|
Residential Community
A residential community is a community, usually a small town or city, that is composed mostly of residents, as opposed to commercial businesses and/or industrial facilities, all three of which are considered to be the three main types of occupants of the typical community. Residential communities are typically communities that help support more commercial or industrial communities with consumers and workers. That phenomenon is probably because some people prefer not to live in an urban or industrial area, but rather a suburban or rural setting. For that reason, they are also called dormitory towns, bedroom communities, or commuter towns. An example of a residential community would include a small town or city outside a larger city or a large town located near a smaller but more commercially- or industrially-centered town or city, for instance Taitou in Gaocun, Wuqing, Tianjin, China. China In the People's Republic of China, a community (), also called residential ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
China (other)
China, officially the People's Republic of China, is a country in East Asia. China may also refer to: Places China-related regions, polities, and concepts * Dynasties in Chinese history, the historical dynasties that ruled and represented China * Greater China, a geographical region encompassing mainland China, Hong Kong, Macao, and Taiwan * Mainland China, the geographical territory controlled by the People's Republic of China, excluding the special administrative regions of Hong Kong and Macao, and territories controlled by the Republic of China * Taiwan, officially the ''Republic of China'' * Free area of the Republic of China, the geographical territory under the ''de facto'' control of the Republic of China, including Taiwan, Penghu, Kinmen, Matsu, and various other minor islands * Republic of China (1912–1949), a sovereign state based in Mainland China prior to its government's relocation to Taiwan * China proper, also called "Inner China" or the "Eighteen Provinces", ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Commercial Press
The Commercial Press () is the first modern publishing organisation in China. History In 1897, 26-year-old Xia Ruifang and three of his friends (including the Bao brothers Bao Xian'en and Bao Xianchang) founded The Commercial Press in Shanghai. All four were Protestant Christians who received their training at the American Presbyterian Mission Press. The group soon received financial backing and began publishing books such as Bibles. In 1914, Xia attempted to buy out a Japanese company that had invested in The Commercial Press. Four days later he was assassinated. There was much speculation as to who was behind the assassination; no one was ever arrested for the crime. From 1903 Zhang Yuanji (张元济) (1867-1959), reacting to China's moves towards a new curriculum, created a number of textbook and translation series, and from 1904 and in subsequent years he launched popular periodicals, such as ''Dongfang dazhi'' (Eastern Miscellany)(1904), ''Jiaoyu zazhi'' (The Chinese E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Habitats
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, and language. Humans are highly social and tend to live in complex social structures composed of many cooperating and competing groups, from families and kinship networks to political states. Social interactions between humans have established a wide variety of values, social norms, and rituals, which bolster human society. Its intelligence and its desire to understand and influence the environment and to explain and manipulate phenomena have motivated humanity's development of science, philosophy, mythology, religion, and other fields of study. Although some scientists equate the term ''humans'' with all members of the genus ''Homo'', in common usage, it generally refers to ''Homo sapiens'', the only extant member. Anatomically mode ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Society Of China
Chinese culture () is one of the world's oldest cultures, originating thousands of years ago. The culture prevails across a large geographical region in East Asia and is extremely diverse and varying, with customs and traditions varying greatly between provinces, cities, and even towns as well. The terms 'China' and the geographical landmass of 'China' have shifted across the centuries, with the last name being the Great Qing before the name 'China' became commonplace in modernity. Chinese civilization is historically considered a dominant culture of East Asia. With China being one of the earliest ancient civilizations, Chinese culture exerts profound influence on the philosophy, virtue, etiquette, and traditions of Asia. Chinese characters, ceramics, architecture, music, dance, literature, martial arts, cuisine, visual arts, philosophy, business etiquette, religion, politics, and history have had global influence, while its traditions and festivals are celebrated, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microdistrict
Microdistrict, or microraion (russian: микрорайо́н, ''mikrorajón''), is a residential complex—a primary structural element of the residential area construction in the Soviet Union and in some post-Soviet and former Socialist states. Residential districts in most of the cities and towns in Russia and the republics of the former Soviet Union were built in accordance with this concept. According to the Construction Rules and Regulations of the Soviet Union, a typical microdistrict covered the area of 10–60 hectares (30–160 acres), up to but not exceeding 80 hectares (200 acres) in some cases, and comprised residential dwellings (usually multi-story apartment buildings) and public service buildings. As a general rule, major motor roads, greenways, and natural obstacles served as boundaries between microdistricts, allowing an overall reduction in city road construction and maintenance costs and emphasizing public transportation. Major motor r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Age-restricted Community
An age-restricted community is a residential community, often gated, that legally discriminates on the basis of age to limit residency to a majority fraction of older individuals—typically 80% over a set age. The minimum age is frequently set at 55 years old, but it can vary. These communities are set up to accommodate older individuals who would like to live in an area without the perceived problems of having children around. In most cases a younger spouse or significant other is permitted to live in the community as long as one member meets the minimum age requirement. Age-qualified communities, also known as 55+ communities, active adult communities, lifestyle communities, or retirement communities, are often planned communities that offer homes and community features that are attractive to 55+ adults. These might include a clubhouse or lifestyle center with a good many activities, sometimes with indoor and outdoor swimming pools, exercise facilities, craft rooms, demonstra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Administrative Divisions Of China
The administrative divisions of China have consisted of several levels since ancient times, due to China's large population and geographical area. The constitution of China provides for three levels of government. However in practice, there are five levels of local government; the provincial (province, autonomous region, municipality, and special administrative region), prefecture, county, township, and village. Since the 17th century, provincial boundaries in China have remained largely static. Major changes since then have been the reorganisation of provinces in the northeast after the establishment of the People's Republic of China and the formation of autonomous regions, based on Soviet ethnic policies. The provinces serve an important cultural role in China, as people tend to identify with their native province. Levels The Constitution of China provides for three levels: the provincial, the county level, and the township level. However, in practice, there are four leve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Danwei
A work unit or ''danwei'' () is the name given to a place of employment in the People's Republic of China. The term ''danwei'' remains in use today, as people still use it to refer to their workplace. However, it is more appropriate to use ''danwei'' to refer to a place of employment during the period when the Chinese economy was not as developed and more heavily reliant on welfare for access to long-term urban workers or when used in the context of state-owned enterprises. Prior to Deng Xiaoping's economic reforms, a work unit acted as the first step of a multi-tiered hierarchy linking each individual with the central Communist Party infrastructure. Work units were the principal method of implementing party policy. The work unit provided lifetime employment and extensive socioeconomic welfare -- "a significant feature of socialism and a historic right won through the Chinese Revolution." Danwei system Institutions such as industrial factories, schools and hospitals, and govern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
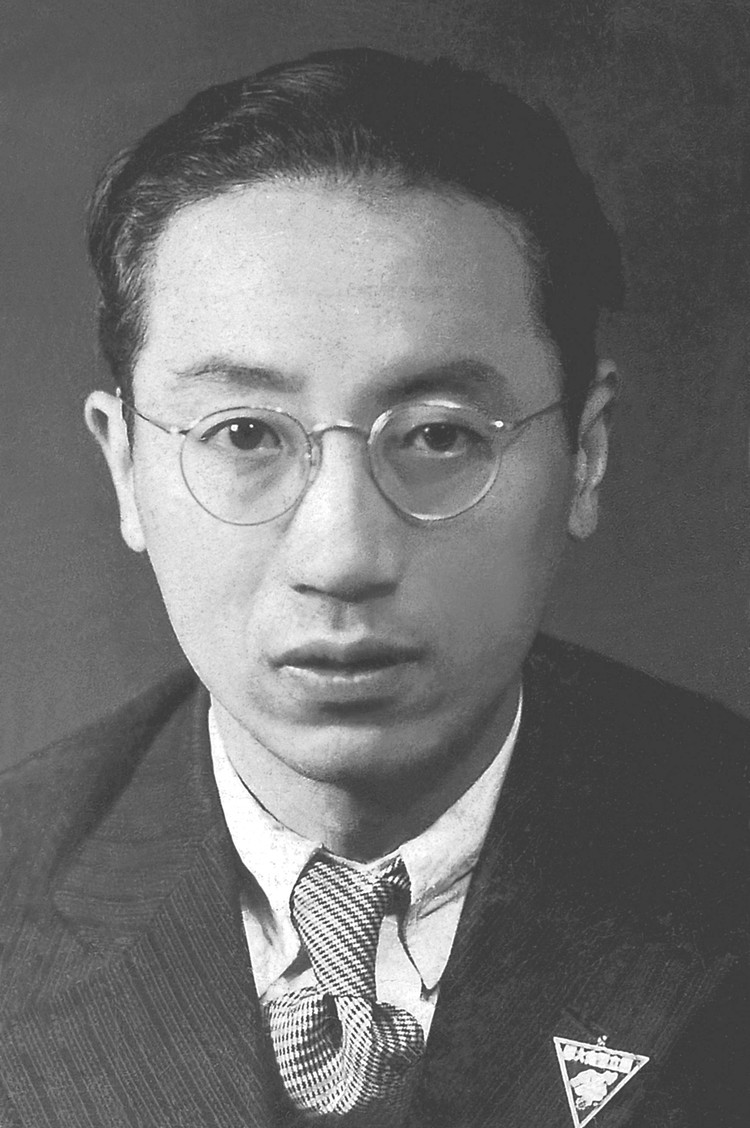
Fei Xiaotong
Fei Xiaotong or Fei Hsiao-tung (November 2, 1910 – April 24, 2005) was a Chinese anthropologist and sociologist. He was a pioneering researcher and professor of sociology and anthropology; he was also noted for his studies in the study of China's ethnic groups as well as a social activist. Starting in the late 1930s, he and his colleagues established Chinese sociology and his works were instrumental in laying a foundation for the development of sociological and anthropological studies in China, as well as in introducing social and cultural phenomena of China to the international community. His last post before his death in 2005 was as Professor of Sociology at Peking University. Early years Fei Xiaotong was born in Wujiang County of Jiangsu province in China on November 2, 1910. His world was one plagued with political corruption and abject poverty. He grew up in a gentry but yet not wealthy family. His father, Fei Pu'an () was educated in the Chinese classics, earned ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Anthropologist
Social anthropology is the study of patterns of behaviour in human societies and cultures. It is the dominant constituent of anthropology throughout the United Kingdom and much of Europe, where it is distinguished from cultural anthropology. In the United States, social anthropology is commonly subsumed within cultural anthropology or sociocultural anthropology. Comparison with cultural anthropology The term ''cultural'' anthropology is generally applied to ethnographic works that are holistic in spirit, are oriented to the ways in which culture affects individual experience, or aim to provide a rounded view of the knowledge, customs, and institutions of a people. ''Social'' anthropology is a term applied to ethnographic works that attempt to isolate a particular system of social relations such as those that comprise domestic life, economy, law, politics, or religion, give analytical priority to the organizational bases of social life, and attend to cultural phenomena as somewhat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Language
Chinese (, especially when referring to written Chinese) is a group of languages spoken natively by the ethnic Han Chinese majority and many minority ethnic groups in Greater China. About 1.3 billion people (or approximately 16% of the world's population) speak a variety of Chinese as their first language. Chinese languages form the Sinitic branch of the Sino-Tibetan languages family. The spoken varieties of Chinese are usually considered by native speakers to be variants of a single language. However, their lack of mutual intelligibility means they are sometimes considered separate languages in a family. Investigation of the historical relationships among the varieties of Chinese is ongoing. Currently, most classifications posit 7 to 13 main regional groups based on phonetic developments from Middle Chinese, of which the most spoken by far is Mandarin (with about 800 million speakers, or 66%), followed by Min (75 million, e.g. Southern Min), Wu (74 million, e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subdistricts Of The People's Republic Of China
A subdistrict ()' is one of the smaller administrative divisions of China. It is a form of township-level division which is typically part of a larger urban area, as opposed to a discrete town (zhèn, 镇) surrounded by rural areas, or a rural township (xiāng, 乡). In general, urban areas are divided into subdistricts and a subdistrict is sub-divided into several residential communities or neighbourhood A neighbourhood (British English, Irish English, Australian English and Canadian English) or neighborhood (American English; see spelling differences) is a geographically localised community within a larger city, town, suburb or rural a ...s as well as into villagers' groups (居民区/居住区, 小区/社区, 村民小组). The subdistrict's administrative agency is the subdistrict office ()"【街道办事处】 jiēdào bànshìchù 市辖区、不设区的市的人民政府派出机关。在上一级政府领导下,负责本辖区内的社区服务、经 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |