|
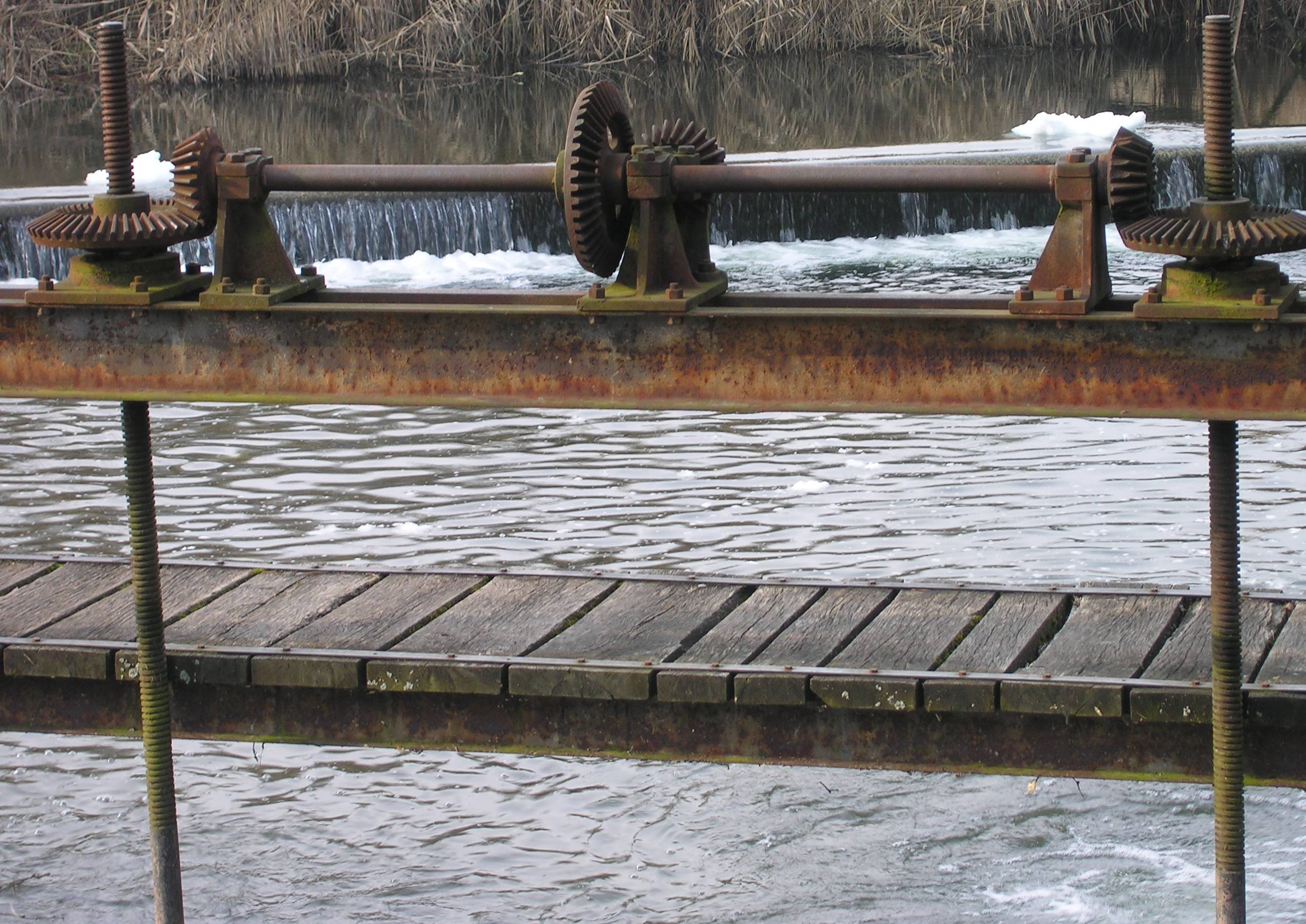
Screw Thread
A screw thread, often shortened to thread, is a helical structure used to convert between rotational and linear movement or force. A screw thread is a ridge wrapped around a cylinder or cone in the form of a helix, with the former being called a ''straight'' thread and the latter called a ''tapered'' thread. A screw thread is the essential feature of the screw as a simple machine and also as a threaded fastener. The mechanical advantage of a screw thread depends on its ''lead'', which is the linear distance the screw travels in one revolution. In most applications, the lead of a screw thread is chosen so that friction is sufficient to prevent linear motion being converted to rotary, that is so the screw does not slip even when linear force is applied, as long as no external rotational force is present. This characteristic is essential to the vast majority of its uses. The tightening of a fastener's screw thread is comparable to driving a wedge into a gap until it sticks fast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micrometer (device)
A micrometer, sometimes known as a micrometer screw gauge, is a device incorporating a calibrated screw widely used for accurate measurement of components in mechanical engineering and machining as well as most mechanical trades, along with other metrological instruments such as dial, vernier, and digital calipers. Micrometers are usually, but not always, in the form of calipers (opposing ends joined by a frame). The spindle is a very accurately machined screw and the object to be measured is placed between the spindle and the anvil. The spindle is moved by turning the ratchet knob or thimble until the object to be measured is lightly touched by both the spindle and the anvil. Micrometers are also used in telescopes or microscopes to measure the apparent diameter of celestial bodies or microscopic objects. The micrometer used with a telescope was invented about 1638 by William Gascoigne, an English astronomer. History The word ''micrometer'' is a neoclassical coin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brushcutter (garden Tool)
A brushcutter (also called a brush saw or clearing saw) is a powered garden or agricultural tool used to trim weeds, small trees, and other foliage not accessible by a lawn mower or rotary mower. Various blades or trimmer heads can be attached to the machine for specific applications. It consists of: * A power unit held close to the body. * A pole through which the power is transmitted. * A rotary cutting head at the opposite end of the pole to the power unit. Power units There are three main types of power unit: * Gas engines, either two or four stroke, are used on the more powerful units. * Electric motors connected to mains power by a power cord. * Cordless electric motors powered by rechargeable batteries. Shaft There are three types of shaft: * Basic consumer units use a curved shaft, similar to a basic line trimmer. * More professional units use a straight shaft with a gearbox at the cutting head end. * Top-of-the-line units use a straight "split" shaft with a disconnecti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torque
In physics and mechanics, torque is the rotational equivalent of linear force. It is also referred to as the moment of force (also abbreviated to moment). It represents the capability of a force to produce change in the rotational motion of the body. The concept originated with the studies by Archimedes of the usage of levers, which is reflected in his famous quote: "''Give me a lever and a place to stand and I will move the Earth''". Just as a linear force is a push or a pull, a torque can be thought of as a twist to an object around a specific axis. Torque is defined as the product of the magnitude of the perpendicular component of the force and the distance of the line of action of a force from the point around which it is being determined. The law of conservation of energy can also be used to understand torque. The symbol for torque is typically \boldsymbol\tau, the lowercase Greek letter '' tau''. When being referred to as moment of force, it is commonly denoted by . ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lug Nut
A lug nut or wheel nut is a fastener, specifically a nut, used to secure a wheel on a vehicle. Typically, lug nuts are found on automobiles, trucks (lorries), and other large vehicles using rubber tires. Design A lug nut is a nut fastener with one rounded or conical (tapered) end, used on steel and most aluminum wheels. A set of lug nuts is typically used to secure a wheel to threaded wheel studs and thereby to a vehicle's axles. Some designs (Audi, BMW, Mercedes-Benz, Saab, Volkswagen) use lug bolts or wheel bolts instead of nuts, which screw into a tapped (threaded) hole in the wheel's hub or brake drum or brake disc. The conical lug's taper is normally 60 degrees (although 45 degrees is common for wheels designed for racing applications), and is designed to help center the wheel accurately on the axle, and to reduce the tendency for the nut to loosen due to fretting induced precession, as the car is driven. One popular alternative to the conical lug seating design i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bench Grinder
A bench grinder is a benchtop type of grinding machine used to drive abrasive wheels. A pedestal grinder is a similar or larger version of grinder that is mounted on a pedestal, which may be bolted to the floor or may sit on rubber feet. These types of grinders are commonly used to hand grind various cutting tools and perform other rough grinding. Depending on the bond and grade of the grinding wheel, it may be used for sharpening cutting tools such as tool bits, drill bits, chisels, and gouges. Alternatively, it may be used to roughly shape metal prior to welding or fitting. A wire brush wheel or buffing wheels can be interchanged with the grinding wheels in order to clean or polish workpieces. Stiff buffing wheels can also be used when deburring is the task at hand. Some buffing machines (buffers) are built on the same concept as bench grinders except for longer housings and arbors with buffing wheels instead of grinding wheels. Bench grinders are standard equipment in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bicycle
A bicycle, also called a pedal cycle, bike or cycle, is a human-powered or motor-powered assisted, pedal-driven, single-track vehicle, having two wheels attached to a frame, one behind the other. A is called a cyclist, or bicyclist. Bicycles were introduced in the 19th century in Europe. By the early 21st century, more than 1 billion were in existence. These numbers far exceed the number of cars, both in total and ranked by the number of individual models produced. They are the principal means of transportation in many regions. They also provide a popular form of recreation, and have been adapted for use as children's toys, general fitness, military and police applications, courier services, bicycle racing, and bicycle stunts. The basic shape and configuration of a typical upright or "safety bicycle", has changed little since the first chain-driven model was developed around 1885. However, many details have been improved, especially since the advent of modern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
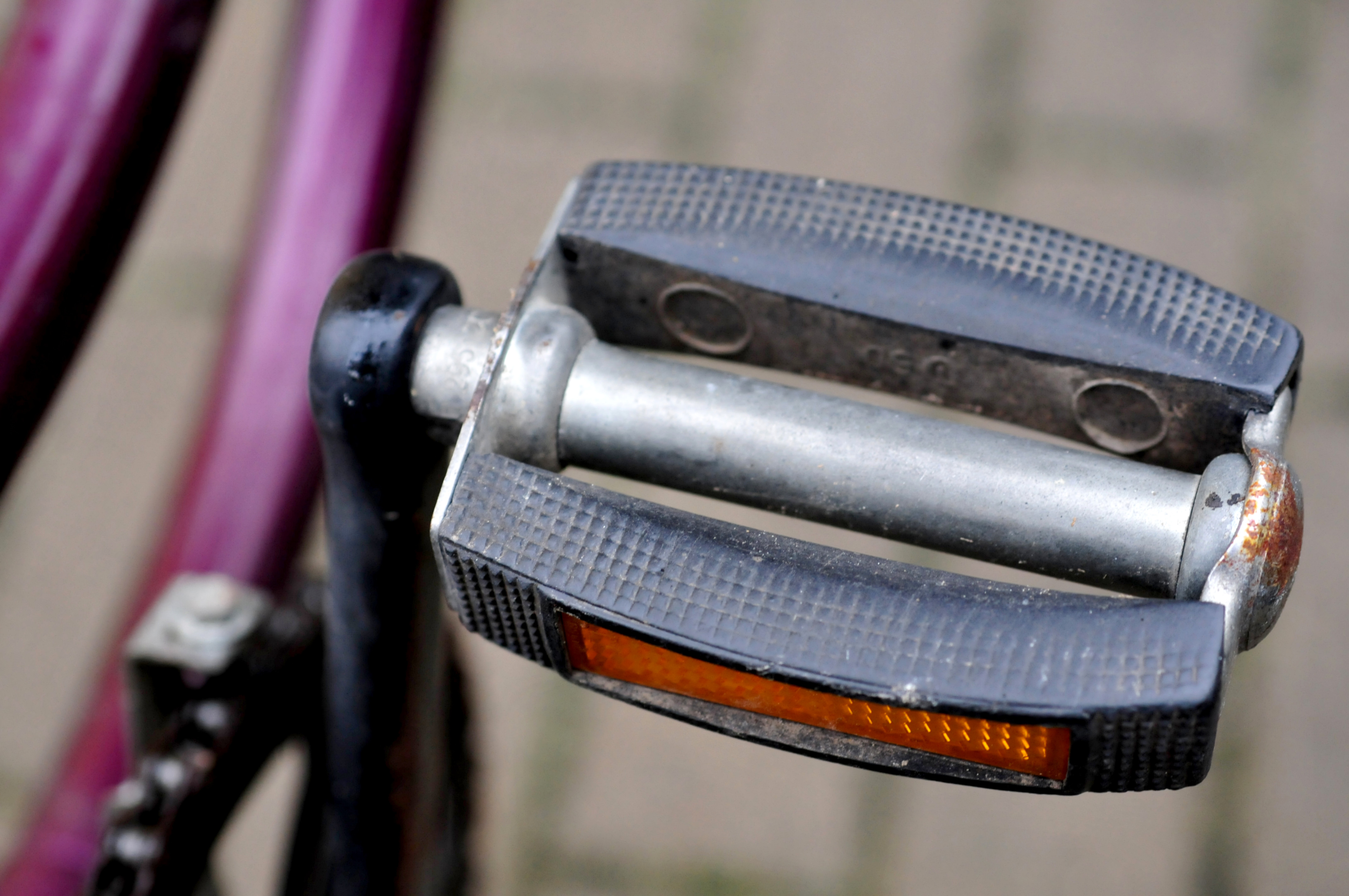
Bicycle Pedal
The pedal is the part of a bicycle that the rider pushes with their foot to propel the vehicle. It provides the connection between the cyclist's foot or shoe and the crank allowing the leg to turn the bottom bracket spindle and propel the bicycle's wheels. A pedal usually consists of a spindle that threads into the end of the crank, and a body on which the foot rest is attached, that is free to rotate on bearings with respect to the spindle. Pedals were initially attached to cranks connecting directly to the driven (usually front) wheel. The safety bicycle, as it is known today, came into being when the pedals were attached to a crank driving a sprocket that transmitted power to the driven wheel by means of a roller chain. Types Just as bicycles come in many varieties, there are different types of pedals to support different types of cycling. Flat and platform Traditionally, platform pedals were pedals with a relatively large flat area for the foot to rest on, in contrast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Precession (mechanical)
Precession is the process of a round part in a round hole, rotating with respect to each other, wherein the inner part begins rolling around the circumference of the outer bore, in a direction opposite of rotation. This is caused by too much clearance between them and a radial force on the part that constantly changes direction. The direction of rotation of the inner part is opposite to the direction of rotation of the radial force. In a rotating machine, such as motor, engine, gear train, etc., precession can occur when too much clearance exists between a shaft and a bushing, or between the races and rolling elements in roller and ball bearings. Often a result of wear, inadequate lubrication (too little or too thin), or lack of precision engineering, such precession is usually accompanied by excess vibration and an audible rubbing or buzzing noise. This tends to accelerate the wear process, possibly leading to spalling, galling, or false brinelling (fretting wear) of the conta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Right Hand Grip Rule
In mathematics and physics, the right-hand rule is a common mnemonic for understanding orientation of axes in three-dimensional space. It is also a convenient method for quickly finding the direction of a cross-product of 2 vectors. Most of the various left-hand and right-hand rules arise from the fact that the three axes of three-dimensional space have two possible orientations. One can see this by holding one's hands outward and together, palms up, with the thumbs out-stretched to the right and left, and the fingers making a curling motion from straight outward to pointing upward. (Note the picture to right is not an illustration of this.) The curling motion of the fingers represents a movement from the first (''x'' axis) to the second (''y'' axis); the third (''z'' axis) can point along either thumb. Left-hand and right-hand rules arise when dealing with coordinate axes. The rule can be used to find the direction of the magnetic field, rotation, spirals, electromagnetic fiel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clockwise
Two-dimensional rotation can occur in two possible directions. Clockwise motion (abbreviated CW) proceeds in the same direction as a clock's hands: from the top to the right, then down and then to the left, and back up to the top. The opposite sense of rotation or revolution is (in Commonwealth English) anticlockwise (ACW) or (in North American English) counterclockwise (CCW). Terminology Before clocks were commonplace, the terms "sunwise" and "deasil", "deiseil" and even "deocil" from the Scottish Gaelic language and from the same root as the Latin "dexter" ("right") were used for clockwise. " Widdershins" or "withershins" (from Middle Low German "weddersinnes", "opposite course") was used for counterclockwise. The terms clockwise and counterclockwise can only be applied to a rotational motion once a side of the rotational plane is specified, from which the rotation is observed. For example, the daily rotation of the Earth is clockwise when viewed from above the South Pole ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Right-hand Grip Rule
In mathematics and physics, the right-hand rule is a common mnemonic for understanding orientation of axes in three-dimensional space. It is also a convenient method for quickly finding the direction of a cross-product of 2 vectors. Most of the various left-hand and right-hand rules arise from the fact that the three axes of three-dimensional space have two possible orientations. One can see this by holding one's hands outward and together, palms up, with the thumbs out-stretched to the right and left, and the fingers making a curling motion from straight outward to pointing upward. (Note the picture to right is not an illustration of this.) The curling motion of the fingers represents a movement from the first (''x'' axis) to the second (''y'' axis); the third (''z'' axis) can point along either thumb. Left-hand and right-hand rules arise when dealing with coordinate axes. The rule can be used to find the direction of the magnetic field, rotation, spirals, electromagnetic fiel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |