|
Saqlabi
Saqaliba ( ar, صقالبة, ṣaqāliba, singular ar, صقلبي, ṣaqlabī) is a term used in medieval Arabic sources to refer to Slavs and other peoples of Central, Southern, and Eastern Europe, or in a broad sense to European slaves. The term originates from the Middle Greek '' slavos/sklavenos'' (Slav), which in Hispano-Arabic came to designate first Slavic slaves and then, similarly to the semantic development of the term in other West-European languages, foreign slaves in general. The word was often used to refer specifically to Slavic slaves, but it could also refer more broadly to Europeans traded by the Arab traders. There were several major routes for the trading of Slavic slaves into the Arab world: through Central Asia ( Mongols, Tatars, Khazars, etc.) for the East Slavs; through the Balkans for the South Slavs; through Central and Western Europe for the West Slavs and to al-Andalus. The Volga trade route and other European routes, according to Ibrahim ibn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter de Gruyter GmbH & Co. KG, Berlin/Boston, 2011. Having emerged in the 1st century, it is named after the Arab people; the term "Arab" was initially used to describe those living in the Arabian Peninsula, as perceived by geographers from ancient Greece. Since the 7th century, Arabic has been characterized by diglossia, with an opposition between a standard prestige language—i.e., Literary Arabic: Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) or Classical Arabic—and diverse vernacular varieties, which serve as mother tongues. Colloquial dialects vary significantly from MSA, impeding mutual intelligibility. MSA is only acquired through formal education and is not spoken natively. It is the language of literature, official documents, and formal writ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
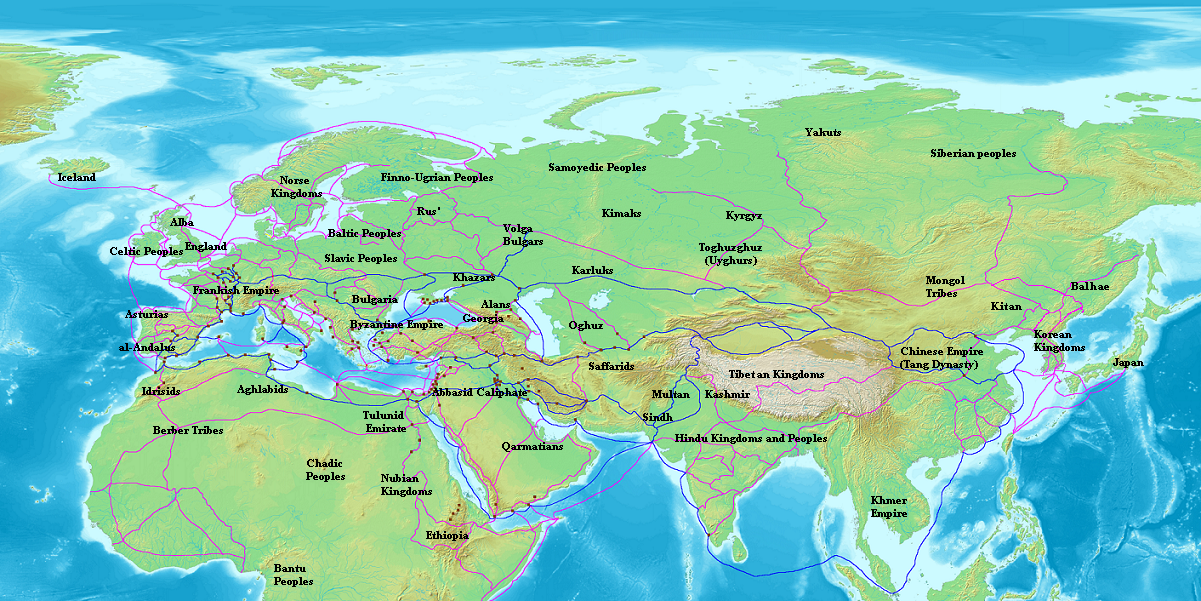
Al-Andalus
Al-Andalus translit. ; an, al-Andalus; ast, al-Ándalus; eu, al-Andalus; ber, ⴰⵏⴷⴰⵍⵓⵙ, label= Berber, translit=Andalus; ca, al-Àndalus; gl, al-Andalus; oc, Al Andalús; pt, al-Ândalus; es, al-Ándalus () was the Muslim-ruled area of the Iberian Peninsula. The term is used by modern historians for the former Islamic states in modern Spain and Portugal. At its greatest geographical extent, it occupied most of the peninsula and a part of present-day southern France, Septimania (8th century). For nearly a hundred years, from the 9th century to the 10th, al-Andalus extended its presence from Fraxinetum into the Alps with a series of organized raids and chronic banditry. The name describes the different Arab and Muslim states that controlled these territories at various times between 711 and 1492. These boundaries changed constantly as the Christian Reconquista progressed,"Para los autores árabes medievales, el término Al-Andalus designa la totalida ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archon
''Archon'' ( gr, ἄρχων, árchōn, plural: ἄρχοντες, ''árchontes'') is a Greek word that means "ruler", frequently used as the title of a specific public office. It is the masculine present participle of the verb stem αρχ-, meaning "to be first, to rule", derived from the same root as words such as monarch and hierarchy. Ancient Greece In the early literary period of ancient Greece the chief magistrates of various Greek city states were called ''archontes''. The term was also used throughout Greek history in a more general sense, ranging from "club leader" to "master of the tables" at ''syssitia'' to "Roman governor". In Athens, a system of three concurrent archons evolved, the three office holders being known as ''archon eponymos'' (), the ''polemarch'' (), and the ''archon basileus'' (). According to Aristotle's '' Constitution of the Athenians'', the power of the king first devolved to the archons, and these offices were filled from the aristocracy b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neboulos
Neboulos ( el, Νέβουλος) was a South Slavic or Bulgar military commander in the service of the Byzantine emperor Justinian II (r. 685–695 and 705–711), who defected with many of his men to the Arabs during the crucial Battle of Sebastopolis.. In 688/9, Justinian II forcibly transplanted Slavic populations from the Balkans and settled them in the depopulated Opsician Theme. From them, he recruited a special military corps, allegedly 30,000 strong, which was called in Greek λαός περιούσιος, "the chosen people"... In about 690, Neboulos, who already held the rank of '' skribon'' and possibly served in the imperial guard, was placed as their commander (''archon''). Neboulos's own origin is disputed between scholars, with some suggesting a Bulgar origin and others a South Slavic one. According to the account of Patriarch Nikephoros, he was chosen from among the nobility of the Slav settlers. In 692/3, after the corps' training had been completed, they were e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Sebastopolis
The Battle of Sebastopolis was fought at Sebastopolis (mostly identified with Elaiussa Sebaste in Cilicia but also with modern Sulusaray) in 692 CE between the Byzantine Empire and the Umayyad Caliphate under Abd al-Malik ibn Marwan. The battle ended the peace that had existed between the two powers since 680. The Umayyad army was led by Muhammad ibn Marwan. The Byzantines were led by Leontios Leontius ( el, Λεόντιος, Leóntios; – 15 February 706), was Byzantine emperor from 695 to 698. Little is known of his early life, other than that he was born in Isauria in Asia Minor. He was given the title of ''patrikios'', and m ... and included a "special army" of 30,000 Slavs under their leader, Neboulos. The Umayyads, incensed at the breaking of the treaty, used copies of its texts in the place of a flag. Though the battle seemed to be tilting to the Byzantine advantage, the defection of upwards of 20,000 Slavs ensured a Byzantine defeat.Ostrogorsky, George, ''His ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country located in the Eastern Mediterranean and the Levant. It is a unitary state, unitary republic that consists of Governorates of Syria, 14 governorates (subdivisions), and is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the west, Turkey to the north, Iraq to Iraq–Syria border, the east and southeast, Jordan to Jordan–Syria border, the south, and Israel and Lebanon to Lebanon–Syria border, the southwest. Cyprus lies to the west across the Mediterranean Sea. A country of fertile plains, high mountains, and deserts, Syria is home to demographics of Syria, diverse ethnic and religious groups, including the majority Syrians, Syrian Arabs, Kurds in Syria, Kurds, Syrian Turkmen, Turkmens, Assyrians in Syria, Assyrians, Armenians in Syria, Armenians, Circa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mercenary
A mercenary, sometimes also known as a soldier of fortune or hired gun, is a private individual, particularly a soldier, that joins a military conflict for personal profit, is otherwise an outsider to the conflict, and is not a member of any other official military. Mercenaries fight for money or other forms of payment rather than for political interests. Beginning in the 20th century, mercenaries have increasingly come to be seen as less entitled to protections by rules of war than non-mercenaries. The Geneva Conventions declare that mercenaries are not recognized as legitimate combatants and do not have to be granted the same legal protections as captured service personnel of the armed forces. In practice, whether or not a person is a mercenary may be a matter of degree, as financial and political interests may overlap. Modern mercenary organizations are generally referred to as private military companies or PMCs. Laws of war Protocol Additional GC 1977 (APGC77) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muawiyah I
Mu'awiya I ( ar, معاوية بن أبي سفيان, Muʿāwiya ibn Abī Sufyān; –April 680) was the founder and first caliph of the Umayyad Caliphate, ruling from 661 until his death. He became caliph less than thirty years after the death of the Islamic prophet Muhammad and immediately after the four Rashidun ('rightly-guided') caliphs. Unlike his predecessors, who had been close, early companions of Muhammad, Mu'awiya was a relatively late follower of the Islamic prophet. Mu'awiya and his father Abu Sufyan had opposed Muhammad, their distant Qurayshite kinsman and later Mu'awiya's brother-in-law, until Muhammad captured Mecca in 630. Afterward, Mu'awiya became one of Muhammad's scribes. He was appointed by Caliph Abu Bakr () as a deputy commander in the conquest of Syria. He moved up the ranks through Umar's caliphate () until becoming governor of Syria during the reign of his Umayyad kinsman, Caliph Uthman (). He allied with the province's powerful Banu Kalb tri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Umayyad
The Umayyad Caliphate (661–750 CE; , ; ar, ٱلْخِلَافَة ٱلْأُمَوِيَّة, al-Khilāfah al-ʾUmawīyah) was the second of the four major caliphates established after the death of Muhammad. The caliphate was ruled by the Umayyad dynasty ( ar, ٱلْأُمَوِيُّون, ''al-ʾUmawīyūn'', or , ''Banū ʾUmayyah'', "Sons of Umayyah"). Uthman ibn Affan (r. 644–656), the third of the Rashidun caliphs, was also a member of the clan. The family established dynastic, hereditary rule with Muawiya ibn Abi Sufyan, long-time governor of Greater Syria, who became the sixth caliph after the end of the First Fitna in 661. After Mu'awiyah's death in 680, conflicts over the succession resulted in the Second Fitna, and power eventually fell into the hands of Marwan I from another branch of the clan. Greater Syria remained the Umayyads' main power base thereafter, with Damascus serving as their capital. The Umayyads continued the Muslim conquests, incorpor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theophanes The Confessor
Theophanes the Confessor ( el, Θεοφάνης Ὁμολογητής; c. 758/760 – 12 March 817/818) was a member of the Byzantine aristocracy who became a monk and chronicler. He served in the court of Emperor Leo IV the Khazar before taking up the religious life. Theophanes attended the Second Council of Nicaea in 787 and resisted the iconoclasm of Leo V the Armenian, for which he was imprisoned. He died shortly after his release. Theophanes the Confessor, venerated on 12 March in both the Eastern Orthodox and the Roman Catholic churches, should not be confused with Theophanes of Nicaea, whose feast is commemorated on 11 October. Biography Theophanes was born in Constantinople of wealthy and noble iconodule parents: Isaac, governor of the islands of the Aegean Sea, and Theodora, of whose family nothing is known. His father died when Theophanes was three years old, and the Byzantine Emperor Constantine V (740–775) subsequently saw to the boy's education and upb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radanite
The Radhanites or Radanites (; ar, الرذنية, ''ar-Raðaniyya'') were early medieval Jewish merchants, active in the trade between Christendom and the Muslim world during roughly the 8th to 10th centuries. Many trade routes previously established under the Roman Empire continued to function during that period—largely through their efforts. Their trade network covered much of Europe, North Africa, the Middle East, Central Asia, and parts of India and China. Only a limited number of primary sources use the term, and it remains unclear whether they referred to a specific guild, or to a clan, or generically to Jewish merchants in the trans-Eurasian trade network. Name Several etymologies have been suggested for the word "Radhanite". Many scholars, including Barbier de Meynard and Moshe Gil, believe it refers to a district in Mesopotamia called " the land of Radhan" in Arabic and Hebrew texts of the period. Another hypothesis suggests that the name might be derived from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |