|
Rosenheim
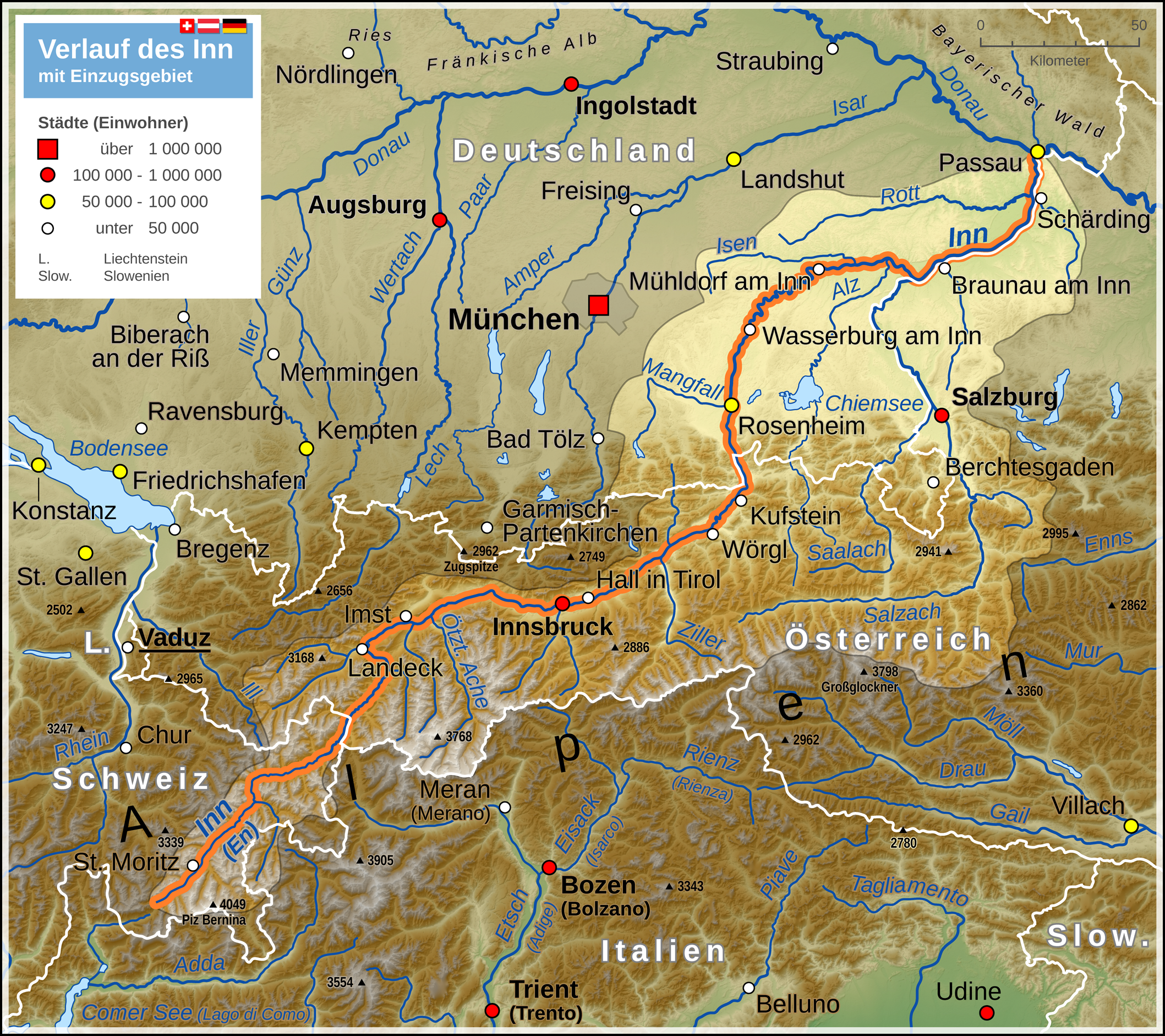
Rosenheim is a city in Bavaria, Germany. It is an independent city located in the centre of the district of Rosenheim (Upper Bavaria), and is also the seat of its administration. It is located on the west bank of the Inn at the confluence of the rivers Inn and Mangfall, in the Bavarian Alpine Foreland. It is the third largest city in Upper Bavaria with over 63,000 inhabitants. Rosenheim is the economic centre and the busiest place in the region. Geography The population of the actual city is approximately 60,000 inhabitants with up to 125,000 in the surrounding area. Rosenheim is situated in the Upper-Bavarian Alpine Foothills, above sea level and covers an area of . The capital of Bavaria, Munich, is North-West of Rosenheim. Rosenheim station is at the junction of the Munich–Rosenheim, the Rosenheim–Salzburg and the Munich–Innsbruck lines. The landscape around Rosenheim was formed during the last ice age from the advancement of the Inn Valley Glacier and later the R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rosenheim Heilig Geist
Rosenheim is a city in Bavaria, Germany. It is an independent city located in the centre of the district of Rosenheim (Upper Bavaria), and is also the seat of its administration. It is located on the west bank of the Inn at the confluence of the rivers Inn and Mangfall, in the Bavarian Alpine Foreland. It is the third largest city in Upper Bavaria with over 63,000 inhabitants. Rosenheim is the economic centre and the busiest place in the region. Geography The population of the actual city is approximately 60,000 inhabitants with up to 125,000 in the surrounding area. Rosenheim is situated in the Upper-Bavarian Alpine Foothills, above sea level and covers an area of . The capital of Bavaria, Munich, is North-West of Rosenheim. Rosenheim station is at the junction of the Munich–Rosenheim, the Rosenheim–Salzburg and the Munich–Innsbruck lines. The landscape around Rosenheim was formed during the last ice age from the advancement of the Inn Valley Glacier and later the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rosenheim–Salzburg Railway
The Rosenheim–Salzburg railway is a continuous double track and electrified main line railway almost entirely within the German state of Bavaria. It is an international transport corridor, linking to Salzburg in Austria. History Planning, treaty and Munich-Rosenheim-Salzburg Railway Society The first plan for a railway line between Rosenheim and Salzburg was in Friedrich List’s proposal in September 1828, which laid out as the main lines of the Bavarian network, a line from Bamberg via Nuremberg, Augsburg and Memmingen to Lindau, another from Kitzingen via Nuremberg and Augsburg to Munich and a third from Günzburg via Augsburg and Munich towards Austria. Simon Freiherr von Eichthal, a banker to the King of Bavaria, also called for a railway from Munich to Salzburg in 1835. On 5 January 1836, von Eichthal began a preliminary investigation of the building of the line. A messenger of the Bavarian government reported to the Austrian government on 7 April 1836 on the planned co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Munich–Rosenheim Railway
The Munich–Rosenheim railway is a 65 kilometre-long double-track main line of the German railways. It connects Munich Hauptbahnhof with Rosenheim station, where it connects with the Rosenheim–Salzburg railway, which connects with the line to Vienna at Salzburg, and the line to Kufstein, which continues to Innsbruck and the Brenner line to Italy. The line is part of the " Main line for Europe", connecting Paris with Bratislava and Budapest and the almost identical line 17 of Trans-European Transport Networks (TEN-T). It is part of the line 1 of TEN-T. It is electrified at 15 kV, 16.7 Hz. It was opened between Munich and Rosenheim in 1871. History Already in the 1860s, it was clear that the Mangfall Valley Railway (''Mangfalltalbahn''), which had been opened between 1854 and 1857, could no longer absorb the increase in traffic on the main lines towards Austria. Duplication of the Mangfall Valley Railway was not an option due to its twisty and hilly route. In addi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rosenheim Station
Rosenheim station (german: Bahnhof Rosenheim) is the main railway station in the city of Rosenheim in Bavaria, Germany. It is the seventh largest passenger station in Bavaria and an important railway hub between the Munich–Rosenheim railway line and the lines to Salzburg, Kufstein/Innsbruck and Mühldorf, as well as the Mangfall Valley Railway. Rosenheim is operated by DB Station&Service, a subsidiary of Deutsche Bahn AG, and is classified as a Category 2 station History A first station on the Rosenheim–Kufstein–Innsbruck line, promoted by industrialist Joseph Maffei and King Maximilian II of Bavaria, was opened on 31 October 1857. Located south of the city centre, it soon proved to be too small after the opening of the line to Salzburg in 1860 and the Austrian Brenner Railway in 1867. From 1873 onwards, a new station at the present site was built; it was inaugurated on 19 April 1876. After only 18 years of usage, the old station building was sold to the City of Ros ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rosenheim–Kufstein Railway
The Rosenheim–Kufstein railway (German: ''Bahnstrecke Rosenheim–Kufstein'') is a 32 kilometre-long double-track main line of the German railways. It connects the Munich–Rosenheim and the Rosenheim–Salzburg lines at Rosenheim with the line to Innsbruck, thus connecting Germany, Salzburg and eastern Austria with Innsbruck and the Brenner line to Italy and the Arlberg line to far western Austria. The line is part of the Line 1 of Trans-European Transport Networks (TEN-T). It is electrified at 15 kV, 16.7 Hz. History A treaty between Austria and Bavaria, signed on 21 June 1851, regulated the access of each state to the other in relation to the building of railways. As there was no direct rail link between Vienna and the Tyrol at that time, Bavaria agreed in Article 1 that it would build railways from Munich to the border at Salzburg and from Rosenheim to the border at Kufstein. Austria committed itself under Article 2 to build a railway from Salzburg to Bruck an der Mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rosenheim (district)
Rosenheim is a ''Landkreis'' (district) in the south of Bavaria, Germany. Neighboring districts are, clockwise from the west, Miesbach, Munich, Ebersberg, Mühldorf, and Traunstein, with the Austrian province Tirol across the southern border. The district entirely surrounds the city of Rosenheim, which is independently administered but hosts the district's administration; both the city and the district share the "RO" designation for their license plates. History The district was created in 1972 when the former districts Rosenheim, Bad Aibling, and parts of Wasserburg am Inn were merged. Geography The Rosenheim district is located in the foothills of the Alps, the Chiemgau. The landscape is dominated by moraines created by the Inn Glacier in the last glacial period, including many lakes. To the east of the district is the largest of these lakes, the Chiemsee. The main rivers in the district are the Inn and the Mangfall, which meet in the city of Rosenheim. Mountain range ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mangfall
The Mangfall is a river of Upper Bavaria, Germany. The Mangfall is the outflow of the Tegernsee lake and discharges in Rosenheim from the left into the Inn. It is long. Towns and villages on the Mangfall * Gmund am Tegernsee * Valley * Weyarn * Grub (district of Valley) * Feldkirchen-Westerham * Feldolling * Bruckmühl * (district of Bruckmühl) * (district of Bruckmühl) * Bad Aibling * Kolbermoor * Rosenheim See also *List of rivers of Bavaria A list of rivers of Bavaria, Germany: A * Aalbach * Abens * Ach * Afferbach *Affinger Bach *Ailsbach * Aisch * Aiterach *Alpbach * Alster * Altmühl * Alz *Amper * Anlauter * Arbach *Arbachgraben *Aschaff * Aschbach *Attel * Aubach, tributary of ... References External links bike trail along the MangfallFlux of the Mangfall in Rosenheim during the last 30 days {{Authority control Rivers of Bavaria Miesbach (district) Rosenheim (district) Rivers of Germany ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wasserburg Am Inn
Wasserburg am Inn (Central Bavarian: ''Wassabuag am Inn'') is a town in Rosenheim district in Upper Bavaria, Germany. The historic centre is a peninsula formed by the meandering river Inn. Many Medieval structures remain intact, giving the city a unique view. History The town was first mentioned in a document (now considered to be a fake) in 1137, when Hallgraf Engelbert moved his residence from the nearby castle Limburg to his "Wasserburg" (Water Castle). It is one of the most historic towns of Old Bavaria – somewhat older than Munich, continually fought over by the Bavarian nobility and, up to the 16th century, on an equal footing with larger cities. The privileges afforded by this enabled the salt trade to flourish right into the 19th century. At the junction of the main overland route with the main water route, Wasserburg became the most important trade centre with the Balkans, Austria and Italy, a means of attaining power and wealth for the shipping owners and merchants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inn Valley Glacier
The Inn Glacier (german: Inn-Gletscher), also called the Inn Valley Glacier (''Inntal-Gletscher''). was the ice age glacier of the Alpine river, the Inn (river), Inn. Originating in the Swiss Upper Engadine, Upper and Lower Engadine (in the present Canton (country subdivision), canton of Graubünden), it flowed through the state of Tyrol (state), Tyrol in Austria (occupying the present day Inn Valley). On German territory it pushed its ice front far into the Bavarian Alpine Foreland. The Inn Glacier attained its greatest thickness and extent during the Riss glaciation (Old moraines). The overwhelming part of the landforms seen today in the valley carved by the Inn Glacier date, however, to the last ice age, the Würm glaciation (Young moraines). Literature * Carl Troll, Troll, Carl; (1924) Der diluviale Inn-Chiemsee-Gletscher. Das geographische Bild eines typischen Alpenvorlandgletschers. External links Fischbacher Gletscherschliffi References [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simssee
Simssee is a lake in the Alpine foothills, Bavaria, Germany Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwee .... At an elevation of 470.1 metres, its surface area is 6.5 km² making it the largest lake in the Rosenheim district. The maximum depth of the lake is 22.5 m. It drains into the river Sims. The retention period of the Simssee is about one and a half years and its catchment area covers 59.51 km². It is the last remain of Lake Rosenheim, which stretched over the area at the end of the Würm glaciation. See also * List of lakes in Bavaria External links * Lakes of Bavaria Rosenheim (district) {{Rosenheimdistrict-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bavaria
Bavaria ( ; ), officially the Free State of Bavaria (german: Freistaat Bayern, link=no ), is a state in the south-east of Germany. With an area of , Bavaria is the largest German state by land area, comprising roughly a fifth of the total land area of Germany. With over 13 million inhabitants, it is second in population only to North Rhine-Westphalia, but due to its large size its population density is below the German average. Bavaria's main cities are Munich (its capital and largest city and also the third largest city in Germany), Nuremberg, and Augsburg. The history of Bavaria includes its earliest settlement by Iron Age Celtic tribes, followed by the conquests of the Roman Empire in the 1st century BC, when the territory was incorporated into the provinces of Raetia and Noricum. It became the Duchy of Bavaria (a stem duchy) in the 6th century AD following the collapse of the Western Roman Empire. It was later incorporated into the Holy Roman Empire, be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inn Valley
The Inn ( la, Aenus; rm, En) is a river in Switzerland, Austria and Germany. The river is long. It is a right tributary of the Danube and it is the third largest tributary of the Danube by discharge. The highest point of its drainage basin is the summit of Piz Bernina at . The Engadine, the valley of the En, is the only Swiss valley whose waters end up in the Black Sea (via the Danube). Etymology The name Inn is derived from the old Celtic words ''en'' and ''enios'', meaning ''water''. In a document of 1338, the river was named ''Wasser'' (German for water). The first written mention from the years 105 to 109 (Publii Corneli Taciti historiarium liber tertius) reads: "''... Sextilius Felix... ad occupandam ripam Aeni fluminis, quod Raetos Noricosque interfluit, missus...''" ("... Sextilius Felix was sent to capture the banks of the Inn, which flows between the Rhaetian people and the Noric people.") The river is also mentioned by other authors of the Roman Empire as ''Ainos'' (G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)