline's thrust from to and propellant load by 3.1%. This increased the Saturn I's low Earth orbit payload capability from to , enough for early flight tests of a half-fueled Apollo command and service module (CSM) or a fully fueled Apollo Lunar Module (LM), before the larger Saturn V needed for lunar flight was ready. By sharing the S-IVB upper stage, the Saturn IB and Saturn V provided a common interface to the Apollo spacecraft. The only major difference was that the S-IVB on the Saturn V burned only part of its propellant to achieve Earth orbit, so it could be restarted for trans-lunar inj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apollo Command And Service Module
The Apollo command and service module (CSM) was one of two principal components of the United States Apollo spacecraft, used for the Apollo program, which landed astronauts on the Moon between 1969 and 1972. The CSM functioned as a mother ship, which carried a crew of three astronauts and the second Apollo spacecraft, the Apollo Lunar Module, to lunar orbit, and brought the astronauts back to Earth. It consisted of two parts: the conical command module, a cabin that housed the crew and carried equipment needed for atmospheric reentry and splashdown; and the cylindrical service module which provided propulsion, electrical power and storage for various consumables required during a mission. An umbilical connection transferred power and consumables between the two modules. Just before reentry of the command module on the return home, the umbilical connection was severed and the service module was cast off and allowed to burn up in the atmosphere. The CSM was developed and buil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
S-IVB
The S-IVB (pronounced "S-four-B") was the third stage on the Saturn V and second stage on the Saturn IB launch vehicles. Built by the Douglas Aircraft Company, it had one J-2 rocket engine. For lunar missions it was fired twice: first for Earth orbit insertion after second stage cutoff, and then for translunar injection (TLI). History The S-IVB evolved from the upper stage of the Saturn I rocket, the S-IV, and was the first stage of the Saturn V to be designed. The S-IV used a cluster of six engines but used the same fuels as the S-IVB – liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen. It was also originally meant to be the fourth stage of a planned rocket called the C-4, hence the name S-IV. Eleven companies submitted proposals for being the lead contractor on the stage by the deadline of 29 February 1960. NASA administrator T. Keith Glennan decided on 19 April that Douglas Aircraft Company would be awarded the contract. Convair had come a close second but Glennan did not want to monopol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil List of government space agencies, space program, aeronautics research, and outer space, space research. NASA was National Aeronautics and Space Act, established in 1958, succeeding the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA), to give the U.S. space development effort a distinctly civilian orientation, emphasizing peaceful applications in space science. NASA has since led most American space exploration, including Project Mercury, Project Gemini, the 1968-1972 Apollo program, Apollo Moon landing missions, the Skylab space station, and the Space Shuttle. NASA supports the International Space Station and oversees the development of the Orion (spacecraft), Orion spacecraft and the Space Launch System for the crewed lunar Artemis program, Commercial Crew Program, Commercial Crew ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Station
A space station is a spacecraft capable of supporting a human crew in orbit for an extended period of time, and is therefore a type of space habitat. It lacks major propulsion or landing systems. An orbital station or an orbital space station is an artificial satellite (i.e. a type of orbital spaceflight). Stations must have docking ports to allow other spacecraft to dock to transfer crew and supplies. The purpose of maintaining an orbital outpost varies depending on the program. Space stations have most often been launched for scientific purposes, but military launches have also occurred. Space stations have harboured so far the only long-duration direct human presence in space. After the first station Salyut 1 (1971) and its tragic Soyuz 11 crew, space stations have been operated consecutively since Skylab (1973), having allowed a progression of long-duration direct human presence in space. Stations have been occupied by consecutive crews since 1987 with the Salyut succes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saturn INT-21
The Saturn INT-21 was a study for an American orbital launch vehicle of the 1970s. It was derived from the Saturn V rocket used for the Apollo program, using its first and second stages, but lacking the third stage. The guidance unit would be moved from the top of the third stage to the top of the second stage. The INT-21 was never flown. A related variant was launched once, from the Kennedy Space Center, Florida carrying the Skylab space station into orbit, at 17:30 UTC, on May 14, 1973. As ''Skylab'' was built from an S-IVB stage, there was no need to move the guidance unit. This version was intended to be used for other flights in the Apollo Applications Program, and would have also been used to launch other American space stations, including Skylab B. See also *Comparison of orbital launch systems * Apollo program *Saturn I *Saturn IB * Saturn V *Skylab *Apollo Applications Program *S-IC *S-II *Saturn I SA-1 Saturn-Apollo 1 (SA-1) was the first flight of the Satur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)

.jpg)