|
Secretoglobin, Family 1A, Member 1 (uteroglobin)
Uteroglobin, or blastokinin, also known as secretoglobin family 1A member 1 (SCGB1A1), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SCGB1A1'' gene. SCGB1A1 is the founding member of the secretoglobin family of small, secreted, disulfide-bridged dimeric proteins found only in mammals. This antiparallel disulfide linked homodimeric protein is multifunctional and found in various tissues in various names such as: uteroglobin (UG, UGB), uteroglobin-like antigen (UGL), blastokinin, club-cell secretory protein (CCSP), Clara-cell 16 kD protein (17 in rat/mice), club-cell-specific 10 kD protein (CC10), human protein 1, urine protein 1 (UP-1), polychlorinated biphenyl-binding protein (PCB-BP), human club cell phospholipid-binding protein (hCCPBP), secretoglobin 1A member 1 (SCGB1A1). This protein is specifically expressed in club cells in the lungs. Function The precise physiological role of uteroglobin is not yet known. Putative functions are: # Immunomodulation # Progesterone bindin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secretoglobin
Secretoglobins (SCGBs) are a family of small, alpha-helical, disulfide linked, dimeric proteins found only in mammals. This family was formerly known as the Uteroglobin/Clara cell 10-kDa family, after the two aliases of its founding member Uteroglobin. Structure and function The proteins are mostly alpha-helical, and the dimer is formed in an antiparallel way. The dimer interface features a cavity formed across the two monomers, which can accommodate small to medium sized ligands like steroids and phospholipids. The binding and release may be coupled with the redox state of the cystines, i.e. the presence of these disulfide bonds. Many have regulatory functions. Classification The family was classified by sequence homology into 6 subfamilies in 2006. The human and mouse genomes only contain the first three families, per an 2011 update. Not every family is monophyletic. Rat prostatein (rat prostatic steroid binding protein) is a three component, tetrameric protein comple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
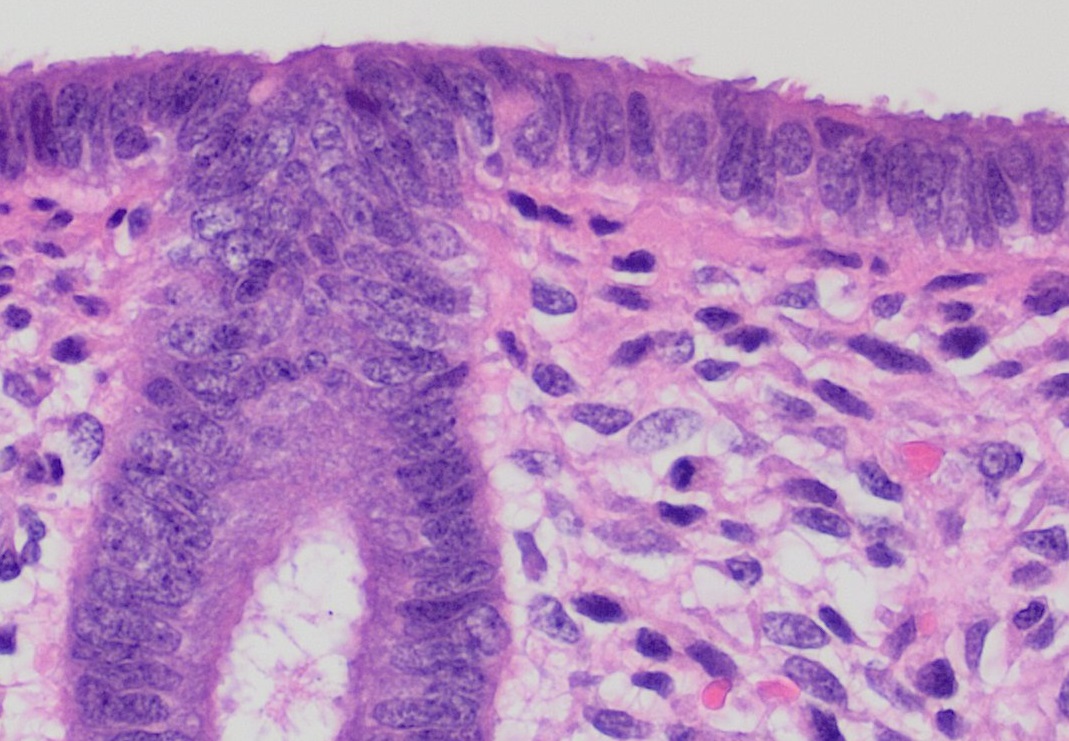
Club Cell
Club cells, also known as bronchiolar exocrine cells, and formerly known as Clara cells, are low columnar/cuboidal cells with short microvilli, found in the small airways (bronchioles) of the lungs. Club cells are found in the ciliated simple epithelium. These cells may secrete glycosaminoglycans to protect the bronchiole lining. Bronchiolar cells gradually increase in number as the number of goblet cells decrease. One of the main functions of club cells is to protect the bronchiolar epithelium. They do this by secreting a small variety of products, including club cell secretory protein uteroglobin, and a solution similar in composition to pulmonary surfactant. They are also responsible for detoxifying harmful substances inhaled into the lungs. Club cells accomplish this with cytochrome P450 enzymes found in their smooth endoplasmic reticulum. Club cells also act as a stem cell, multiplying and differentiating into ciliated cells to regenerate the bronchiolar epithelium. Function ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progesterone
Progesterone (P4) is an endogenous steroid and progestogen sex hormone involved in the menstrual cycle, pregnancy, and embryogenesis of humans and other species. It belongs to a group of steroid hormones called the progestogens and is the major progestogen in the body. Progesterone has a variety of important functions in the body. It is also a crucial metabolic intermediate in the production of other endogenous steroids, including the sex hormones and the corticosteroids, and plays an important role in brain function as a neurosteroid. In addition to its role as a natural hormone, progesterone is also used as a medication, such as in combination with estrogen for contraception, to reduce the risk of uterine or cervical cancer, in hormone replacement therapy, and in feminizing hormone therapy. It was first prescribed in 1934. Biological activity Progesterone is the most important progestogen in the body. As a potent agonist of the nuclear progesterone receptor (nPR) (wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endometrium
The endometrium is the inner epithelial layer, along with its mucous membrane, of the mammalian uterus. It has a basal layer and a functional layer: the basal layer contains stem cells which regenerate the functional layer. The functional layer thickens and then is shed during menstruation in humans and some other mammals, including apes, Old World monkeys, some species of bat, the elephant shrew and the Cairo spiny mouse. In most other mammals, the endometrium is reabsorbed in the estrous cycle. During pregnancy, the glands and blood vessels in the endometrium further increase in size and number. Vascular spaces fuse and become interconnected, forming the placenta, which supplies oxygen and nutrition to the embryo and fetus.Blue Histology - Female Reproductive System . School ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lagomorphs
The lagomorphs are the members of the taxonomic order Lagomorpha, of which there are two living families: the Leporidae (hares and rabbits) and the Ochotonidae (pikas). The name of the order is derived from the Ancient Greek ''lagos'' (λαγώς, "hare") + ''morphē'' (μορφή, "form"). There are 110 recent species of lagomorph of which 109 are extant, including 34 species of pika, 42 species of rabbit, and 33 species of hare. Taxonomy and evolutionary history Other names used for this order, now considered synonymous, include: ''Duplicidentata'' - Illiger, 1811; ''Leporida'' - Averianov, 1999; ''Neolagomorpha'' - Averianov, 1999; ''Ochotonida'' - Averianov, 1999; and ''Palarodentia'' - Haeckel, 1895, Lilian, 2016. The evolutionary history of the lagomorphs is still not well understood. Until recently, it was generally agreed that '' Eurymylus'', which lived in eastern Asia and dates back to the late Paleocene or early Eocene, was an ancestor of the lagomorphs. More rec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phospholipase A2
The enzyme phospholipase A2 (EC 3.1.1.4, PLA2, systematic name phosphatidylcholine 2-acylhydrolase) catalyse the cleavage of fatty acids in position 2 of phospholipids, hydrolyzing the bond between the second fatty acid “tail” and the glycerol molecule: :phosphatidylcholine + H2O = 1-acylglycerophosphocholine + a carboxylate This particular phospholipase specifically recognizes the ''sn''2 acyl bond of phospholipids and catalytically hydrolyzes the bond, releasing arachidonic acid and lysophosphatidic acid. Upon downstream modification by cyclooxygenases or lipoxygenases, arachidonic acid is modified into active compounds called eicosanoids. Eicosanoids include prostaglandins and leukotrienes, which are categorized as anti-inflammatory and inflammatory mediators. PLA2 enzymes are commonly found in mammalian tissues as well as arachnid, insect, and snake venom. Venom from bees is largely composed of melittin, which is a stimulant of PLA2. Due to the increased ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphatidylcholine
Phosphatidylcholines (PC) are a class of phospholipids that incorporate choline as a headgroup. They are a major component of biological membranes and can be easily obtained from a variety of readily available sources, such as egg yolk or soybeans, from which they are mechanically or chemically extracted using hexane. They are also a member of the lecithin group of yellow-brownish fatty substances occurring in animal and plant tissues. Dipalmitoyl phosphatidylcholine (a.k.a. lecithin) is a major component of pulmonary surfactant and is often used in the L/S ratio to calculate fetal lung maturity. While phosphatidylcholines are found in all plant and animal cells, they are absent in the membranes of most bacteria, including ''Escherichia coli''. Purified phosphatidylcholine is produced commercially. The name ''lecithin'' was derived from Greek λέκιθος, ''lekithos'' 'egg yolk' by Theodore Nicolas Gobley, a French chemist and pharmacist of the mid-19th century, who applied ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphatidylinositol
Phosphatidylinositol (or Inositol Phospholipid) consists of a family of lipids as illustrated on the right, where red is x, blue is y, and black is z, in the context of independent variation, a class of the phosphatidylglycerides. In such molecules the isomer of the inositol group is assumed to be the myo- conformer unless otherwise stated. Typically phosphatidylinositols form a minor component on the cytosolic side of eukaryotic cell membranes. The phosphate group gives the molecules a negative charge at physiological pH. The form of phosphatidylinositol comprising the isomer ''muco''-inositol acts as a sensory receptor in the taste function of the sensory system. In this context it is often referred to as PtdIns, but that does not imply any molecular difference from phosphatidylinositols comprising the myo- conformers of inositol. The phosphatidylinositol can be phosphorylated to form phosphatidylinositol phosphate (PI-4-P, referred to as PIP in close context or inform ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
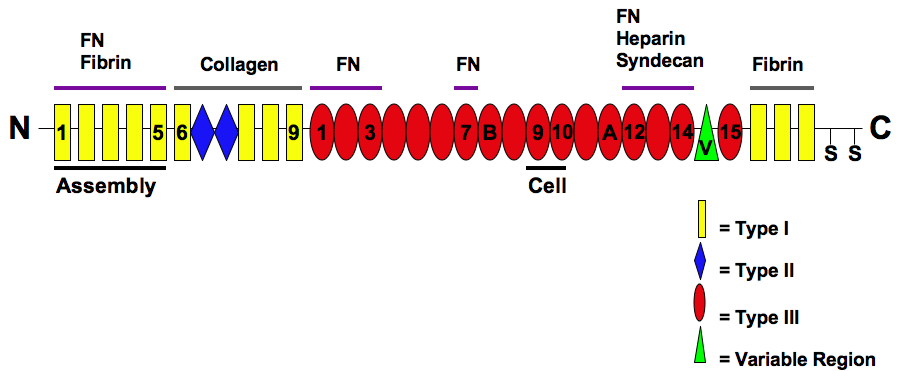
Fibronectin
Fibronectin is a high- molecular weight (~500-~600 kDa) glycoprotein of the extracellular matrix that binds to membrane-spanning receptor proteins called integrins. Fibronectin also binds to other extracellular matrix proteins such as collagen, fibrin, and heparan sulfate proteoglycans (e.g. syndecans). Fibronectin exists as a protein dimer, consisting of two nearly identical monomers linked by a pair of disulfide bonds. The fibronectin protein is produced from a single gene, but alternative splicing of its pre-mRNA leads to the creation of several isoforms. Two types of fibronectin are present in vertebrates: * soluble plasma fibronectin (formerly called "cold-insoluble globulin", or CIg) is a major protein component of blood plasma (300 μg/ml) and is produced in the liver by hepatocytes. * insoluble cellular fibronectin is a major component of the extracellular matrix. It is secreted by various cells, primarily fibroblasts, as a soluble protein dimer and is then ass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goodpasture's Syndrome
Goodpasture syndrome (GPS), also known as anti–glomerular basement membrane disease, is a rare autoimmune disease in which antibodies attack the basement membrane in lungs and kidneys, leading to bleeding from the lungs, glomerulonephritis, and kidney failure. It is thought to attack the alpha-3 subunit of type IV collagen, which has therefore been referred to as Goodpasture's antigen. Goodpasture syndrome may quickly result in permanent lung and kidney damage, often leading to death. It is treated with medications that suppress the immune system such as corticosteroids and cyclophosphamide, and with plasmapheresis, in which the antibodies are removed from the blood. The disease was first described by an American pathologist Ernest Goodpasture of Vanderbilt University in 1919 and was later named in his honor. Signs and symptoms The anti– glomerular basement membrane (GBM) antibodies primarily attack the kidneys and lungs, although, generalized symptoms like malai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |