|
Sabratha
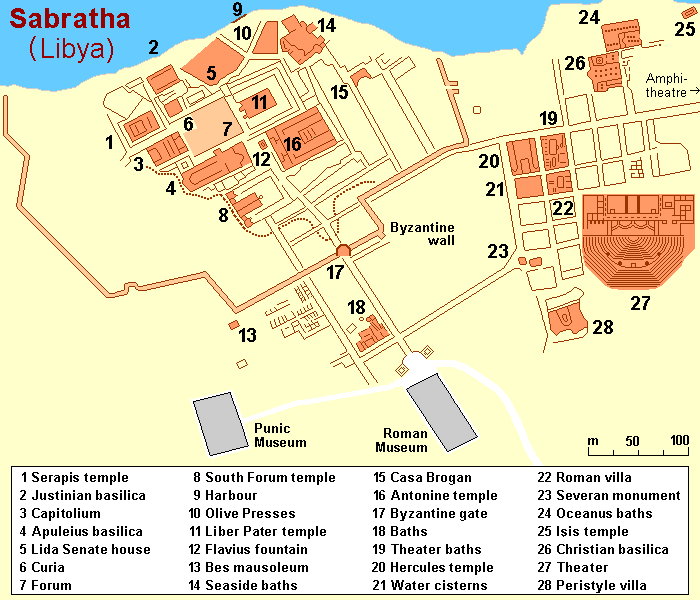
Sabratha ( ar, صبراتة, Ṣabrāta; also ''Sabratah'', ''Siburata''), in the Zawiya District''شعبيات الجماهيرية العظمى''Sha'biyat of Great Jamahiriya accessed 20 July 2009, in Arabic of Libya, was the westernmost of the ancient "three cities" of Roman Tripolis, alongside and . From 2001 to 2007 it was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Libya
Libya (; ar, ليبيا, Lībiyā), officially the State of Libya ( ar, دولة ليبيا, Dawlat Lībiyā), is a country in the Maghreb region in North Africa. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to the east, Sudan to the southeast, Chad to the south, Niger to the southwest, Algeria to the west, and Tunisia to the northwest. Libya is made of three historical regions: Tripolitania, Fezzan, and Cyrenaica. With an area of almost 700,000 square miles (1.8 million km2), it is the fourth-largest country in Africa and the Arab world, and the 16th-largest in the world. Libya has the 10th-largest proven oil reserves in the world. The largest city and capital, Tripoli, is located in western Libya and contains over three million of Libya's seven million people. Libya has been inhabited by Berbers since the late Bronze Age as descendants from Iberomaurusian and Capsian cultures. In ancient times, the Phoenicians established city-states and tradin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tripoli, Libya
Tripoli (; ar, طرابلس الغرب, translit= Ṭarābulus al-Gharb , translation=Western Tripoli) is the capital and largest city of Libya, with a population of about 1.1 million people in 2019. It is located in the northwest of Libya on the edge of the desert, on a point of rocky land projecting into the Mediterranean Sea and forming a bay. It includes the port of Tripoli and the country's largest commercial and manufacturing center. It is also the site of the University of Tripoli. The vast barracks, which includes the former family estate of Muammar Gaddafi, is also located in the city. Colonel Gaddafi largely ruled the country from his residence in this barracks. Tripoli was founded in the 7th century BC by the Phoenicians, who gave it the Libyco-Berber name ( xpu, 𐤅𐤉𐤏𐤕, ) before passing into the hands of the Greek rulers of Cyrenaica as Oea ( grc-gre, Ὀία, ). Due to the city's long history, there are many sites of archeological ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Districts Of Libya
In Libya there are currently 106 districts, second level administrative subdivisions known in Arabic as ''baladiyat'' (singular ''baladiyah''). The number has varied since 2013 between 99 and 108. The first level administrative divisions in Libya are currently the governorates (''muhafazat''), which have yet to be formally deliniated, but which were originally tripartite as: Tripolitania in the northwest, Cyrenaica in the east, and Fezzan in the southwest; and later divided into ten governorates. Prior to 2013 there were twenty-two first level administrative subdivisions known by the term ''shabiyah'' (Arabic singular ''šaʿbiyya'', plural ''šaʿbiyyāt'') which constituted the districts of Libya. In the 1990s the shabiyat had replaced an older baladiyat system. Historically the area of Libya was considered three provinces (or states), Tripolitania in the northwest, Cyrenaica in the east, and Fezzan in the southwest. It was the conquest by Italy in the Italo-Turki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sabratha Wa Sorman District
Sabratha wa Surman (Sabratha and Surman) was one of the districts of Libya from 1998 to 2007, in the Northwest. Since 2007 the area has been part of Zawiya District. , accessed 6 September 2009, in Arabic In the north, Sabratha wa Surman had a shoreline on the . On land, it bordered the following districts: * Zawiya - east * - southeast, at a |
Zawiya District
Zawiya, officially Zawia ( ar, محافظة الزاوية ''Az Zāwiya''), is one of the districts of Libya. It is located in the north western part of the country, in what had been the historical region of Tripolitania. Its capital is also named Zawia. the province of Az Zawiya has three major municipalities; according to the new laws of local governance, includes Central Az Zawiya municipality, Southern Az Zawia municipality and Eastern Az zawiya municipality. In the north, Zawiya province has a shoreline bordering the Mediterranean Sea, while it borders Tripoli in east, Jafara in southeast, Jabal al Gharbi in south, Surman in the west. Per the census of 2012, the total population in the region was 157,747. The average size of the household in the country was 6.9. There were totally 22,713 households in the district, with 20,907 Libyan ones. The population density of the district was 1.86 persons per sq. km. Geography In the north, Zawiya has a shoreline bordering the Med ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tripolis (region Of Africa)
Tripolitania ( ar, طرابلس '; ber, Ṭrables, script=Latn; from Vulgar Latin: , from la, Regio Tripolitana, from grc-gre, Τριπολιτάνια), historically known as the Tripoli region, is a historic region and former province of Libya. The region had been settled since antiquity, first coming to prominence as part of the Carthaginian empire. Following the defeat of Carthage in the Punic Wars, Ancient Rome organized the region (along with what is now modern day Tunisia and eastern Algeria), into a province known as Africa, and placed it under the administration of a proconsul. During the Diocletian reforms of the late 3rd century, all of North Africa was placed into the newly created Diocese of Africa, of which Tripolitania was a constituent province. After the Fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century, Tripolitania changed hands between the Vandals and the Byzantine Empire, until it was taken during the Muslim conquest of the Maghreb in the 8th ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leptis Magna
Leptis or Lepcis Magna, also known by other names in antiquity, was a prominent city of the Carthaginian Empire and Roman Libya at the mouth of the Wadi Lebda in the Mediterranean. Originally a 7th-centuryBC Phoenician foundation, it was greatly expanded under Roman Emperor Septimius Severus (), who was born in the city. The 3rd Augustan Legion was stationed here to defend the city against Berber incursions. After the legion's dissolution under in 238, the city was increasingly open to raids in the later part of the 3rd century. Diocletian reinstated the city as provincial capital, and it grew again in prosperity until it fell to the Vandals in 439. It was reincorporated into the Eastern Empire in 533 but continued to be plagued by Berber raids and never recovered its former importance. It fell to the Muslim invasion in and was subsequently abandoned. Its ruins are within present-day Khoms, Libya, east of Tripoli. They are among the best-preserved Roman sites in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
365 Crete Earthquake
The 365 Crete earthquake occurred at about sunrise on 21 July 365 in the Eastern Mediterranean, with an assumed epicentre near Crete. Geologists today estimate the undersea earthquake to have been a moment magnitude 8.5 or higher. It caused widespread destruction in the central and southern Diocese of Macedonia (modern Greece), Africa Proconsularis (northern Libya), Egypt, Cyprus, Sicily, and Hispania (Spain). On Crete, nearly all towns were destroyed. The earthquake was followed by a tsunami which devastated the southern and eastern coasts of the Mediterranean, particularly Libya, Alexandria, and the Nile Delta, killing thousands and hurling ships inland.Ammianus Marcellinus"Res Gestae" 26.10.15–19 The quake left a deep impression on the late antique mind, and numerous writers of the time referred to the event in their works. Geological evidence Recent (2001) geological studies view the 365 Crete earthquake in connection with a clustering of major seismic activity in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kathleen Kenyon
Dame Kathleen Mary Kenyon, (5 January 1906 – 24 August 1978) was a British archaeologist of Neolithic culture in the Fertile Crescent. She led excavations of Tell es-Sultan, the site of ancient Jericho, from 1952 to 1958, and has been called one of the most influential archaeologists of the 20th century. She was Principal of St Hugh's College, Oxford, from 1962 to 1973 and studied herself at Somerville College, Oxford . Biography Kathleen Kenyon was born in London, England, in 1906. She was the eldest daughter of Sir Frederic Kenyon, biblical scholar and later director of the British Museum . Her grandfather was lawyer and Fellow of All Souls College, John Robert Kenyon, and her great-great-grandfather was the politician and lawyer Lloyd Kenyon, 1st Baron Kenyon. She grew up in Bloomsbury, London, in a house attached to the British Museum, with her mother, Amy Kenyon, and sister Nora Kenyon . Known for being hard-headed and stubborn, Kathleen grew up as a tomboy, fishing, c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tripolitania
Tripolitania ( ar, طرابلس '; ber, Ṭrables, script=Latn; from Vulgar Latin: , from la, Regio Tripolitana, from grc-gre, Τριπολιτάνια), historically known as the Tripoli region, is a historic region and former province of Libya. The region had been settled since antiquity, first coming to prominence as part of the Carthaginian empire. Following the defeat of Carthage in the Punic Wars, Ancient Rome organized the region (along with what is now modern day Tunisia and eastern Algeria), into a province known as Africa, and placed it under the administration of a proconsul. During the Diocletian reforms of the late 3rd century, all of North Africa was placed into the newly created Diocese of Africa, of which Tripolitania was a constituent province. After the Fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century, Tripolitania changed hands between the Vandals and the Byzantine Empire, until it was taken during the Muslim conquest of the Maghreb in the 8th cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Ward-Perkins
John Bryan Ward-Perkins, (3 February 1912 – 28 May 1981) was a British Classical architectural historian and archaeologist, and director of the British School at Rome. Family and early life John Bryan Ward-Perkins was born on 3 February 1912 in Bromley, Kent, the eldest son of Bryan Ward-Perkins, a British civil servant in India, and Winifred Mary Hickman. He attended Winchester College and New College, Oxford, graduating in 1934. He was awarded the Craven travelling fellowship at Magdalen College, which he used to study archaeology in Great Britain and France. Career Ward-Perkins served as assistant under Sir R. E. Mortimer Wheeler (1890–1976) from 1936 to 1939 at the London Museum. There he wrote a catalogue of the museum's collection. During these years he was also involved in the excavation of a Roman villa near Welwyn Garden City. In 1939 he became chair of archaeology at the Royal University of Malta. During the Second World War, Ward-Perkins saw military servi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
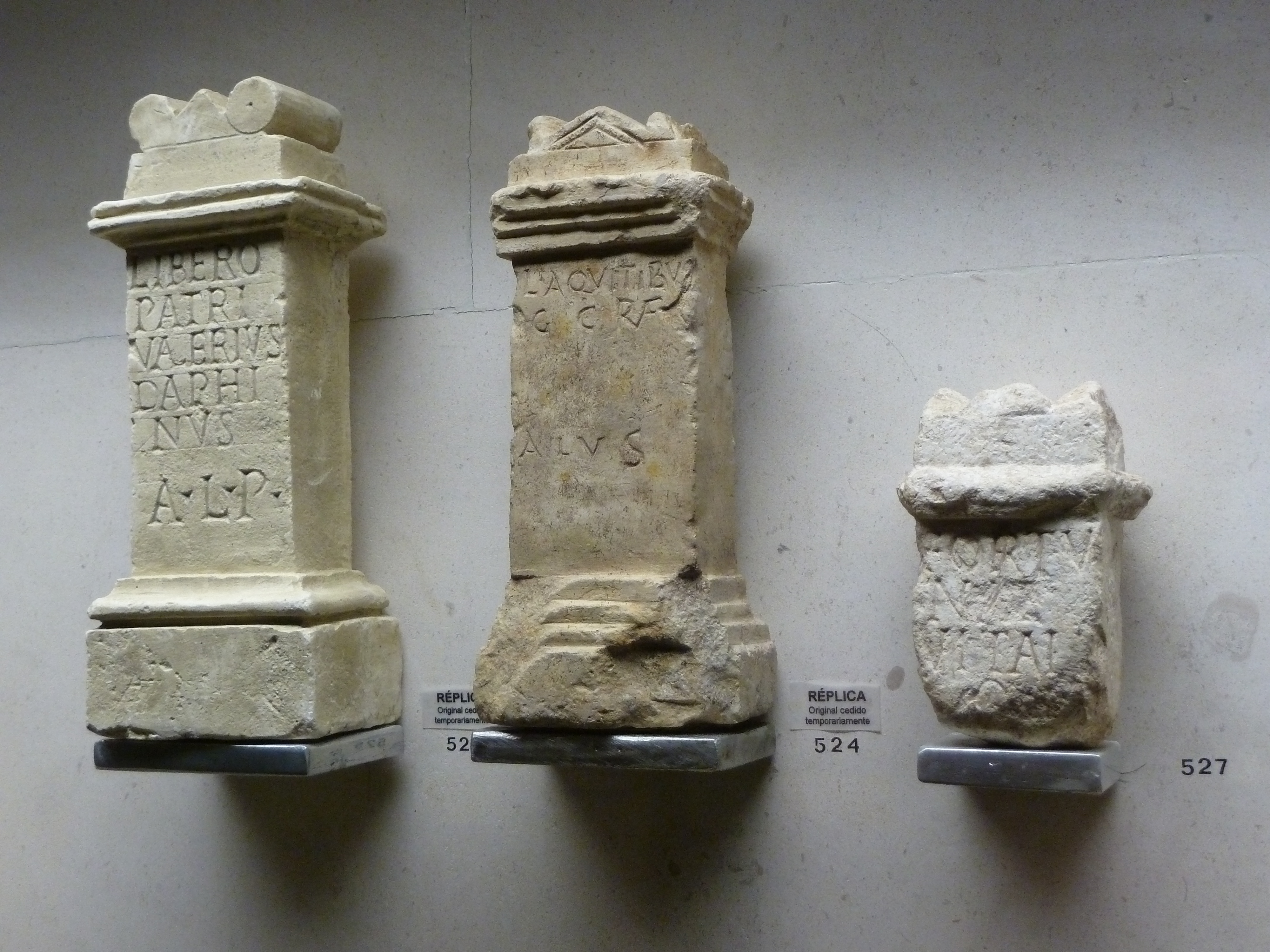
Liber
In Religion in ancient Rome, ancient Roman religion and Roman mythology, mythology, Liber ( , ; "the free one"), also known as Liber Pater ("the free Father"), was a god of viticulture and wine, male fertility and freedom. He was a patron deity of Rome's Plebeians, plebeians and was part of their Aventine Triad. His festival of Liberalia (March 17) became associated with free speech and the rights attached to coming of age. His cult and functions were increasingly associated with Romanised forms of the Greek Dionysus/Bacchus, whose mythology he came to share. Etymology The name ''Līber'' ('free') stems from Proto-Italic language, Proto-Italic ''*leuþero'', and ultimately from Proto-Indo-European language, Proto-Indo-European ''*h₁leudʰero'' ('belonging to the people', hence 'free'). Origins and establishment Before his official adoption as a Roman deity, Liber was companion to two different goddesses in two separate, archaic Italian fertility cults; Ceres (Roman mytho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_(8288918733).jpg)


