|
STS-111
STS-111 was a space shuttle mission to the International Space Station (ISS) flown by Space Shuttle ''Endeavour''. STS-111 resupplied the station and replaced the Expedition 4 crew with the Expedition 5 crew. It was launched on 5 June 2002, from Kennedy Space Center, Florida. Crew Mission highlights STS-111, in addition to providing supplies, rotated the crews aboard the International Space Station, exchanging the three Expedition 4 members (1 Russian, 2 American) for the three Expedition 5 members (2 Russian, 1 American). The Multi-Purpose Logistics Module (MPLM) carried experiment racks and three stowage and resupply racks to the station. The mission also installed a component of the Canadarm2 called the Mobile Base System (MBS) to the Mobile Transporter (MT) (which was installed during STS-110); This was the second component of the Canadian Mobile Servicing System, or MSS. This gave the mechanical arm the capability to "inchworm" from the U.S. Lab fixture to the MBS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Expedition 5
Expedition 5 was the fifth long-duration stay on the International Space Station (ISS). The crew, consisting of three people, remained in space for 184 days, 178 of which were spent aboard the ISS. Expedition 5 was a continuation of an uninterrupted human presence in space, as of November 2022, which was begun by Expedition 1 in 2000-2001. The crew of Expedition 5 launched to space aboard the Space Shuttle ''Endeavour'' aboard the STS-111 mission on 5 June 2002. Their tenure aboard the station, however, did not begin until they docked with the ISS two days later on 7 June. Crew Mission parameters *Perigee: 384 km *Apogee: 396 km *Inclination Orbital inclination measures the tilt of an object's orbit around a celestial body. It is expressed as the angle between a reference plane and the orbital plane or axis of direction of the orbiting object. For a satellite orbiting the Ea ...: 51.6° * Period: 92 min left, 250px, Peggy A. Whitson, Expedition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philippe Perrin
Philippe Perrin (Colonel, French Air Force) (born January 6, 1963) is a French test pilot, engineer and former CNES and European Space Agency astronaut. Background Perrin was born 6 January 1963, in Meknes, Morocco, but considers Avignon, Provence, to be his hometown. He entered the École polytechnique in 1982 and graduated in 1985. Perrin then received his Test Pilot Licence in 1993 from the École du personnel navigant d'essais et de réception (EPNER), the French Test Pilot School at Istres Air Force Base and received his Air Line Pilot Certificate in 1995. Military and flight career Prior to graduating from the École polytechnique, Perrin completed military duty in the French Navy, where he was trained in ship piloting and navigation, and spent six months at sea in the Indian Ocean. Following École polytechnique, he entered the French Air Force in 1985, was awarded his pilot's wings in 1986, and was assigned to the 33rd Reconnaissance Wing at Strasbourg Air Force ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Expedition 4
Expedition 4 was the fourth expedition to the International Space Station (7 December 2001 - 15 June 2002). Crew Mission parameters *Perigee: 384 km *Apogee: 396 km *Inclination: 51.6° *Period: 92 min Mission objectives The International Space Station expanded its science investigations, almost doubling the previous amount of experiments performed during the Expedition Four mission. The fourth resident crew launched on 5 December 2001 on board Space Shuttle Endeavour during mission STS-108. They became official station residents at 20:03 UTC on 7 December 2001, and remained on board until June 2002, when they landed on STS-111. An international crew of three were the fourth crew to live aboard the International Space Station. The team was led by Russian Yuri I. Onufrienko and joined by American crewmates Daniel W. Bursch and Carl E. Walz, both flight engineers. As a part of the STS-108 mission, Endeavour delivered the Expedition 4 crew to the station. They retur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sergei Treshchov
Sergey Yevgenyevich Treshchov (russian: Сергей Евгеньевич Трещёв; born 18 August 1958) is a former cosmonaut of the RSC Energia. He spent 184 days in space as a flight engineer of the International Space Station long duration Expedition 5 crew. During the mission he also conducted a spacewalk. Personal Treshchov was born in Volynsky District, in the Lipetsk Region of Russia. His father is Evgueniy Georgievich Treshchov, his mother is Nina Davydovna Treshchova. Treshchov and his wife, Elvira Viktorovna Treshchova have two sons, Dmitriy born in 1988 and Aleksey born in 1992. His hobbies include soccer, volleyball, ice hockey, hiking, tennis, music, photography, and video. Education In 1976 Treshchov graduated from technical school as an electric welder. In 1982 he graduated from the Moscow Power Institute specializing in "engineer-teacher of electrical power disciplines". Experience From 1982 to 1984, Treschov served as a group leader in an Air force re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STS-110
STS-110 was a Space Shuttle mission to the International Space Station (ISS) on 8–19 April 2002 flown by Space Shuttle ''Atlantis''. The main purpose was to install the S0 Truss segment, which forms the backbone of the truss structure on the station. Crew Mission highlights The main purpose of STS-110 was to attach the stainless steel S0 Truss segment to the International Space Station (ISS) to the Destiny Laboratory Module. It forms the backbone of the station to which the S1 and P1 truss segments were attached (on the following missions STS-112 and STS-113, respectively). STS-110 also delivered the Mobile Transporter (MT), which is an (1,950 lb) assembly that glides down rails on the station integrated trusses. The MT was designed and manufactured by Astro Aerospace in Carpinteria, CA. During the next shuttle mission, STS-111, the Mobile Base System (MBS) was mounted to the MT. This Mobile Servicing System (MSS) allows the Canadarm2 to travel down the len ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STS-112
STS-112 ( ISS assembly flight 9A) was an 11-day Space Shuttle mission to the International Space Station (ISS) flown by . Space Shuttle ''Atlantis'' was launched on 7 October 2002 at 19:45 UTC from the Kennedy Space Center's launch pad 39B to deliver the 28,000 pound Starboard 1 (S1) truss segment to the Space Station. Ending a 4.5-million-mile journey, ''Atlantis'' landed at 15:44 UTC on 18 October 2002 on runway 33 at the Kennedy Space Center's Shuttle Landing Facility. During the launch, the ET bipod ramp shed a chunk of foam that caused a dent ~4" wide and 3" deep into the metal SRB-ET Attach Ring near the bottom of the left Space Shuttle Solid Rocket Booster. Prior to the next mission ( STS-113), an upper-level decision was made at NASA to continue with launches as scheduled. The launch subsequent to that was the Space Shuttle ''Columbia'' disaster, the ill-fated STS-107. Space Shuttle ''Atlantis'' had been scheduled to visit the International Space Station (ISS) again on t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PMA-2
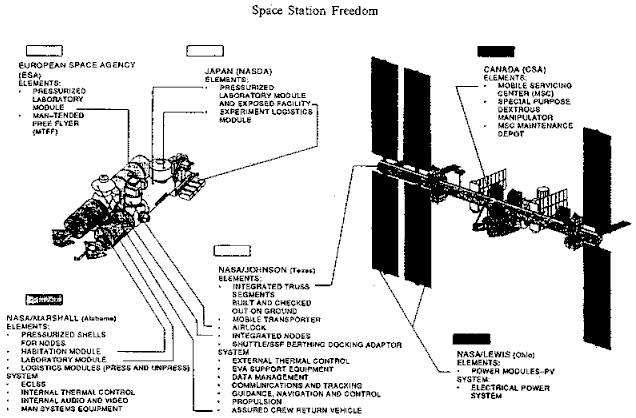
The Pressurized Mating Adapter (PMA) is a class of spacecraft adapters that convert the Common Berthing Mechanism (CBM) used on the US Orbital Segment to APAS-95 docking ports. There are three PMAs located on the International Space Station (ISS); the first two were launched with the ''Unity'' connecting module in 1998 aboard STS-88, and the third was launched in 2000 aboard STS-92. All three of the PMAs are now used to permanently connect parts of the ISS, so they are no longer available as docking ports for visiting spacecraft. Design/History Its origins lie in designs for the Pressurized Docking Mast, consisting of an off-axis frustoconical docking tunnel contained within a framework and a retractable coupling mechanism, later part of the Pressurized Berthing Adapter assembly that appeared in designs for Space Station Freedom 1987, and the reduced design referred to as 'Fred' 1991. After 1992-93 and the Russian integration into the International Space Station Alpha pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
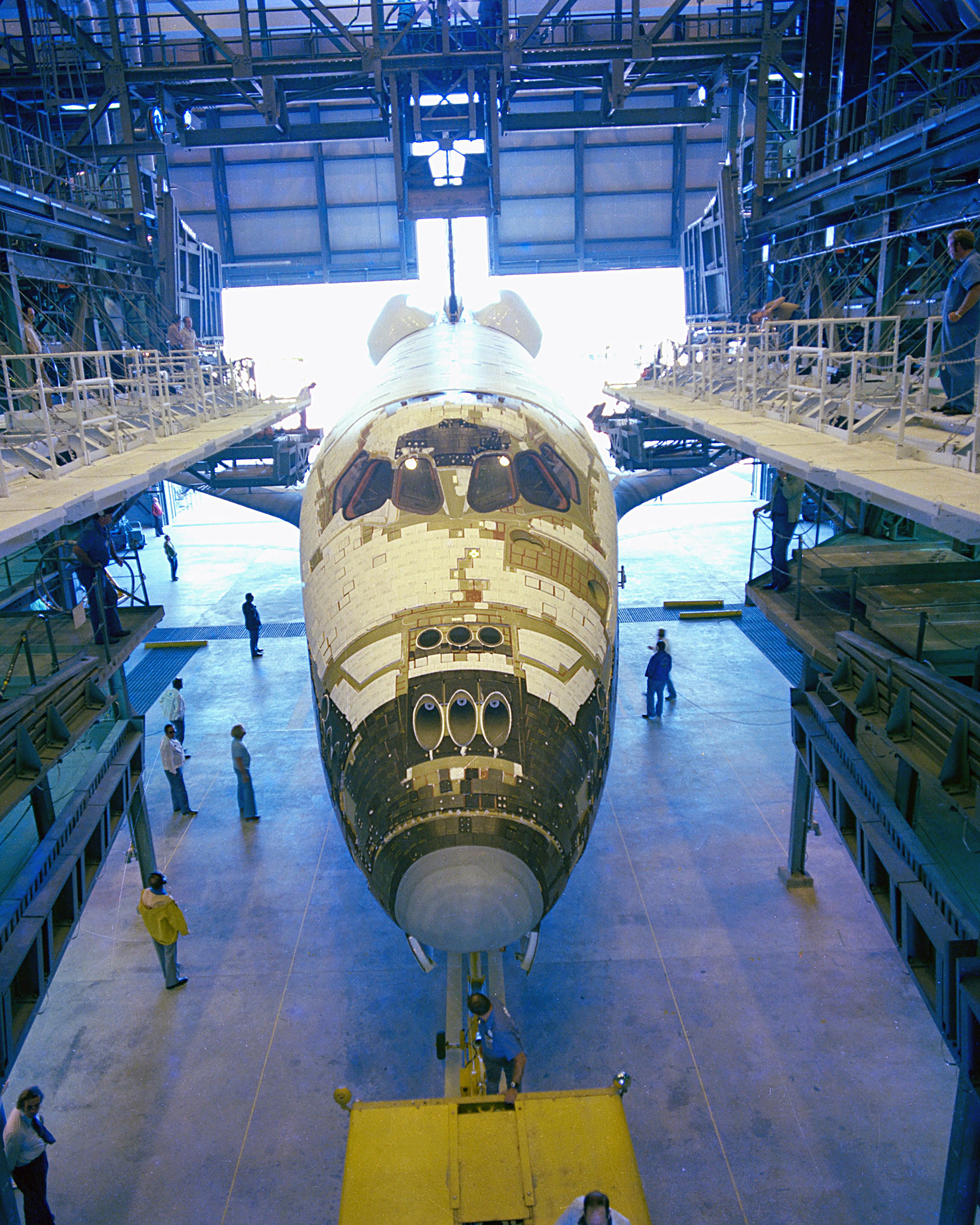
Space Shuttle Endeavour
Space Shuttle ''Endeavour'' ( Orbiter Vehicle Designation: OV-105) is a retired orbiter from NASA's Space Shuttle program and the fifth and final operational Shuttle built. It embarked on its first mission, STS-49, in May 1992 and its 25th and final mission, STS-134, in May 2011. STS-134 was expected to be the final mission of the Space Shuttle program, but with the authorization of STS-135 by the United States Congress, ''Atlantis'' became the last shuttle to fly. The United States Congress approved the construction of ''Endeavour'' in 1987 to replace the Space Shuttle ''Challenger'', which was destroyed in 1986. NASA chose, on cost grounds, to build much of ''Endeavour'' from spare parts rather than refitting the Space Shuttle ''Enterprise'', and used structural spares built during the construction of '' Discovery'' and ''Atlantis'' in its assembly. History Following the loss of ''Challenger'', in 1986 NASA was authorized to begin the procurement process for a repl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Low Earth Orbit
A low Earth orbit (LEO) is an orbit around Earth with a period of 128 minutes or less (making at least 11.25 orbits per day) and an eccentricity less than 0.25. Most of the artificial objects in outer space are in LEO, with an altitude never more than about one-third of the radius of Earth. The term ''LEO region'' is also used for the area of space below an altitude of (about one-third of Earth's radius). Objects in orbits that pass through this zone, even if they have an apogee further out or are sub-orbital, are carefully tracked since they present a collision risk to the many LEO satellites. All crewed space stations to date have been within LEO. From 1968 to 1972, the Apollo program's lunar missions sent humans beyond LEO. Since the end of the Apollo program, no human spaceflights have been beyond LEO. Defining characteristics A wide variety of sources define LEO in terms of altitude. The altitude of an object in an elliptic orbit can vary significantly along the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Shuttle Program
The Space Shuttle program was the fourth human spaceflight program carried out by the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), which accomplished routine transportation for Earth-to-orbit crew and cargo from 1981 to 2011. Its official name, Space Transportation System (STS), was taken from a 1969 plan for a system of reusable spacecraft of which it was the only item funded for development. It flew 135 missions and carried 355 astronauts from 16 countries, many on multiple trips. The Space Shuttle—composed of an orbiter launched with two reusable solid rocket boosters and a disposable external fuel tank—carried up to eight astronauts and up to of payload into low Earth orbit (LEO). When its mission was complete, the orbiter would reenter the Earth's atmosphere and land like a glider at either the Kennedy Space Center or Edwards Air Force Base. The Shuttle is the only winged crewed spacecraft to have achieved orbit and landing, and the first re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Transportation System
The Space Transportation System (STS), also known internally to NASA as the Integrated Program Plan (IPP), was a proposed system of reusable crewed space vehicles envisioned in 1969 to support extended operations beyond the Apollo program. (NASA appropriated the name for its Space Shuttle Program, the only component of the proposal to survive Congressional funding approval). The purpose of the system was two-fold: to reduce the cost of spaceflight by replacing the current method of launching capsules on expendable rockets with reusable spacecraft; and to support ambitious follow-on programs including permanent orbiting space stations around Earth and the Moon, and a human landing mission to Mars. In February 1969, President Richard Nixon appointed a Space Task Group headed by Vice President Spiro Agnew to recommend human space projects beyond Apollo. The group responded in September with the outline of the STS, and three different program levels of effort culminating with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Shuttle
The Space Shuttle is a retired, partially reusable low Earth orbital spacecraft system operated from 1981 to 2011 by the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) as part of the Space Shuttle program. Its official program name was Space Transportation System (STS), taken from a 1969 plan for a system of reusable spacecraft where it was the only item funded for development. The first ( STS-1) of four orbital test flights occurred in 1981, leading to operational flights (STS-5) beginning in 1982. Five complete Space Shuttle orbiter vehicles were built and flown on a total of 135 missions from 1981 to 2011. They launched from the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) in Florida. Operational missions launched numerous satellites, interplanetary probes, and the Hubble Space Telescope (HST), conducted science experiments in orbit, participated in the Shuttle-''Mir'' program with Russia, and participated in construction and servicing of the International Space Station (IS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_Radiator.jpg)

.jpg)
