|
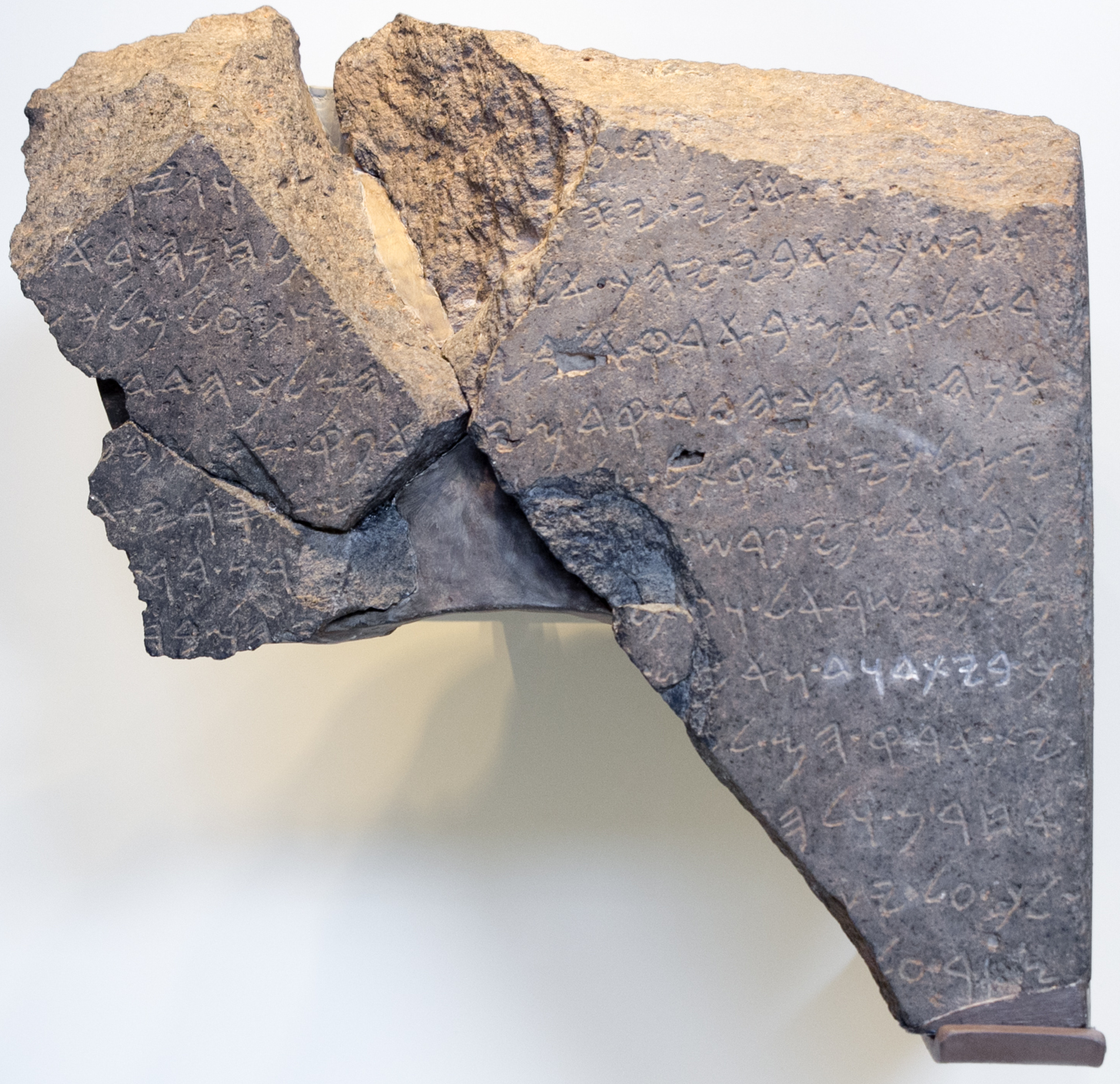
Sennacherib's Prism
Sennacherib's Annals are the annals of the Assyrian king Sennacherib. They are found inscribed on a number of artifacts, and the final versions were found in three clay prisms inscribed with the same text: the Taylor Prism is in the British Museum, the Oriental Institute Prism in the Oriental Institute of Chicago, and the Jerusalem Prism is in the Israel Museum in Jerusalem. The Taylor Prism is one of the earliest cuneiform artifacts analysed in modern Assyriology, having been found a few years before the modern deciphering of cuneiform. The annals themselves are notable for describing Sennacherib's siege of Jerusalem during the reign of king Hezekiah. This event is recorded in several books contained in the Bible including Isaiah chapters 36 and 37; 2 Kings ; 2 Chronicles . The invasion is mentioned by Herodotus, who does not refer to Judea and says the invasion ended at Pelusium on the edge of the Nile Delta. Description and discovery The prisms contain six paragraphs of cun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Judah
The Kingdom of Judah ( he, , ''Yəhūdā''; akk, 𒅀𒌑𒁕𒀀𒀀 ''Ya'údâ'' 'ia-ú-da-a-a'' arc, 𐤁𐤉𐤕𐤃𐤅𐤃 ''Bēyt Dāwīḏ'', " House of David") was an Israelite kingdom of the Southern Levant during the Iron Age. Centered in Judea, the kingdom's capital was Jerusalem. The other Israelite polity, the Kingdom of Israel, lay to the north. Jews are named after Judah and are primarily descended from it. The Hebrew Bible depicts the Kingdom of Judah as a successor to the United Kingdom of Israel, a term denoting the united monarchy under biblical kings Saul, David and Solomon and covering the territory of Judah and Israel. However, during the 1980s, some biblical scholars began to argue that the archaeological evidence for an extensive kingdom before the late-8th century BCE is too weak, and that the methodology used to obtain the evidence is flawed. In the 10th and early 9th centuries BCE, the territory of Judah appears to have been sparsely populate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2 Kings
The Book of Kings (, '' Sēfer Məlāḵīm'') is a book in the Hebrew Bible, found as two books (1–2 Kings) in the Old Testament of the Christian Bible. It concludes the Deuteronomistic history, a history of Israel also including the books of Joshua, Judges and Samuel. Biblical commentators believe the Books of Kings were written to provide a theological explanation for the destruction of the Kingdom of Judah by Babylon in c. 586 BCE and to provide a foundation for a return from Babylonian exile.Sweeney, p1/ref> The two books of Kings present a history of ancient Israel and Judah, from the death of King David to the release of Jehoiachin from imprisonment in Babylon—a period of some 400 years (). Scholars tend to treat the books as consisting of a first edition from the late 7th century BCE and of a second and final edition from the mid-6th century BCE.Fretheim, p. 7 Contents The Jerusalem Bible divides the two Books of Kings into eight sections: *1 Kings 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taylor Prism-3
Taylor, Taylors or Taylor's may refer to: People * Taylor (surname) **List of people with surname Taylor * Taylor (given name), including Tayla and Taylah * Taylor sept, a branch of Scottish clan Cameron * Justice Taylor (other) Places Australia * Electoral district of Taylor, South Australia * Taylor, Australian Capital Territory, planned suburb Canada * Taylor, British Columbia United States * Taylor, Alabama * Taylor, Arizona * Taylor, Arkansas * Taylor, Indiana * Taylor, Louisiana * Taylor, Maryland * Taylor, Michigan * Taylor, Mississippi * Taylor, Missouri * Taylor, Nebraska * Taylor, North Dakota * Taylor, New York * Taylor, Beckham County, Oklahoma * Taylor, Cotton County, Oklahoma * Taylor, Pennsylvania * Taylors, South Carolina * Taylor, Texas * Taylor, Utah * Taylor, Washington * Taylor, West Virginia * Taylor, Wisconsin * Taylor, Wyoming * Taylor County (other) * Taylor Township (other) Businesses and organisations * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John George Taylor
John George Taylor (active 1851–1861; also known as J E Taylor and J G Taylor) was a British official of the Foreign Office, and also an important early archaeologist investigating the antiquities of the Middle East. He was one of the first archaeologists to explore the prominent burial mounds in the area of the Persian Gulf, and he made some very important discoveries. He also worked for the British East India Company. Family He was the son of Captain (later Colonel) R.(short for Robert) Taylor, who was the British Assistant Political Agent in Basra from 1818 to 1822. Colonel R. Taylor may have been the one who originally acquired the famous Taylor prism in 1830. It was purchased from Colonel Taylor's widow in 1850 by the British Museum. Career John Taylor was appointed as Agent for the British East India Company, and the British Vice-Consul at Basra from 1851 to 1858. At Basra, he was instructed by the Mandaean ''ganzibra'' (high priest) Adam Yuhana, the father of Yahya ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pierre-Victorien Lottin
Pierre-Victorien Lottin, known as Victor Lottin de Laval (1810-1903) was a French archaeologist and Orientalist painter. Biography He was born into the modest family of a small-town hatter. His mother died when he was only seven so, by 1820, he was compelled to go live with an uncle in Paris, to relieve some of the financial burden on his father, and try to support himself. While there, he developed a passion for reading and was largely self-taught. Later, with a recommendation from then Minister of Education François Guizot, he was able to obtain a position as secretary to the Comte d'Avesnes. During his time there, he began to write poetry and plays and often served as the Count's representative at the Hôtel de ville. There, he came into contact with many of that era's artistic personalities; including Victor Hugo, Eugène Delacroix, Alexandre Dumas, Hector Berlioz and George Sand. After 1833, he began using the pseudonym "Lottin de Laval", after his mother's maiden na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sir Henry Rawlinson, 1st Baronet
Sir Henry Creswicke Rawlinson, 1st Baronet, KLS (5 April 1810 – 5 March 1895) was a British East India Company army officer, politician and Orientalist, sometimes described as the Father of Assyriology. His son, also Henry, was to become a senior commander in the British Army during World War I. Early life and army service Rawlinson was born on 5 April 1810, at the place now known as Chadlington, Oxfordshire, England. He was the second son of Abram Tyack Rawlinson, and elder brother of the historian George Rawlinson. In 1827, having become proficient in the Persian language, he was sent to Persia in company with other British officers to drill and reorganize the Shah's troops. Disagreements between the Persian court and the British government ended in the departure of the British officers. Rawlinson began to study Persian inscriptions, more particularly those in the cuneiform character, which had only been partially deciphered by Grotefend and Saint-Martin. From 183 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squeeze Paper
A squeeze or squeeze paper is a reverse copy of an inscription, made by applying moist filter paper and pushing into the indentations by percussive use of a stiff brush. The paper is allowed to dry and then removed. The image is reversed from the inscription, and protrudes from the squeeze paper. The use of a squeeze allows more information to be gleaned than examining the original inscription, for example curves inside the cuts can identify the scribe who originally carved the inscription.Taking Inscriptions Home University of Reading, Ure Museum Squeezes can also (and some have been since the 1950s) be made by applying layers of liquid latex. This method works best on horizontal surfaces. Modern digitising methods mean that the image can be restored to the original orientation. Large collections of squeezes are held by the '' Inscriptiones Graecae'' and other epigraphic collections. See also *Rubbing A rubbing ('' frottage'') is a reproduction of the texture of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assyrian Empire
Assyrian may refer to: * Assyrian people, the indigenous ethnic group of Mesopotamia. * Assyria, a major Mesopotamian kingdom and empire. ** Early Assyrian Period ** Old Assyrian Period ** Middle Assyrian Empire ** Neo-Assyrian Empire * Assyrian language (other) * Assyrian Church (other) * SS ''Assyrian'', several cargo ships * ''The Assyrian'' (novel), a novel by Nicholas Guild * The Assyrian (horse), winner of the 1883 Melbourne Cup See also * Assyria (other) * Syriac (other) * Assyrian homeland, a geographic and cultural region in Northern Mesopotamia traditionally inhabited by Assyrian people * Syriac language, a dialect of Middle Aramaic that is the minority language of Syrian Christians * Upper Mesopotamia * Church of the East (other) Church of the East, also called ''Nestorian Church'', an Eastern Christian denomination formerly spread across Asia, separated since the schism of 1552. Church of the East may also refer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nineveh
Nineveh (; akk, ; Biblical Hebrew: '; ar, نَيْنَوَىٰ '; syr, ܢܝܼܢܘܹܐ, Nīnwē) was an ancient Assyrian city of Upper Mesopotamia, located in the modern-day city of Mosul in northern Iraq. It is located on the eastern bank of the Tigris River and was the capital and largest city of the Neo-Assyrian Empire, as well as the largest city in the world for several decades. Today, it is a common name for the half of Mosul that lies on the eastern bank of the Tigris, and the country's Nineveh Governorate takes its name from it. It was the largest city in the world for approximately fifty years until the year 612 BC when, after a bitter period of civil war in Assyria, it was sacked by a coalition of its former subject peoples including the Babylonians, Medes, Persians, Scythians and Cimmerians. The city was never again a political or administrative centre, but by Late Antiquity it was the seat of a Christian bishop. It declined relative to Mosul during the Mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuneiform Script
Cuneiform is a logo- syllabic script that was used to write several languages of the Ancient Middle East. The script was in active use from the early Bronze Age until the beginning of the Common Era. It is named for the characteristic wedge-shaped impressions (Latin: ) which form its signs. Cuneiform was originally developed to write the Sumerian language of southern Mesopotamia (modern Iraq). Cuneiform is the earliest known writing system. Over the course of its history, cuneiform was adapted to write a number of languages in addition to Sumerian. Akkadian texts are attested from the 24th century BC onward and make up the bulk of the cuneiform record. Akkadian cuneiform was itself adapted to write the Hittite language in the early second millennium BC. The other languages with significant cuneiform corpora are Eblaite, Elamite, Hurrian, Luwian, and Urartian. The Old Persian and Ugaritic alphabets feature cuneiform-style signs; however, they are unrelated to the cune ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
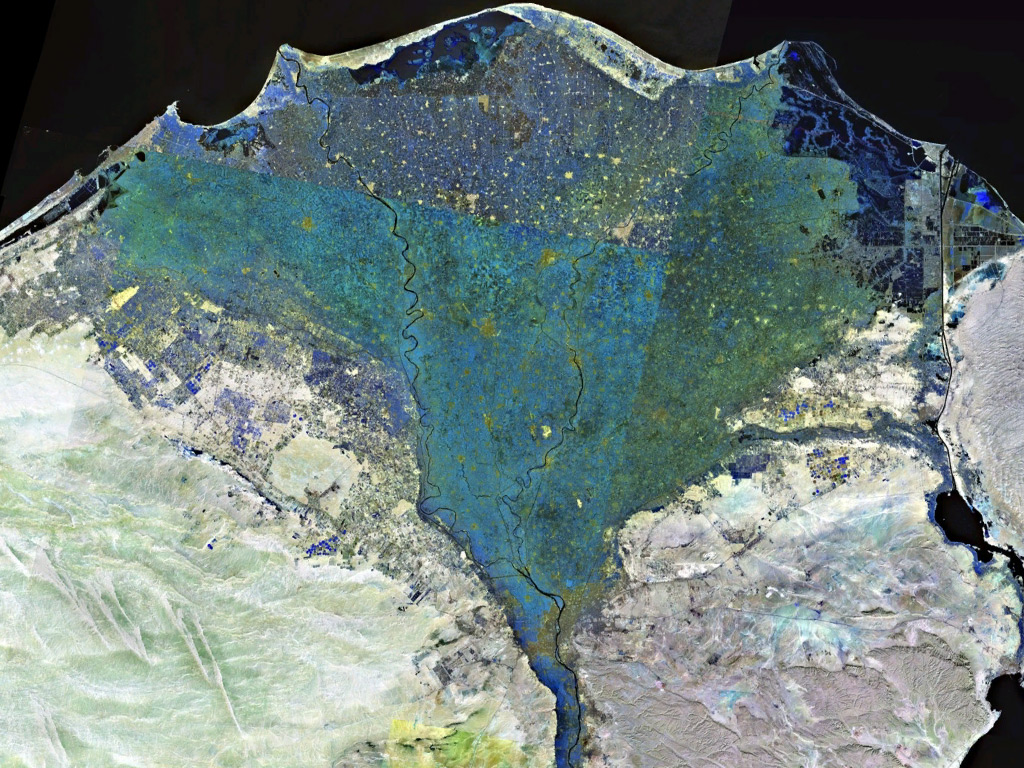
Nile Delta
The Nile Delta ( ar, دلتا النيل, or simply , is the delta formed in Lower Egypt where the Nile River spreads out and drains into the Mediterranean Sea. It is one of the world's largest river deltas—from Alexandria in the west to Port Said in the east, it covers of Mediterranean coastline and is a rich agricultural region. From north to south the delta is approximately in length. The Delta begins slightly down-river from Cairo. Geography From north to south, the delta is approximately in length. From west to east, it covers some of coastline. The delta is sometimes divided into sections, with the Nile dividing into two main distributaries, the Damietta and the Rosetta, flowing into the Mediterranean at port cities with the same name. In the past, the delta had several distributaries, but these have been lost due to flood control, silting and changing relief. One such defunct distributary is Wadi Tumilat. The Suez Canal is east of the delta and enters ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pelusium
Pelusium ( Ancient Egyptian: ; cop, /, romanized: , or , romanized: ; grc, Πηλουσιον, Pēlousion; la, Pēlūsium; Arabic: ; Egyptian Arabic: ) was an important city in the eastern extremes of Egypt's Nile Delta, 30 km to the southeast of the modern Port Said. It became a Roman provincial capital and Metropolitan archbishopric and remained a multiple Catholic titular see and an Eastern Orthodox active archdiocese. Location Pelusium lay between the seaboard and the marshes of the Nile Delta, about two-and-a-half miles from the sea. The port was choked by sand as early as the first century BC, and the coastline has now advanced far beyond its ancient limits that the city, even in the third century AD, was at least four miles from the Mediterranean. The principal product of the neighbouring lands was flax, and the ''linum Pelusiacum'' (Pliny's Natural History xix. 1. s. 3) was both abundant and of a very fine quality. Pelusium was also known for being an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.png)