|
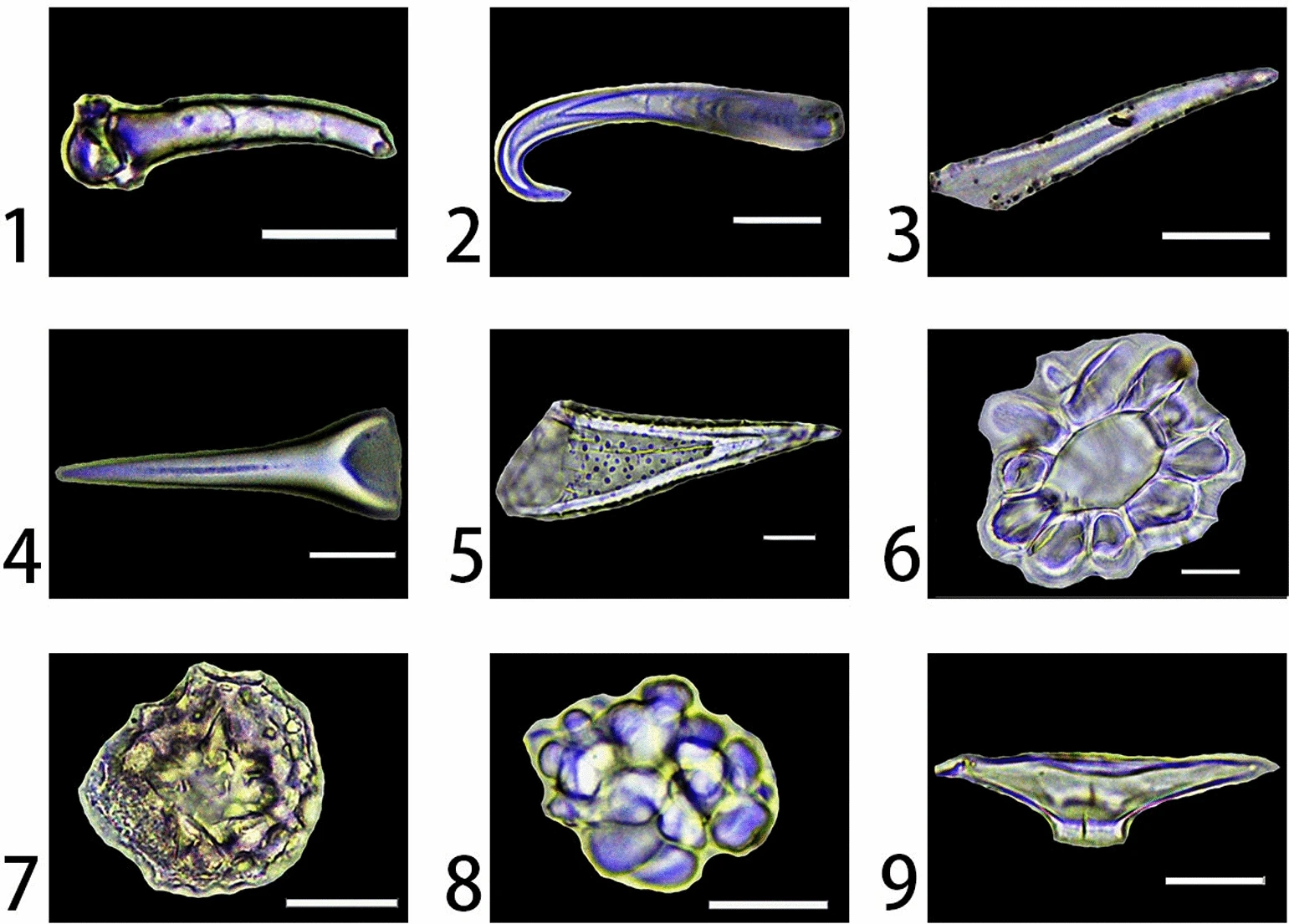
Phytoliths
Phytoliths (from Greek, "plant stone") are rigid, microscopic structures made of silica, found in some plant tissues and persisting after the decay of the plant. These plants take up silica from the soil, whereupon it is deposited within different intracellular and extracellular structures of the plant. Phytoliths come in varying shapes and sizes. Although some use "phytolith" to refer to all mineral secretions by plants, it more commonly refers to siliceous plant remains. In contrast, mineralized calcium secretions in cacti are composed of calcium oxalates.Piperno, Dolores R. (2006). Phytoliths: A Comprehensive Guide for Archaeologists and Paleoecologists. AltaMira Press . The silica is absorbed in the form of monosilicic acid (Si(OH)4), and is carried by the plant's vascular system to the cell walls, cell lumen, and intercellular spaces. Depending on the plant taxa and soil condition, absorbed silica can range from 0.1% to 10% of the plant's total dry weight. When deposited, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthosilicic Acid
Orthosilicic acid () is an inorganic compound with the formula . Although rarely observed, it is the key compound of silica and silicates and the Precursor (chemistry), precursor to other silicic acids . Silicic acids play important roles in biomineralization and technology.N. N. Greenwood, A. Earnshaw, ''Chemistry of the Elements'', 2nd ed., Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford, UK, 1997. Isolation Typically orthosilicic acid is assumed to be a product of the hydrolysis of the ortho esters , as is practiced in sol-gel syntheses. These conditions are however too vigorous to allow isolation of the parent acid. Orthosilicic acid can be produced by Pd-catalyzed hydrogenolysis of tetrabenzoxysilicon: : The acid was crystallized from a solution of dimethylacetamide and tetrabutylammonium chloride. As established by X-ray crystallography, the chloride anions interact with the acid via hydrogen bonds. Otherwise, the structure consists of the expected tetrahedral silicon center. React ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pittosporum
''Pittosporum'' ( or ) is a genus of about 200 species of flowering plants in the family Pittosporaceae. The genus is probably Gondwanan in origin; its present range extends from Australasia, Oceania, eastern Asia and some parts of Africa. '' Citriobatus'' can be included here, but might be a distinct (though closely related) genus. They are commonly known as pittosporums or, more ambiguously, cheesewoods. The species are trees and shrubs growing to 2–30 m tall. The leaves are spirally arranged or whorled, simple, with an entire or waved (rarely lobed) margin. The flowers are produced singly or in umbels or corymbs, each flower with five sepals and five petals; they are often sweetly scented. The fruit is a woody seed capsule, which bursts on ripening to release the numerous seeds. The seeds are coated with a sticky resinous substance. The genus is named after their sticky seeds, from the Greek meaning "pitch-seed". Tarata (''P. eugenioides'') and kohuhu (''P. tenuifolium'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annual Reviews (publisher)
Annual Reviews is an independent, non-profit academic publishing company based in San Mateo, California. As of 2021, it publishes 51 journals of review articles and ''Knowable Magazine'', covering the fields of life, biomedical, physical, and social sciences. Review articles are usually “peer-invited” solicited submissions, often planned one to two years in advance, which go through a peer-review process. The organizational structure has three levels: a volunteer board of directors, editorial committees of experts for each journal, and paid employees. Annual Reviews' stated mission is to synthesize and integrate knowledge "for the progress of science and the benefit of society". The first Annual Reviews journal, the ''Annual Review of Biochemistry'', was published in 1932 under the editorship of Stanford University chemist J. Murray Luck, who wanted to create a resource that provided critical reviews on contemporary research. The second journal was added in 1939. By ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Darwin
Charles Robert Darwin ( ; 12 February 1809 – 19 April 1882) was an English naturalist, geologist, and biologist, widely known for his contributions to evolutionary biology. His proposition that all species of life have descended from a common ancestor is now generally accepted and considered a fundamental concept in science. In a joint publication with Alfred Russel Wallace, he introduced his scientific theory that this branching pattern of evolution resulted from a process he called natural selection, in which the struggle for existence has a similar effect to the artificial selection involved in selective breeding. Darwin has been described as one of the most influential figures in human history and was honoured by burial in Westminster Abbey. Darwin's early interest in nature led him to neglect his medical education at the University of Edinburgh; instead, he helped to investigate marine invertebrates. His studies at the University of Cambridge's Christ's Col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg
Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg (19 April 1795 – 27 June 1876) was a German naturalist, zoologist, comparative anatomist, geologist, and microscopist. Ehrenberg was an evangelist and was considered to be of the most famous and productive scientists of his time. Early collections The son of a judge, Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg was born in Delitzsch, near Leipzig. He first studied theology at the University of Leipzig, then medicine and natural sciences in Berlin and became a friend of the famous explorer Alexander von Humboldt. In 1818, he completed his doctoral dissertation on fungi, ''Sylvae mycologicae Berolinenses.'' In 1820–1825, on a scientific expedition to the Middle East with his friend Wilhelm Hemprich, he collected thousands of specimens of plants and animals. He investigated parts of Egypt, the Libyan Desert, the Nile valley and the northern coasts of the Red Sea, where he made a special study of the corals. Subsequently, parts of Syria, Arabia and Abyss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dolores Piperno
Dolores Rita Piperno (born 1949) is an American archaeologist specializing in archaeobotany. She is a senior scientist emeritus of the Smithsonian Tropical Research Institute in Balboa, Panama and the Smithsonian National Museum of Natural History, Washington. Early life and education Piperno grew up in Philadelphia before her family moved to Pennsauken, N.J. Piperno earned a B.S. in Medical Technology (Rutgers University, 1971). After graduating, she began her career as a medical technician at the Hematology Research Center of Presbyterian Hospital in Philadelphia. She says she used this training and experience in this field when she moved into archaeology. She then pursued an M.A. in Anthropology (Temple University, 1979), and a Ph.D. in Anthropology (Temple University, 1983). Research and career Dr. Piperno has worked extensively in the Amazon and Central America. She has also worked in Israel. Her research interests include the study of phytoliths, starch grains, and pollen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baobab
''Adansonia'' is a genus made up of eight species of medium-to-large deciduous trees known as baobabs ( or ). They are placed in the Malvaceae family, subfamily Bombacoideae. They are native to Madagascar, mainland Africa, and Australia.Tropicos.org. Missouri Botanical Garden. 8 Jul 2020 http://www.tropicos.org The trees have also been introduced to other regions such as Asia. The generic name honours Michel Adanson, the French naturalist and explorer who described ''Adansonia digitata''. The baobab is also known as the "upside down tree", a name that originates from several myths. They are among the most long-lived of vascular plantsAdrian Patrut et al. (2018) The demise of the largest and oldest African baobabs. Nature Plants 4: 423–426. DOI: 10.1038/s41477-018-0170-5 and have large flowers that are reproductive for a maximum of 15 hours.Baum, D.A., 1995, A Systematic Revision of Adansonia (Bombacaceae). Annals of the Missouri Botanical Garden, 1995, Vol. 82, No. 3 (1995), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stomata
In botany, a stoma (from Greek ''στόμα'', "mouth", plural "stomata"), also called a stomate (plural "stomates"), is a pore found in the epidermis of leaves, stems, and other organs, that controls the rate of gas exchange. The pore is bordered by a pair of specialized parenchyma cells known as guard cells that are responsible for regulating the size of the stomatal opening. The term is usually used collectively to refer to the entire stomatal complex, consisting of the paired guard cells and the pore itself, which is referred to as the stomatal aperture. Air, containing oxygen, which is used in respiration, and carbon dioxide, which is used in photosynthesis, passes through stomata by gaseous diffusion. Water vapour diffuses through the stomata into the atmosphere in a process called transpiration. Stomata are present in the sporophyte generation of all land plant groups except liverworts. In vascular plants the number, size and distribution of stomata varies widely. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy into chemical energy that, through cellular respiration, can later be released to fuel the organism's activities. Some of this chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules, such as sugars and starches, which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water – hence the name ''photosynthesis'', from the Greek ''phōs'' (), "light", and ''synthesis'' (), "putting together". Most plants, algae, and cyanobacteria perform photosynthesis; such organisms are called photoautotrophs. Photosynthesis is largely responsible for producing and maintaining the oxygen content of the Earth's atmosphere, and supplies most of the energy necessary for life on Earth. Although photosynthesis is performed differently by different species, the process always begins when energy from light is absorbed by proteins called reaction centers that contain green chlorophyll (and other colored) pigments/chromoph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cacti
A cactus (, or less commonly, cactus) is a member of the plant family Cactaceae, a family comprising about 127 genera with some 1750 known species of the order Caryophyllales. The word ''cactus'' derives, through Latin, from the Ancient Greek word (''káktos''), a name originally used by Theophrastus for a spiny plant whose identity is now not certain. Cacti occur in a wide range of shapes and sizes. Although some species live in quite humid environments, most cacti live in habitats subject to at least some drought. Many live in extremely dry environments, even being found in the Atacama Desert, one of the driest places on Earth. Because of this, cacti show many adaptations to conserve water. For example, almost all cacti are succulents, meaning they have thickened, fleshy parts adapted to store water. Unlike many other succulents, the stem is the only part of most cacti where this vital process takes place. Most species of cacti have lost true leaves, retaining only spines, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Dioxide
Carbon dioxide (chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is transparent to visible light but absorbs infrared radiation, acting as a greenhouse gas. It is a trace gas in Earth's atmosphere at 421 parts per million (ppm), or about 0.04% by volume (as of May 2022), having risen from pre-industrial levels of 280 ppm. Burning fossil fuels is the primary cause of these increased CO2 concentrations and also the primary cause of climate change.IPCC (2022Summary for policy makersiClimate Change 2022: Mitigation of Climate Change. Contribution of Working Group III to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA Carbon dioxide is soluble in water and is found in groundwater, lakes, ice caps, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aluminium
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. It has a great affinity towards oxygen, and forms a protective layer of oxide on the surface when exposed to air. Aluminium visually resembles silver, both in its color and in its great ability to reflect light. It is soft, non-magnetic and ductile. It has one stable isotope, 27Al; this isotope is very common, making aluminium the twelfth most common element in the Universe. The radioactivity of 26Al is used in radiodating. Chemically, aluminium is a post-transition metal in the boron group; as is common for the group, aluminium forms compounds primarily in the +3 oxidation state. The aluminium cation Al3+ is small and highly charged; as such, it is polarizing, and bonds aluminium forms tend towards covalency. The strong affinity tow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |