|
Proxemics
Proxemics is the study of human use of space and the effects that population density has on behaviour, communication, and social interaction. Proxemics is one among several subcategories in the study of nonverbal communication, including haptics (touch), kinesics (body movement), vocalics (paralanguage), and chronemics (structure of time). Edward T. Hall, the cultural anthropologist who coined the term in 1963, defined proxemics as "the interrelated observations and theories of humans use of space as a specialized elaboration of culture". In his foundational work on proxemics, ''The Hidden Dimension,'' Hall emphasized the impact of proxemic behavior (the use of space) on interpersonal communication. According to Hall, the study of proxemics is valuable in evaluating not only the way people interact with others in daily life, but also "the organization of space in heirhouses and buildings, and ultimately the layout of heirtowns". Proxemics remains a hidden component of interper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Personal Space
Proxemics is the study of human use of space and the effects that population density has on behaviour, communication, and social interaction. Proxemics is one among several subcategories in the study of nonverbal communication, including haptics (touch), kinesics (body movement), vocalics (paralanguage), and chronemics (structure of time). Edward T. Hall, the cultural anthropologist who coined the term in 1963, defined proxemics as "the interrelated observations and theories of humans use of space as a specialized elaboration of culture". In his foundational work on proxemics, ''The Hidden Dimension,'' Hall emphasized the impact of proxemic behavior (the use of space) on interpersonal communication. According to Hall, the study of proxemics is valuable in evaluating not only the way people interact with others in daily life, but also "the organization of space in heirhouses and buildings, and ultimately the layout of heirtowns". Proxemics remains a hidden component of interper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
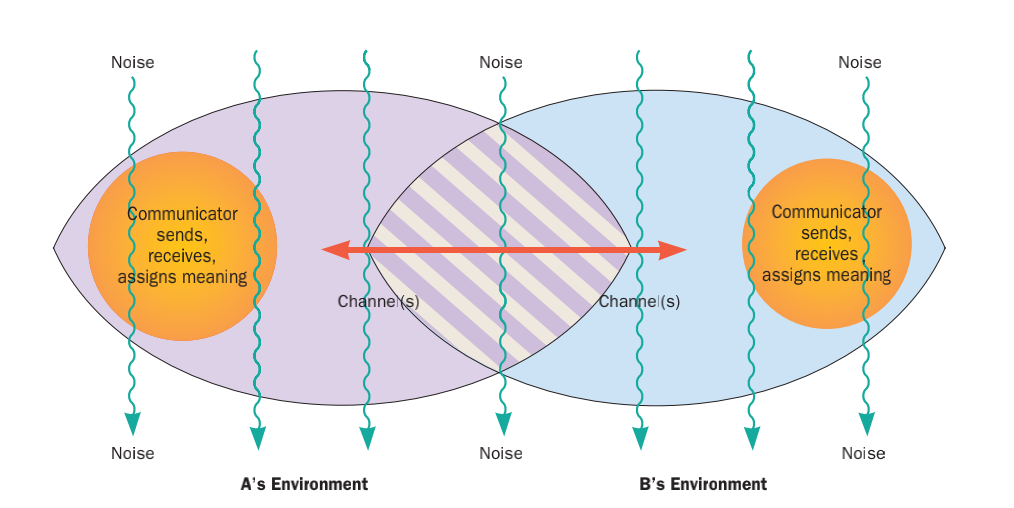
Nonverbal Communication
Nonverbal communication (NVC) is the transmission of messages or signals through a nonverbal platform such as eye contact, facial expressions, gestures, posture, and body language. It includes the use of social cues, kinesics, distance ( proxemics) and physical environments/appearance, of voice ( paralanguage) and of touch ( haptics). A signal has three different parts to it, including the basic signal, what the signal is trying to convey, and how it is interpreted. These signals that are transmitted to the receiver depend highly on the knowledge and empathy that this individual has. It can also include the use of time ( chronemics) and eye contact and the actions of looking while talking and listening, frequency of glances, patterns of fixation, pupil dilation, and blink rate ( oculesics). The study of nonverbal communication started in 1872 with the publication of ''The Expression of the Emotions in Man and Animals'' by Charles Darwin. Darwin began to study nonverbal commu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caressing
Physical intimacy is sensual proximity or touching. It is an act or reaction, such as an expression of feelings (including close friendship, platonic love, romantic love or sexual attraction), between people. Examples of physical intimacy include being inside someone's personal space, holding hands, hugging, kissing, caressing and sexual activity. Physical intimacy can often convey the real meaning or intention of an interaction in a way that accompanying speech cannot do. Physical intimacy can be exchanged between any people but as it is often used to communicate positive and intimate feelings, it most often occurs in people who have a preexisting relationship, whether familial, platonic or romantic, with romantic relationships having increased physical intimacy. Several forms of romantic touch have been noted including holding hands, hugging, kissing, cuddling, as well as caressing and massaging. Physical affection is highly correlated with overall relationship and partn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinesics
Kinesics is the interpretation of body motion communication such as facial expressions and gestures, nonverbal behavior related to movement of any part of the body or the body as a whole. The equivalent popular culture term is body language, a term Ray Birdwhistell, considered the founder of this area of study, neither used nor liked (on the grounds that what can be conveyed with the body does not meet the linguist's definition of language). Birdwhistell's work Kinesics was first used in 1952 by an anthropologist named Ray Birdwhistell. Birdwhistell wished to study how people communicate through posture, gesture, stance and movement. His ideas over several decades were synthesized and resulted in the book ''Kinesics and Context.'' Interest in kinesics specifically and nonverbal behaviour generally was popularized in the late 1960s and early 1970s by such popular mass-market (nonacademic) publications as ''How to Read a Person Like a Book''. Part of Birdwhistell's work involved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paralanguage
Paralanguage, also known as vocalics, is a component of meta-communication that may modify meaning, give nuanced meaning, or convey emotion, by using techniques such as prosody, pitch, volume, intonation, etc. It is sometimes defined as relating to nonphonemic properties only. Paralanguage may be expressed consciously or unconsciously. The study of paralanguage is known as paralinguistics and was invented by George L. Trager in the 1950s, while he was working at the Foreign Service Institute of the U.S. Department of State. His colleagues at the time included Henry Lee Smith, Charles F. Hockett (working with him on using descriptive linguistics as a model for paralanguage), Edward T. Hall developing proxemics, and Ray Birdwhistell developing kinesics. Trager published his conclusions in 1958, 1960 and 1961. His work has served as a basis for all later research, especially those investigating the relationship between paralanguage and culture (since paralanguage is le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interpersonal Communication
Interpersonal communication is an exchange of information between two or more people. It is also an area of research that seeks to understand how humans use verbal and nonverbal cues to accomplish a number of personal and relational goals. Interpersonal communication research addresses at least six categories of inquiry: 1) how humans adjust and adapt their verbal communication and nonverbal communication during face-to-face communication; 2) how messages are produced; 3) how uncertainty influences behavior and information-management strategies; 4) deceptive communication; 5) relational dialectics; and 6) social interactions that are mediated by technology. A large number of scholars have described their work as research into interpersonal communication. There is considerable variety in how this area of study is conceptually and operationally defined.Knapp & Daly, 2011) Researchers in interpersonal communication come from many different research paradigms and theoretical tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Space
A social space is physical or virtual space such as a social center, online social media, or other gathering place where people gather and interact. Some social spaces such as town squares or parks are public places; others such as pubs, websites, or shopping malls are privately owned and regulated. Henri Lefebvre emphasised that in human society all 'space is social: it involves assigning more or less appropriated places to social relations....social space has thus always been a social product'. Social space becomes thereby a metaphor for the very experience of social life - 'society experienced alternatively as a deterministic environment or force (''milieu'') and as our very element or beneficent shell (''ambience'')'. In this sense 'social space spans the dichotomy between "public" and "private" space...is also linked to subjective and phenomenological space'. History Émile Durkheim coined the term ''social space''. Maximilien Sorre and Paul-Henry Chombart de Lauwe fur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael Graziano
Michael Steven Anthony Graziano (born May 22, 1967) is an American scientist and novelist who is currently a professor of Psychology and Neuroscience at Princeton University. His scientific research focuses on the brain basis of awareness. He has proposed the "attention schema" theory, an explanation of how, and for what adaptive advantage, brains attribute the property of awareness to themselves. His previous work focused on how the |
Vocal Effort
The human voice consists of sound made by a human being using the vocal tract, including talking, singing, laughing, crying, screaming, shouting, humming or yelling. The human voice frequency is specifically a part of human sound production in which the vocal folds (vocal cords) are the primary sound source. (Other sound production mechanisms produced from the same general area of the body involve the production of unvoiced consonants, clicks, whistling and whispering.) Generally speaking, the mechanism for generating the human voice can be subdivided into three parts; the lungs, the vocal folds within the larynx (voice box), and the articulators. The lungs, the "pump" must produce adequate airflow and air pressure to vibrate vocal folds. The vocal folds (vocal cords) then vibrate to use airflow from the lungs to create audible pulses that form the laryngeal sound source. The muscles of the larynx adjust the length and tension of the vocal folds to 'fine-tune' pitch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amygdala
The amygdala (; plural: amygdalae or amygdalas; also '; Latin from Greek, , ', 'almond', 'tonsil') is one of two almond-shaped clusters of nuclei located deep and medially within the temporal lobes of the brain's cerebrum in complex vertebrates, including humans. Shown to perform a primary role in the processing of memory, decision making, and emotional responses (including fear, anxiety, and aggression), the amygdalae are considered part of the limbic system. The term "amygdala" was first introduced by Karl Friedrich Burdach in 1822. Structure The regions described as amygdala nuclei encompass several structures of the cerebrum with distinct connectional and functional characteristics in humans and other animals. Among these nuclei are the basolateral complex, the cortical nucleus, the medial nucleus, the central nucleus, and the intercalated cell clusters. The basolateral complex can be further subdivided into the lateral, the basal, and the accessory basal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Odour
An odor (American English) or odour (Commonwealth English; see spelling differences) is caused by one or more volatilized chemical compounds that are generally found in low concentrations that humans and animals can perceive via their sense of smell. An odor is also called a "smell" or a "scent", which can refer to either a pleasant or an unpleasant odor. While "odor" and "smell" can refer to pleasant and unpleasant odors, the terms "scent", "aroma", and "fragrance" are usually reserved for pleasant-smelling odors and are frequently used in the food and cosmetic industry to describe floral scents or to refer to perfumes. Physiology of smell Sense of smell The perception of odors, or sense of smell, is mediated by the olfactory nerve. The olfactory receptor (OR) cells are neurons present in the olfactory epithelium, which is a small patch of tissue at the back of the nasal cavity. There are millions of olfactory receptor neurons that act as sensory signaling cells. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |