|
Sigurd
Sigurd ( non, Sigurðr ) or Siegfried (Middle High German: ''Sîvrit'') is a legendary hero of Germanic heroic legend, who killed a dragon and was later murdered. It is possible he was inspired by one or more figures from the Frankish Merovingian dynasty, with Sigebert I being the most popular contender. Older scholarship sometimes connected him with Arminius, victor of the Battle of the Teutoburg Forest. He may also have a purely mythological origin. Sigurd's story is first attested on a series of carvings, including runestones from Sweden and stone crosses from the British Isles, dating from the eleventh century. In both the Norse and continental Germanic tradition, Sigurd is portrayed as dying as the result of a quarrel between his wife ( Gudrun/Kriemhild) and another woman, Brunhild, whom he has tricked into marrying the Burgundian king Gunnar/Gunther. His slaying of a dragon and possession of the hoard of the Nibelungen is also common to both traditions. In other r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sigurd Prüft Das Schwert Gram By Johannes Gehrts
Sigurd ( non, Sigurðr ) or Siegfried (Middle High German: ''Sîvrit'') is a legendary hero of Germanic heroic legend, who killed a dragon and was later murdered. It is possible he was inspired by one or more figures from the Frankish Merovingian dynasty, with Sigebert I being the most popular contender. Older scholarship sometimes connected him with Arminius, victor of the Battle of the Teutoburg Forest. He may also have a purely mythological origin. Sigurd's story is first attested on a series of carvings, including runestones from Sweden and stone crosses from the British Isles, dating from the eleventh century. In both the Norse and continental Germanic tradition, Sigurd is portrayed as dying as the result of a quarrel between his wife (Gudrun/Kriemhild) and another woman, Brunhild, whom he has tricked into marrying the Burgundian king Gunnar/Gunther. His slaying of a dragon and possession of the hoard of the Nibelungen is also common to both traditions. In other respec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brunhild
Brunhild, also known as Brunhilda or Brynhild ( non, Brynhildr , gmh, Brünhilt, german: Brünhild , label= Modern German or ), is a female character from Germanic heroic legend. She may have her origins in the Visigothic princess Brunhilda of Austrasia. In the Norse tradition, Brunhild is a shieldmaiden or valkyrie, who appears as a main character in the and some Eddic poems treating the same events. In the continental Germanic tradition, where she is a central character in the , she is a powerful Amazon-like queen. In both traditions, she is instrumental in bringing about the death of the hero Sigurd or Siegfried after he deceives her into marrying the Burgundian king Gunther or Gunnar. In both traditions, the immediate cause for her desire to have Sigfried murdered is a quarrel with the hero's wife, Gudrun or Kriemhild. In the Scandinavian tradition, but not in the continental tradition, Brunhild kills herself after Sigurd's death. Richard Wagner made Brunhild (as ) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Völsunga Saga
The ''Völsunga saga'' (often referred to in English as the ''Volsunga Saga'' or ''Saga of the Völsungs'') is a legendary saga, a late 13th-century poetic rendition in Old Norse of the origin and decline of the Völsung clan (including the story of Sigurd and Brynhild and the destruction of the Burgundians). It is one of the most famous legendary sagas and an example of a "heroic saga" that deals with Germanic heroic legend. The saga covers topics including the quarrel between Sigi and Skaði, a huge family tree of great kings and powerful conquerors, the quest led by Sigmund and Sinfjǫtli to save princess Signý from the evil king Siggeir, and, most famously, Sigurd killing the serpent/dragon Fáfnir and obtaining the cursed ring Andvaranaut that Fáfnir guarded. Context and overview The saga is largely based on the epic poetry of the historic '' Elder Edda''. The earliest known pictorial representation of this tradition is the Ramsund carving in Sweden, which was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gudrun
Gudrun ( ; non, Guðrún) or Kriemhild ( ; gmh, Kriemhilt) is the wife of Sigurd/Siegfried and a major figure in Germanic heroic legend and literature. She is believed to have her origins in Ildico, last wife of Attila the Hun, and two queens of the Merovingian dynasty, Brunhilda of Austrasia and Fredegund. In both the Continental (German) and Scandinavian traditions, Gudrun/Kriemhild is the sister of the Burgundian king Gunther/Gunnar and marries the hero Siegfried/Sigurd. Both traditions also feature a major rivalry between Gudrun and Brunhild, Gunther's wife, over their respective ranks. In both traditions, once Sigurd has been murdered, Gudrun is married to Etzel/Atli, the legendary analogue of Attila the Hun. In the Norse tradition, Atli desires the hoard of the Nibelungen, which the Burgundians had taken after murdering Sigurd, and invites them to his court; intending to kill them. Gudrun then avenges her brothers by killing Atli and burning down his hall. The N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gunther
Gundaharius or Gundahar (died 437), better known by his legendary names Gunther ( gmh, Gunther) or Gunnar ( non, Gunnarr), was a historical king of Burgundy in the early 5th century. Gundahar is attested as ruling his people shortly after they crossed the Rhine into Roman Gaul. He was involved in the campaigns of the failed Roman usurper Jovinus before the latter's defeat, after which he was settled on the left bank of the Rhine as a Roman ally. In 436, Gundahar launched an attack from his kingdom on the Roman province of Belgica Prima. He was defeated by the Roman general Flavius Aetius, who destroyed Gundahar's kingdom with the help of Hunnish mercenaries the following year, resulting in Gundahar's death. The historical Gundahar's death became the basis for a tradition in Germanic heroic legend in which the legendary Gunther met his death at the court of Attila the Hun (Etzel/Atli). The character also became attached to other legends: most notably he is associated with Si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germanic Heroic Legend
Germanic heroic legend (german: germanische Heldensage) is the heroic literary tradition of the Germanic-speaking peoples, most of which originates or is set in the Migration Period (4th-6th centuries AD). Stories from this time period, to which others were added later, were transmitted orally, traveled widely among the Germanic speaking peoples, and were known in many variants. These legends typically reworked historical events or personages in the manner of oral poetry, forming a heroic age. Heroes in these legends often display a heroic ethos emphasizing honor, glory, and loyalty above other concerns. Like Germanic mythology, heroic legend is a genre of Germanic folklore. Heroic legends are attested in Anglo-Saxon England, medieval Scandinavia, and medieval Germany. Many take the form of Germanic heroic poetry (german: germanische Heldendichtung): shorter pieces are known as heroic lays, whereas longer pieces are called Germanic heroic epic (). The early Middle Ages preserve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Runestone
A runestone is typically a raised stone with a runic inscription, but the term can also be applied to inscriptions on boulders and on bedrock. The tradition began in the 4th century and lasted into the 12th century, but most of the runestones date from the late Viking Age. Most runestones are located in Scandinavia, but there are also scattered runestones in locations that were visited by Norsemen during the Viking Age. Runestones are often memorials to dead men. Runestones were usually brightly coloured when erected, though this is no longer evident as the colour has worn off. The vast majority of runestones are found in Sweden. History The tradition of raising stones that had runic inscriptions first appeared in the 4th and 5th century, in Norway and Sweden, and these early runestones were usually placed next to graves. The earliest Danish runestones appeared in the 8th and 9th centuries, and there are about 50 runestones from the Migration Period in Scandinavia. Most rune ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poetic Edda
The ''Poetic Edda'' is the modern name for an untitled collection of Old Norse anonymous narrative poems, which is distinct from the ''Prose Edda'' written by Snorri Sturluson. Several versions exist, all primarily of text from the Icelandic medieval manuscript known as the '' Codex Regius'', which contains 31 poems. The ''Codex Regius'' is arguably the most important extant source on Norse mythology and Germanic heroic legends. Since the early 19th century, it has had a powerful influence on Scandinavian literature, not only through its stories, but also through the visionary force and the dramatic quality of many of the poems. It has also been an inspiration for later innovations in poetic meter, particularly in Nordic languages, with its use of terse, stress-based metrical schemes that lack final rhymes, instead focusing on alliterative devices and strongly concentrated imagery. Poets who have acknowledged their debt to the ''Codex Regius'' include Vilhelm Ekelund, August S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nibelungenlied
The ( gmh, Der Nibelunge liet or ), translated as ''The Song of the Nibelungs'', is an epic poem written around 1200 in Middle High German. Its anonymous poet was likely from the region of Passau. The is based on an oral tradition of Germanic heroic legend that has some of its origin in historic events and individuals of the 5th and 6th centuries and that spread throughout almost all of Germanic-speaking Europe. Scandinavian parallels to the German poem are found especially in the heroic lays of the ''Poetic Edda'' and in the ''Völsunga saga''. The poem is split into two parts. In the first part, the prince Siegfried comes to Worms to acquire the hand of the Burgundian princess Kriemhild from her brother King Gunther. Gunther agrees to let Siegfried marry Kriemhild if Siegfried helps Gunther acquire the warrior-queen Brünhild as his wife. Siegfried does this and marries Kriemhild; however, Brünhild and Kriemhild become rivals, leading eventually to Siegfried's murder ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
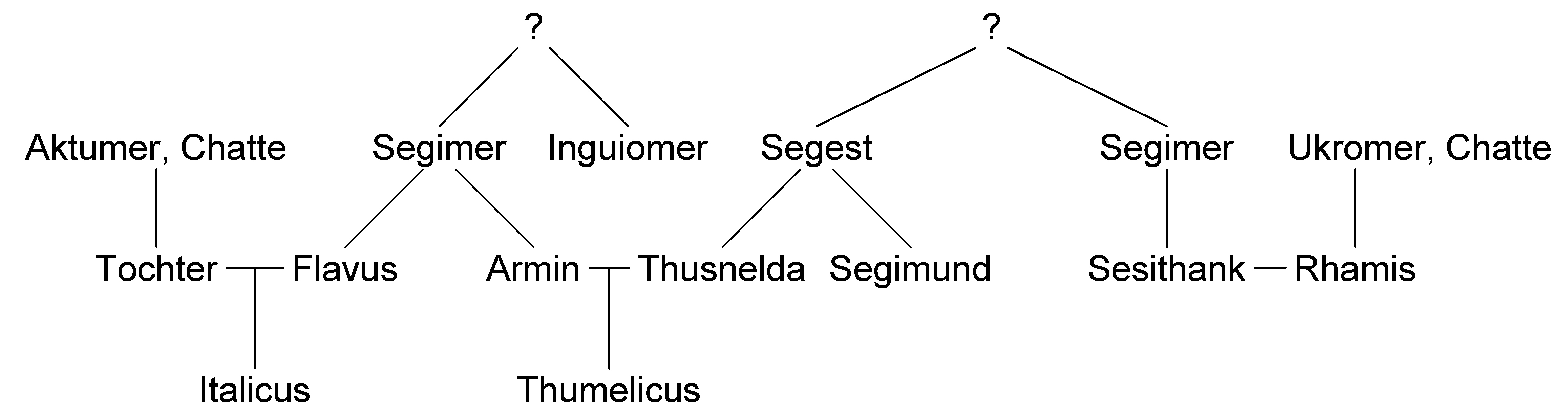
Arminius
Arminius ( 18/17 BC – 21 AD) was a chieftain of the Germanic Cherusci tribe who is best known for commanding an alliance of Germanic tribes at the Battle of the Teutoburg Forest in 9 AD, in which three Roman legions under the command of general Publius Quinctilius Varus were destroyed. His victory at Teutoburg Forest would precipitate the Roman Empire's permanent strategic withdrawal from Germania Magna. Modern historians have regarded Arminius' victory as one of Rome's greatest defeats. As it prevented the Romanization of Germanic peoples east of the Rhine, it has also been considered one of the most decisive battles in history and a turning point in human history. Born a prince of the Cherusci tribe, Arminius was part of the Roman friendly faction of the tribe. He learned Latin and served in the Roman military, which gained him Roman citizenship and the rank of ''eques''. After serving with distinction in the Great Illyrian Revolt, he was sent to Germania to aid the lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Götterdämmerung
' (; ''Twilight of the Gods''), WWV 86D, is the last in Richard Wagner's cycle of four music dramas titled (''The Ring of the Nibelung'', or ''The Ring Cycle'' or ''The Ring'' for short). It received its premiere at the on 17 August 1876, as part of the first complete performance of the whole work. The title is a translation into German of the Old Norse phrase ', which in Norse mythology refers to a prophesied war among various beings and gods that ultimately results in the burning, immersion in water, and renewal of the world. As with the rest of the ''Ring'', however, Wagner's account diverges significantly from these Old Norse sources. Composition Roles Synopsis Prologue Prelude to the Prologue Scene 1 The three Norns, daughters of Erda, the goddess of Nature, gather beside Brünnhilde's rock, weaving the Rope of Destiny. From it they read of the past, the present, and of the future when Walhalla will be set on fire and the end of the gods will c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Wagner
Wilhelm Richard Wagner ( ; ; 22 May 181313 February 1883) was a German composer, theatre director, polemicist, and conductor who is chiefly known for his operas (or, as some of his mature works were later known, "music dramas"). Unlike most opera composers, Wagner wrote both the libretto and the music for each of his stage works. Initially establishing his reputation as a composer of works in the romantic vein of Carl Maria von Weber and Giacomo Meyerbeer, Wagner revolutionised opera through his concept of the ''Gesamtkunstwerk'' ("total work of art"), by which he sought to synthesise the poetic, visual, musical and dramatic arts, with music subsidiary to drama. He described this vision in a series of essays published between 1849 and 1852. Wagner realised these ideas most fully in the first half of the four-opera cycle ''Der Ring des Nibelungen'' (''The Ring of the Nibelung''). His compositions, particularly those of his later period, are notable for their complex texture (mus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |