|
Rolf Bremmer
Rolf Hendrik Bremmer (born 13 August 1950, Zwolle) is a Dutch academic. He is professor of Old and Middle English, and extraordinary professor of Old Frisian, at Leiden University. Biography Rolf Bremmer's father, also named Rolf Hendrik Bremmer (1917–1995), was a theologian and preacher associated with the Reformed Churches in the Netherlands (Liberated) and a student of Klaas Schilder. He married Lucie Gera Arina Lindeboom (b. 1918) in 1943 in The Hague; she was the daughter of a Reformed preacher (Cornelis Lindeboom). Rolf Jr.'s older brother J.N. Bremmer is professor of church history at the University of Groningen. Bremmer received his master's degree in English language and literature from the University of Groningen in 1977. From 1976 to 1977 he studied at Oxford University as a Harting Student, with Anglo-Saxonists such as Bruce Mitchell, Tom Shippey, and J. M. Wallace-Hadrill. In 1986 he gained his PhD from Radboud University Nijmegen, with a dissertation on a late ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zwolle
Zwolle () is a city and municipality in the Northeastern Netherlands. It is the capital of the province of Overijssel and the province's second-largest municipality after Enschede with a population of 130,592 as of 1 December 2021. Zwolle is on the border with Gelderland, which follows the river IJssel, and is located about 50 km north east of Utrecht and 85 km south west of Groningen. The current Mayor of Zwolle is Lorenzo Brands. History Archaeological findings indicate that the area surrounding Zwolle has been inhabited for a long time. A woodhenge that was found in the Zwolle-Zuid suburb in 1993 was dated to the Bronze Age period. During the Roman era, the area was inhabited by Salian Franks. The modern city was founded around 800 CE by Frisian merchants and troops of Charlemagne. Previous spellings of its name include the identically pronounced ''Suolle'', which means "hill" (cf. the English cognate verb "to swell"). This refers to an incline in the landscape between ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radboud University Nijmegen
Radboud University (abbreviated as RU, nl, Radboud Universiteit , formerly ''Katholieke Universiteit Nijmegen'') is a public research university located in Nijmegen, the Netherlands. The university bears the name of Saint Radboud, a 9th century Dutch bishop who was known for his intellect and support of the underprivileged. Established in 1923, Radboud University has consistently been included in the top 150 of universities in the world by four major university ranking tables. As of 2020, it ranks 105th in the Shanghai Academic Ranking of World Universities. Internationally, RU is known for its strong research output. In 2020, 391 PhD degrees were awarded, and 8.396 scientific articles were published. To bolster the international exchange of academic knowledge, Radboud University joined the Guild of European Research-Intensive Universities in 2016. Among its alumni Radboud University counts 12 Spinoza Prize laureates and 1 Nobel Prize laureate, Sir Konstantin Novoselov, the di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alphabet Book
An alphabet book is a type of children's book giving basic instruction in an alphabet. Intended for young children, alphabet books commonly use pictures, simple language and alliteration to aid language learning. Alphabet books are published in several languages, and some distinguish the capitals and lower case letters in a given alphabet. Some alphabet books are intended for older audiences, using the simplicity of the genre as a device to convey humor or other concepts. Purposes Alphabet books introduce the sounds and letters of an ordered alphabet. As elementary educational tools, Alphabet books provide opportunities for: #Developing conversations and proficiency in oral language #Increasing phonemic awareness #Teaching phonics #Making text connections (Activating prior knowledge) #Predicting (Text talk) #Building vocabulary #Inferencing / drawing conclusions #Sequencing #Identifying elements of story structure #Recognizing point of view #Visualizing setting (Time, pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Notes And Queries
''Notes and Queries'', also styled ''Notes & Queries'', is a long-running quarterly scholarly journal that publishes short articles related to " English language and literature, lexicography, history, and scholarly antiquarianism".From the inner sleeve of all modern issues of ''Notes and Queries''. Its emphasis is on "the factual rather than the speculative". The journal has a long history, having been established in 1849 in London;''Notes and Queries'', Series 1, Volume 1, Nov 1849 - May 1850 via it is now published by |
The Heroic Age (journal)
''The Heroic Age: A Journal of Early Medieval Northwestern Europe'' is a peer-reviewed academic journal founded in 1998, with its first issue having been published during spring/summer 1999. The founder and the first editor-in-chief of the journal was Michelle Ziegler. The title of the journal, ''The Heroic Age,'' refers to the early medieval period, though there is certain variation in the definition of the period in focus: it is (or has been, in previous versions of their website, calls for papers, and other sources) defined as stretching "from the early 4th through 13th centuries", "from the beginning of the fourth century through the beginning of the thirteenth", "from the late fourth through eleventh centuries", "from 400-1100 AD", "approximately ..between 300 and 1200 CE", and "from the late Roman empire to the advent of the Norman empire". This variation is (partly, at least) accounted for in the Letter from the Editor in Issue 10 (May 2007) as related to changes in the edi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
De Volkskrant
''de Volkskrant'' (; ''The People's Paper'') is a Dutch daily morning newspaper. Founded in 1919, it has a nationwide circulation of about 250,000. Formerly a leading centre-left Catholic broadsheet, ''de Volkskrant'' today is a medium-sized centrist compact. Pieter Klok is the current editor-in-chief. History and profile ''De Volkskrant'' was founded in 1919 and has been a daily morning newspaper since 1921. Originally ''de Volkskrant'' was a Roman Catholic newspaper closely linked to the Catholic People's Party and the Catholic pillar. The paper temporarily ceased publication in 1941. On its re-founding in 1945, its office moved from Den Bosch to Amsterdam. It became a left-wing newspaper in the 1960s, but began softening its stance in 1980. On 23 August 2006 the ''Volkskrant'' published its 25,000th edition. In 1968, the ownership of De Volkskrant and Het Parool merged into a new parent, De Perscombinatie. Het Parool gained control due to the larger investment in the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beowulf
''Beowulf'' (; ang, Bēowulf ) is an Old English epic poem in the tradition of Germanic heroic legend consisting of 3,182 alliterative lines. It is one of the most important and most often translated works of Old English literature. The date of composition is a matter of contention among scholars; the only certain dating is for the manuscript, which was produced between 975 and 1025. Scholars call the anonymous author the "''Beowulf'' poet". The story is set in pagan Scandinavia in the 6th century. Beowulf, a hero of the Geats, comes to the aid of Hrothgar, the king of the Danes, whose mead hall in Heorot has been under attack by the monster Grendel. After Beowulf slays him, Grendel's mother attacks the hall and is then defeated. Victorious, Beowulf goes home to Geatland and becomes king of the Geats. Fifty years later, Beowulf defeats a dragon, but is mortally wounded in the battle. After his death, his attendants cremate his body and erect a tower on a headla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franciscus Junius (the Younger)
Franciscus Junius (29 January 1591 – 1677), also known as François du Jon, was a pioneer of Germanic philology. As a collector of ancient manuscripts, he published the first modern editions of a number of important texts. In addition, he wrote the first comprehensive overview of ancient writings on the visual arts, which became a cornerstone of classical art theories throughout Europe. Life Junius was born in Heidelberg. He was brought up at Leiden, Netherlands as his father, also called Franciscus Junius, was appointed professor of Hebrew at Leiden University in 1592. In 1602 his parents died, and Junius went to live with his future brother-in-law, the humanist scholar Gerhard Johann Vossius in Dordrecht. His attention was diverted from military to theological studies by the peace of 1609 between Spain and the Netherlands, and he studied theology at Leiden and Middelburg. In 1617, he became a pastor at Hillegersberg, near Rotterdam. He resigned this position the follow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frisian Literature
Frisian literature is works written in the Frisian languages, including that of West Frisian spoken in the province of Friesland in the Netherlands, from which most texts were produced or have survived. The first texts written in Frisian emerge around the 13th century. Medieval and early modern periods Texts written in Frisian first appear in manuscripts from the late medieval period. Records of these, however, are fairly scarce and would generally not constitute literature, even if they did show some poetic merit. In 1498, Dutch became the official language in Friesland for all purposes of writing but Frisian would survive as a spoken language among the common people. Through the Renaissance, some authors would consciously attempt to preserve their language in short written works. Middle Frisian would generally be considered to begin around this time in the mid-16th century. The greatest impact came from the seventeenth-century schoolteacher from Bolsward, Gysbert Japiks, whos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
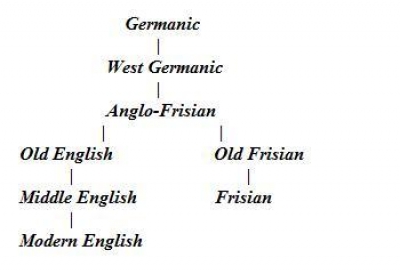
Frisian Languages
The Frisian (, ) languages are a closely related group of West Germanic languages, spoken by about 500,000 Frisian people, who live on the southern fringes of the North Sea in the Netherlands and Germany. The Frisian languages are the closest living language group to the Anglic languages; the two groups make up the Anglo-Frisian languages group and together with the Low German dialects these form the North Sea Germanic languages. However, modern English and Frisian are not mutually intelligible, nor are Frisian languages intelligible among themselves, owing to independent linguistic innovations and foreign influences. There are three different Frisian branches, which are usually called the Frisian languages, despite the fact that their so-called dialects are often not mutually intelligible even within these branches. These branches are: West Frisian, which is by far the most spoken of the three and is an official language in the Dutch province of Friesland, where it is spoke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle English Literature
The term Middle English literature refers to the literature written in the form of the English language known as Middle English, from the late 12th century until the 1470s. During this time the Chancery Standard, a form of London-based English became widespread and the printing press regularized the language. Between the 1470s and the middle of the following century there was a transition to early Modern English. In literary terms, the characteristics of the literary works written did not change radically until the effects of the Renaissance and Reformed Christianity became more apparent in the reign of King Henry VIII. There are three main categories of Middle English literature, religious, courtly love, and Arthurian, though much of Geoffrey Chaucer's work stands outside these. Among the many religious works are those in the Katherine Group and the writings of Julian of Norwich and Richard Rolle. After the Norman conquest of England, Law French became the standard language ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle English Language
Middle English (abbreviated to ME) is a form of the English language that was spoken after the Norman conquest of 1066, until the late 15th century. The English language underwent distinct variations and developments following the Old English period. Scholarly opinion varies, but the ''Oxford English Dictionary'' specifies the period when Middle English was spoken as being from 1150 to 1500. This stage of the development of the English language roughly followed the High to the Late Middle Ages. Middle English saw significant changes to its vocabulary, grammar, pronunciation, and orthography. Writing conventions during the Middle English period varied widely. Examples of writing from this period that have survived show extensive regional variation. The more standardized Old English language became fragmented, localized, and was, for the most part, being improvised. By the end of the period (about 1470) and aided by the invention of the printing press by Johannes Gutenberg in 143 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)
