|
Silver Halide
A silver halide (or silver salt) is one of the chemical compounds that can form between the Chemical element, element silver (Ag) and one of the halogens. In particular, bromine (Br), chlorine (Cl), iodine (I) and fluorine (F) may each combine with silver to produce silver bromide (AgBr), silver chloride (AgCl), silver iodide (AgI), and three forms of silver fluoride, respectively. As a group, they are often referred to as the silver halides, and are often given the pseudo-chemical notation AgX. Although most silver halides involve silver atoms with oxidation states of +1 (Ag+), silver halides in which the silver atoms have oxidation states of +2 (Ag2+) are known, of which silver(II) fluoride is the only known stable one. Silver halides are light-sensitive chemicals, and are commonly used in photographic film and paper. Applications Light sensitivity Silver halides are used in photographic film and photographic paper, including graphic art film and paper, where silver halide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Compound
A chemical compound is a chemical substance composed of many identical molecules (or molecular entities) containing atoms from more than one chemical element held together by chemical bonds. A molecule consisting of atoms of only one element is therefore not a compound. A compound can be transformed into a different substance by a chemical reaction, which may involve interactions with other substances. In this process, bonds between atoms may be broken and/or new bonds formed. There are four major types of compounds, distinguished by how the constituent atoms are bonded together. Molecular compounds are held together by covalent bonds; ionic compounds are held together by ionic bonds; intermetallic compounds are held together by metallic bonds; coordination complexes are held together by coordinate covalent bonds. Non-stoichiometric compounds form a disputed marginal case. A chemical formula specifies the number of atoms of each element in a compound molecule, using ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gelatin
Gelatin or gelatine (from la, gelatus meaning "stiff" or "frozen") is a translucent, colorless, flavorless food ingredient, commonly derived from collagen taken from animal body parts. It is brittle when dry and rubbery when moist. It may also be referred to as hydrolyzed collagen, collagen hydrolysate, gelatine hydrolysate, hydrolyzed gelatine, and collagen peptides after it has undergone hydrolysis. It is commonly used as a gelling agent in food, beverages, medications, drug or vitamin capsules, photographic films, papers, and cosmetics. Substances containing gelatin or functioning in a similar way are called gelatinous substances. Gelatin is an irreversibly hydrolyzed form of collagen, wherein the hydrolysis reduces protein fibrils into smaller peptides; depending on the physical and chemical methods of denaturation, the molecular weight of the peptides falls within a broad range. Gelatin is present in gelatin desserts, most gummy candy and marshmallows, ice creams, di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valence Band
In solid-state physics, the valence band and conduction band are the bands closest to the Fermi level, and thus determine the electrical conductivity of the solid. In nonmetals, the valence band is the highest range of electron energies in which electrons are normally present at absolute zero temperature, while the conduction band is the lowest range of vacant electronic states. On a graph of the electronic band structure of a material, the valence band is located below the Fermi level, while the conduction band is located above it. The distinction between the valence and conduction bands is meaningless in metals, because conduction occurs in one or more partially filled bands that take on the properties of both the valence and conduction bands. Band gap In semiconductors and insulators the two bands are separated by a band gap, while in semimetals the bands overlap. A band gap is an energy range in a solid where no electron states can exist due to the quantization of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atomic Orbital
In atomic theory and quantum mechanics, an atomic orbital is a function describing the location and wave-like behavior of an electron in an atom. This function can be used to calculate the probability of finding any electron of an atom in any specific region around the atom's nucleus. The term ''atomic orbital'' may also refer to the physical region or space where the electron can be calculated to be present, as predicted by the particular mathematical form of the orbital. Each orbital in an atom is characterized by a set of values of the three quantum numbers , , and , which respectively correspond to the electron's energy, angular momentum, and an angular momentum vector component (magnetic quantum number). Alternative to the magnetic quantum number, the orbitals are often labeled by the associated harmonic polynomials (e.g., ''xy'', ). Each such orbital can be occupied by a maximum of two electrons, each with its own projection of spin m_s. The simple names s orbital ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conduction Band
In solid-state physics, the valence band and conduction band are the bands closest to the Fermi level, and thus determine the electrical conductivity of the solid. In nonmetals, the valence band is the highest range of electron energies in which electrons are normally present at absolute zero temperature, while the conduction band is the lowest range of vacant electronic states. On a graph of the electronic band structure of a material, the valence band is located below the Fermi level, while the conduction band is located above it. The distinction between the valence and conduction bands is meaningless in metals, because conduction occurs in one or more partially filled bands that take on the properties of both the valence and conduction bands. Band gap In semiconductors and insulators the two bands are separated by a band gap, while in semimetals the bands overlap. A band gap is an energy range in a solid where no electron states can exist due to the quantization ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photon
A photon () is an elementary particle that is a quantum of the electromagnetic field, including electromagnetic radiation such as light and radio waves, and the force carrier for the electromagnetic force. Photons are massless, so they always move at the speed of light in vacuum, (or about ). The photon belongs to the class of bosons. As with other elementary particles, photons are best explained by quantum mechanics and exhibit wave–particle duality, their behavior featuring properties of both waves and particles. The modern photon concept originated during the first two decades of the 20th century with the work of Albert Einstein, who built upon the research of Max Planck. While trying to explain how matter and electromagnetic radiation could be in thermal equilibrium with one another, Planck proposed that the energy stored within a material object should be regarded as composed of an integer number of discrete, equal-sized parts. To explain the photoelectr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daguerreotype
Daguerreotype (; french: daguerréotype) was the first publicly available photographic process; it was widely used during the 1840s and 1850s. "Daguerreotype" also refers to an image created through this process. Invented by Louis Daguerre and introduced worldwide in 1839, the daguerreotype was almost completely superseded by 1860 with new, less expensive processes, such as ambrotype (collodion process), that yield more readily viewable images. There has been a revival of the daguerreotype since the late 20th century by a small number of photographers interested in making artistic use of early photographic processes. To make the image, a daguerreotypist polished a sheet of silver-plated copper to a mirror finish; treated it with fumes that made its surface light-sensitive; exposed it in a camera for as long as was judged to be necessary, which could be as little as a few seconds for brightly sunlit subjects or much longer with less intense lighting; made the resulting late ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collodion Process
The collodion process is an early photographic process. The collodion process, mostly synonymous with the "collodion wet plate process", requires the photographic material to be coated, sensitized, exposed, and developed within the span of about fifteen minutes, necessitating a portable darkroom for use in the field. Collodion is normally used in its wet form, but it can also be used in dry form, at the cost of greatly increased exposure time. The increased exposure time made the dry form unsuitable for the usual portraiture work of most professional photographers of the 19th century. The use of the dry form was therefore mostly confined to landscape photography and other special applications where minutes-long exposure times were tolerable. History Gustave Le Gray first theorized about the collodion process, publishing a method in 1850 that was "theoretical at best", but Frederick Scott Archer was credited with the invention of the process, which he created in 1848 and publ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Film Developing
Photographic processing or photographic development is the chemical means by which photographic film or paper is treated after photographic exposure to produce a negative or positive image. Photographic processing transforms the latent image into a visible image, makes this permanent and renders it insensitive to light.Karlheinz Keller et al. "Photography" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 2005, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. All processes based upon the gelatin silver process are similar, regardless of the film or paper's manufacturer. Exceptional variations include instant films such as those made by Polaroid and thermally developed films. Kodachrome required Kodak's proprietary K-14 process. Kodachrome film production ceased in 2009, and K-14 processing is no longer available as of December 30, 2010. Ilfochrome materials use the dye destruction process. Deliberately using the wrong process for a film is known as cross processing. Common processes All phot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
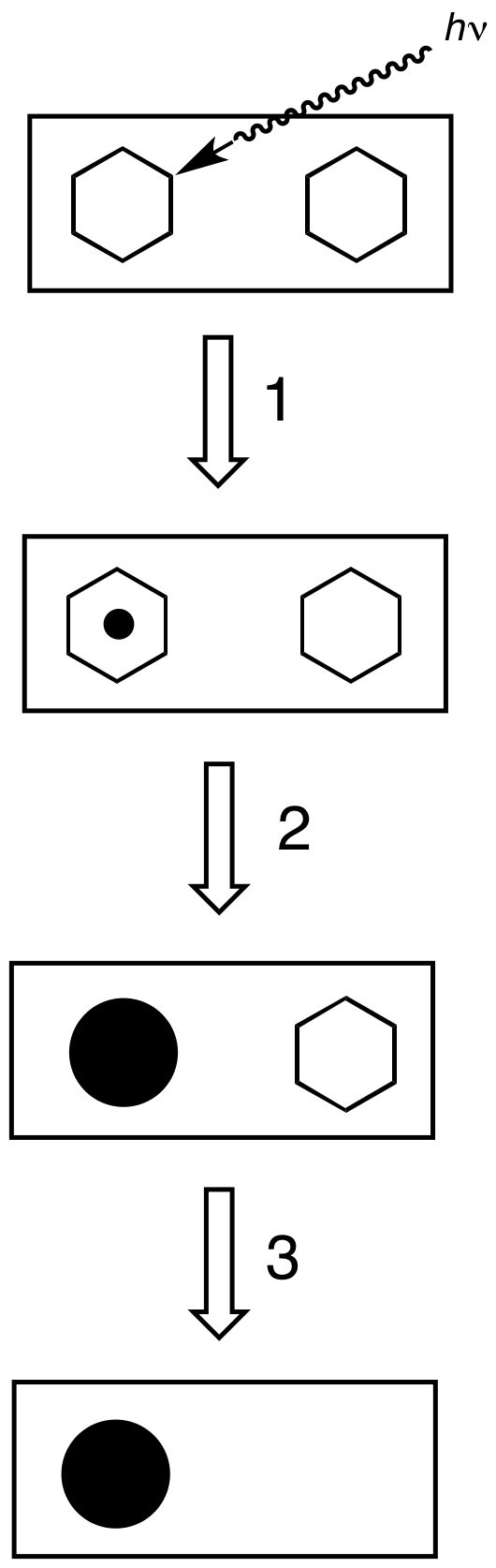
Latent Image
{{citations needed, date=November 2015 A latent image is an invisible image produced by the exposure to light of a photosensitive material such as photographic film. When photographic film is developed, the area that was exposed darkens and forms a visible image. In the early days of photography, the nature of the invisible change in the silver halide crystals of the film's emulsion coating was unknown, so the image was said to be "latent" until the film was treated with photographic developer. In more physical terms, a latent image is a small cluster of metallic silver atoms formed in or on a silver halide crystal due to reduction of interstitial silver ions by photoelectrons (a photolytic silver cluster). If intense exposure continues, such photolytic silver clusters grow to visible sizes. This is called ''printing out'' the image. On the other hand, the formation of a visible image by the action of photographic developer is called ''developing out'' the image. The size ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sensitivity Speck
A sensitivity speck is a place in silver halide crystal where latent image is preferentially formed. This is very often the site of shallow electron traps, such as crystalline defect (particularly edge dislocation) and silver sulfide specks created by sulfur sensitization process. When a photon is absorbed by a silver halide crystal, a free-carrier (electron in the conduction band) is generated. This free-carrier can migrate through the crystal lattice of silver halide, until captured by the shallow electron trap, where the electron is likely to reduce an interstitial silver ion to form an atomic silver. Subsequent exposure can grow the size of silver cluster through the same mechanism. This forms the latent image {{citations needed, date=November 2015 A latent image is an invisible image produced by the exposure to light of a photosensitive material such as photographic film. When photographic film is developed, the area that was exposed darkens and for ... where the silver c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emulsion
An emulsion is a mixture of two or more liquids that are normally immiscible (unmixable or unblendable) owing to liquid-liquid phase separation. Emulsions are part of a more general class of two-phase systems of matter called colloids. Although the terms ''colloid'' and ''emulsion'' are sometimes used interchangeably, ''emulsion'' should be used when both phases, dispersed and continuous, are liquids. In an emulsion, one liquid (the dispersed phase) is dispersed in the other (the continuous phase). Examples of emulsions include vinaigrettes, homogenized milk, liquid biomolecular condensates, and some cutting fluids for metal working. Two liquids can form different types of emulsions. As an example, oil and water can form, first, an oil-in-water emulsion, in which the oil is the dispersed phase, and water is the continuous phase. Second, they can form a water-in-oil emulsion, in which water is the dispersed phase and oil is the continuous phase. Multiple emulsions are also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |