|
Rotifer
The rotifers (, from the Latin , "wheel", and , "bearing"), commonly called wheel animals or wheel animalcules, make up a phylum (Rotifera ) of microscopic and near-microscopic pseudocoelomate animals. They were first described by Rev. John Harris in 1696, and other forms were described by Antonie van Leeuwenhoek in 1703. Most rotifers are around long (although their size can range from to over ), and are common in freshwater environments throughout the world with a few saltwater species. Some rotifers are free swimming and truly planktonic, others move by inchworming along a substrate, and some are sessile, living inside tubes or gelatinous holdfasts that are attached to a substrate. About 25 species are colonial (e.g., ''Sinantherina semibullata''), either sessile or planktonic. Rotifers are an important part of the freshwater zooplankton, being a major foodsource and with many species also contributing to the decomposition of soil organic matter. Most species of the rotif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bdelloidea
Bdelloidea (Greek ''βδέλλα'', ''bdella'', "leech") is a class of rotifers found in freshwater habitats all over the world. There are over 450 described species of bdelloid rotifers (or 'bdelloids'), distinguished from each other mainly on the basis of morphology. The main characteristics that distinguish bdelloids from related groups of rotifers are exclusively parthenogenetic reproduction and the ability to survive in dry, harsh environments by entering a state of desiccation-induced dormancy ( anhydrobiosis) at any life stage. They are often referred to as "ancient asexuals" due to their unique asexual history that spans back to over 25 million years ago through fossil evidence. Bdelloid rotifers are microscopic organisms, typically between 150 and 700 µm in length. Most are slightly too small to be seen with the naked eye, but appear as tiny white dots through even a weak hand lens, especially in bright light. In June 2021, biologists reported the restorati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cephalodella Vittata
''Cephalodella'' is a genus of rotifers in the family Notommatidae. '' Cephalodella vittata'' is a species endemic to Lake Baikal Lake Baikal (, russian: Oзеро Байкал, Ozero Baykal ); mn, Байгал нуур, Baigal nuur) is a rift lake in Russia. It is situated in southern Siberia, between the federal subjects of Irkutsk Oblast to the northwest and the Rep ....Hendrik Segers (2007). Annotated checklist of the rotifers (Phylum Rotifera), with notes on nomenclature, taxonomy Selected species * '' Cephalodella auritculata'' * '' Cephalodella catellina'' * '' Cephalodella elegans'' * '' Cephalodella forficata'' * '' Cephalodella forficula'' * '' Cephalodella gibba'' (Ehrenberg, 1830) * '' Cephalodella hoodi'' * '' Cephalodella marina'' Myers, 1924 * '' Cephalodella sterea'' * '' Cephalodella vittata'' References * O'Reilly, M. (2001). Rotifera, in: Costello, M.J. et al. (Ed.) (2001). European register of marine species: a check-list of the marine species ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
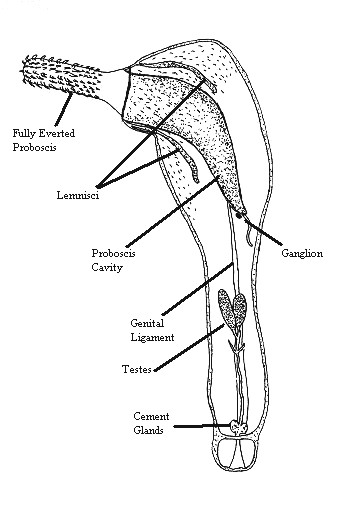
Acanthocephalan
Acanthocephala (Greek , ', thorn + , ', head) is a phylum of parasitic worms known as acanthocephalans, thorny-headed worms, or spiny-headed worms, characterized by the presence of an eversible proboscis, armed with spines, which it uses to pierce and hold the gut wall of its host. Acanthocephalans have complex life cycles, involving at least two hosts, which may include invertebrates, fish, amphibians, birds, and mammals. About 1420 species have been described. The Acanthocephala were thought to be a discrete phylum. Recent genome analysis has shown that they are descended from, and should be considered as, highly modified rotifers. This unified taxon is known as Syndermata. History The earliest recognisable description of Acanthocephala – a worm with a proboscis armed with hooks – was made by Italian author Francesco Redi (1684).Crompton 1985, p. 27 In 1771, Joseph Koelreuter proposed the name Acanthocephala. Philipp Ludwig Statius Müller independently calle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monogononta
Monogononta is a class of rotifers, found mostly in freshwater but also in soil and marine environments. They include both free-swimming and sessile forms. Monogononts generally have a reduced corona, and each individual has a single gonad, which gives the group its name. Males are generally smaller than females, and are produced only during certain times of the year, with females otherwise reproducing through parthenogenesis Parthenogenesis (; from the Greek grc, παρθένος, translit=parthénos, lit=virgin, label=none + grc, γένεσις, translit=génesis, lit=creation, label=none) is a natural form of asexual reproduction in which growth and developmen .... Their mastax is not designed for grinding. They produce mictic and amictic eggs. The class contains 1,570 species. References External links Rotifer World Catalog, by C.D. Jersabek & M.F. Leitner Eurotatoria Protostome classes {{rotifer-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seisonidae
Seisonidae is a family of rotifers, found on the gills of ''Nebalia'', a marine crustacean. Peculiar among rotifers, males and females are both present and equal in size. Males and females are similar with paired gonads. It is considered to have diverged from the other rotifers early on, and in one treatment is placed in a separate class Seisonoidea. They have a large and elongate body with reduced corona. Their muscular system is similar to that of other rotifers: they have longitudinal muscles as well as open annular muscles. Species Two genera with total three species belong to Seisonidae: * '' Paraseison'' Plate, 1887 ** '' Paraseison annulatus'' (Claus, 1876) — ectoparasite of ''Nebalia'' * ''Seison'' Grube, 1861 ** ''Seison nebaliae'' Grube, 1861 – commensal of ''Nebalia'' ** ''Seison africanus ''Seison'' is a genus of rotifers belonging to the family Seisonidae Seisonidae is a family of rotifers, found on the gills of '' Nebalia'', a marine crustacean. Peculia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brachionus Calyciflorus
''Brachionus calyciflorus'' is a planktonic rotifer species occurring in freshwater. It is commonly used as a model organism in toxicology, ecology and evolutionary biology. Its advantages include the small size and short generation time (average generation time of ''B. calyciflorus'' is around 2.2 days at 24 °C). Reproduction ''Brachionus calyciflorus'' normally reproduces by cyclical parthenogenesis Parthenogenesis (; from the Greek grc, παρθένος, translit=parthénos, lit=virgin, label=none + grc, γένεσις, translit=génesis, lit=creation, label=none) is a natural form of asexual reproduction in which growth and development .... Transitions to obligate parthenogenesis have been described. Obligate parthenogens were homozygous for a recessive allele, which caused inability to respond to the chemical signals that normally induce sexual reproduction in this species. Species complex Like the ''Brachionus plicatilis'' cryptic species complex ''Brachionus c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals consume organic material, breathe oxygen, are able to move, can reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage in which their body consists of a hollow sphere of cells, the blastula, during embryonic development. Over 1.5 million living animal species have been described—of which around 1 million are insects—but it has been estimated there are over 7 million animal species in total. Animals range in length from to . They have complex interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as zoology. Most living animal species are in Bilateria, a clade whose members have a bilaterally symmetric body plan. The Bilateria include the protostomes, containing animals such as nematodes, arthropods, flatworms, annelids and molluscs, and the deuterostomes, containing the echinoderms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lecane Bulla
''Lecane'' is a genus of rotifers belonging to the family Lecanidae. It is the only genus in the monotypic family Lecanidae and has a cosmopolitan distribution Species The following species are recognised in the genus ''Colurella'': *'' Lecane abanica'' *'' Lecane acanthinula'' *'' Lecane aculeata'' *'' Lecane acus'' *'' Lecane aeganea'' *'' Lecane affinis'' *'' Lecane agilis'' *'' Lecane althausi'' *'' Lecane amazonica'' *'' Lecane arcuata'' *'' Lecane arcula'' *'' Lecane armata'' *'' Lecane aspasia'' *''Lecane asymmetrica'' *'' Lecane baimaii'' *'' Lecane balatonica'' *'' Lecane batillifer'' *''Lecane bidactyla'' *''Lecane bifastigata'' *''Lecane bifurca'' *''Lecane blachei'' *''Lecane boettgeri'' *''Lecane boliviana'' *''Lecane boorali'' *''Lecane branchicola'' *''Lecane braumi'' *''Lecane braziliensis'' *'' Lecane broaensis'' *'' Lecane bryophila'' *''Lecane bulla'' *'' Lecane calcaria'' *'' Lecane candida'' *'' Lecane carpatica'' *'' Lecane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brachionus Plicatilis
''Brachionus plicatilis'' is a euryhaline (tolerate a wide range of salinity) rotifer in the family '' Brachionidae'', and is possibly the only commercially important rotifer, being raised in the aquaculture industry as food for fish larvae. It has a broad distribution in salt lakes around the world and has become a model system for studies in ecology and evolution. Reproduction ''Brachionus'' species can normally reproduce asexually and sexually (cyclical parthenogenesis). Sexual reproduction (termed Mixis) is usually induced when population density increases. Mixis in Brachionus plicatilis has been shown to be induced by a density-dependent chemical cue. Genome size Haploid '1C' genome sizes in the ''Brachionus plicatilis'' species complex range at least from 0.056 to 0.416 pg. The complete mitochondrial genome of B. plicatilis sensu stricto NH1L has been sequenced. Cryptic species complex Brachionus plicatilis strains have long been divided into ‘L-’ and ‘S-type ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eurotatoria
Eurotatoria is a superclass of rotifer The rotifers (, from the Latin , "wheel", and , "bearing"), commonly called wheel animals or wheel animalcules, make up a phylum (Rotifera ) of microscopic and near-microscopic pseudocoelomate animals. They were first described by Rev. John Ha ...s. References * Ridder M. De 1957a Onderzoekingen over brakwaterrotatorien. I. Assenede. (Biol. Jaarb. 195, 89-131, 11 tab.) * Ridder M. De 1957b Onderzoekingen over brakwaterrotatorien. II. Het Zwin to Knokke. (Natuurw. Tijdschr. 39, 109-126, pl I.) External links * Superclasses (biology) {{rotifer-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinantherina Semibullata
''Sinantherina'' is a genus of rotifers belonging to the family Flosculariidae. The genus has almost cosmopolitan distribution. Species: *''Sinantherina ariprepes'' *''Sinantherina procera'' *''Sinantherina semibullata'' *''Sinantherina socialis'' *''Sinantherina spinosa'' *''Sinantherina triglandularis ''Sinantherina'' is a genus of rotifers belonging to the family Flosculariidae. The genus has almost cosmopolitan distribution. Species: *''Sinantherina ariprepes'' *''Sinantherina procera'' *''Sinantherina semibullata'' *''Sinantherina soc ...'' References {{Taxonbar, from=Q4179687 Rotifers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plankton
Plankton are the diverse collection of organisms found in water (or air) that are unable to propel themselves against a current (or wind). The individual organisms constituting plankton are called plankters. In the ocean, they provide a crucial source of food to many small and large aquatic organisms, such as bivalves, fish and whales. Marine plankton include bacteria, archaea, algae, protozoa and drifting or floating animals that inhabit the saltwater of oceans and the brackish waters of estuaries. Freshwater plankton are similar to marine plankton, but are found in the freshwaters of lakes and rivers. Plankton are usually thought of as inhabiting water, but there are also airborne versions, the aeroplankton, that live part of their lives drifting in the atmosphere. These include plant spores, pollen and wind-scattered seeds, as well as microorganisms swept into the air from terrestrial dust storms and oceanic plankton swept into the air by sea spray. Though many plankton ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |