|
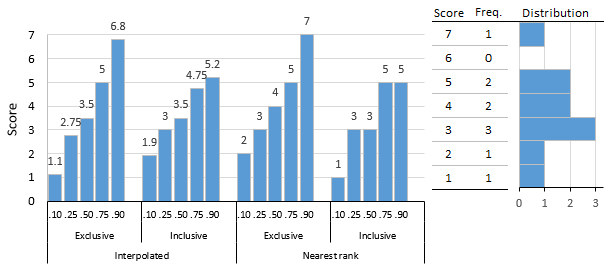
Percentile
In statistics, a ''k''-th percentile (percentile score or centile) is a score ''below which'' a given percentage ''k'' of scores in its frequency distribution falls (exclusive definition) or a score ''at or below which'' a given percentage falls (inclusive definition). For example, the 50th percentile (the median) is the score below which 50% of the scores in the distribution are found (by the "exclusive" definition), or at or below which 50% of the scores are found (by the "inclusive" definition). Percentiles are expressed in the same unit of measurement as the input scores; for example, if the scores refer to human weight, the corresponding percentiles will be expressed in kilograms or pounds. The percentile score and the '' percentile rank'' are related terms. The percentile rank of a score is the percentage of scores in its distribution that are less than it, an exclusive definition, and one that can be expressed with a single, simple formula. Percentile scores and pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Percentile
In statistics, a ''k''-th percentile (percentile score or centile) is a score ''below which'' a given percentage ''k'' of scores in its frequency distribution falls (exclusive definition) or a score ''at or below which'' a given percentage falls (inclusive definition). For example, the 50th percentile (the median) is the score below which 50% of the scores in the distribution are found (by the "exclusive" definition), or at or below which 50% of the scores are found (by the "inclusive" definition). Percentiles are expressed in the same unit of measurement as the input scores; for example, if the scores refer to human weight, the corresponding percentiles will be expressed in kilograms or pounds. The percentile score and the '' percentile rank'' are related terms. The percentile rank of a score is the percentage of scores in its distribution that are less than it, an exclusive definition, and one that can be expressed with a single, simple formula. Percentile scores and pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burstable Billing
Burstable billing is a method of measuring bandwidth based on peak use. It allows usage to exceed a specified threshold for brief periods of time without the financial penalty of purchasing a higher committed information rate (CIR, or ''commitment'') from an Internet service provider (ISP). Most ISPs use a five-minute sampling and 95% usage when calculating usage. 95th percentile The 95th percentile is a widely used mathematical calculation to evaluate the regular and sustained use of a network connection. The 95th percentile method more closely reflects the ''needed capacity'' of the link in question than tracking by other methods such as mean or maximum rate. The bytes that make up the packets themselves do not actually cost money, but the link and the infrastructure on either end of the link cost money to set up and support. This method of billing is commonly used in peering arrangements between corporate networks; it is not often used by ISPs because such entities need comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Percentile Rank
In statistics, the percentile rank (PR) of a given score is the percentage of scores in its frequency distribution that are less than that score. Its mathematical formula is : PR = \frac \times 100, where ''CF''—the cumulative frequency—is the count of all scores less than or equal to the score of interest, ''F'' is the frequency for the score of interest, and ''N'' is the number of scores in the distribution. Alternatively, if ''CF'' is the count of all scores less than the score of interest, then : PR = \frac \times 100. The figure illustrates the percentile rank computation and shows how the 0.5 × ''F'' term in the formula ensures that the percentile rank reflects a percentage of scores less than the specified score. For example, for the 10 scores shown in the figure, 60% of them are below a score of 4 (five less than 4 and half of the two equal to 4) and 95% are below 7 (nine less than 7 and half of the one equal to 7). Occasionally the percentile rank of a score is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Growth Chart
A growth chart is used by pediatricians and other health care providers to follow a child's growth over time. Growth charts have been constructed by observing the growth of large numbers of healthy children over time. The height, weight, and head circumference of a child can be compared to the expected parameters of children of the same age and sex to determine whether the child is growing appropriately. Growth charts can also be used to predict the expected adult height and weight of a child because, in general, children maintain a fairly constant growth curve. When a child deviates from his or her previously established growth curve, investigation into the cause is generally warranted. Parameters used to analyze growth charts include weight velocity (defined as rate of change in weight over time), height velocity (defined as rate of change in stature over time), and whether someone's growth chart crosses percentiles. For instance, endocrine disorders can be associated with a dec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speed Limit
Speed limits on road traffic, as used in most countries, set the legal maximum speed at which vehicles may travel on a given stretch of road. Speed limits are generally indicated on a traffic sign reflecting the maximum permitted speed - expressed as kilometres per hour (km/h) and/or miles per hour (mph). Speed limits are commonly set by the legislative bodies of national or provincial governments and enforced by national or regional police and judicial authorities. Speed limits may also be variable, or in some places nonexistent, such as on most of the Autobahnen in Germany. The first numeric speed limit for automobiles was the limit introduced in the United Kingdom in 1861. the highest posted speed limit in the world is , applied on two motorways in the UAE. Speed limits and safety distance are poorly enforced in the UAE, specifically on the Abu Dhabi to Dubai motorway - which results in dangerous traffic, according to a French-government travel-advisory. Additionally, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quartile
In statistics, a quartile is a type of quantile which divides the number of data points into four parts, or ''quarters'', of more-or-less equal size. The data must be ordered from smallest to largest to compute quartiles; as such, quartiles are a form of order statistic. The three main quartiles are as follows: * The first quartile (''Q''1) is defined as the middle number between the smallest number (minimum) and the median of the data set. It is also known as the ''lower'' or ''25th empirical'' quartile, as 25% of the data is below this point. * The second quartile (''Q''2) is the median of a data set; thus 50% of the data lies below this point. * The third quartile (''Q''3) is the middle value between the median and the highest value (maximum) of the data set. It is known as the ''upper'' or ''75th empirical'' quartile, as 75% of the data lies below this point. Along with the minimum and maximum of the data (which are also quartiles), the three quartiles described above prov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norm-referenced Test
A norm-referenced test (NRT) is a type of test, assessment, or evaluation which yields an estimate of the position of the tested individual in a predefined population, with respect to the trait being measured. Assigning scores on such tests may be described as relative grading, marking on a curve (BrE) or grading on a curve ( AmE, CanE) (also referred to as curved grading, bell curving, or using grading curves). It is a method of assigning grades to the students in a class in such a way as to obtain or approach a pre-specified distribution of these grades having a specific mean and derivation properties, such as a normal distribution (also called Gaussian distribution). The term "curve" refers to the bell curve, the graphical representation of the probability density of the normal distribution, but this method can be used to achieve any desired distribution of the grades – for example, a uniform distribution. The estimate is derived from the analysis of test scores and possibly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Normal Distribution
In statistics, a normal distribution or Gaussian distribution is a type of continuous probability distribution for a real-valued random variable. The general form of its probability density function is : f(x) = \frac e^ The parameter \mu is the mean or expectation of the distribution (and also its median and mode), while the parameter \sigma is its standard deviation. The variance of the distribution is \sigma^2. A random variable with a Gaussian distribution is said to be normally distributed, and is called a normal deviate. Normal distributions are important in statistics and are often used in the natural and social sciences to represent real-valued random variables whose distributions are not known. Their importance is partly due to the central limit theorem. It states that, under some conditions, the average of many samples (observations) of a random variable with finite mean and variance is itself a random variable—whose distribution converges to a normal d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ordinal Scale
Ordinal data is a categorical, statistical data type where the variables have natural, ordered categories and the distances between the categories are not known. These data exist on an ordinal scale, one of four levels of measurement described by S. S. Stevens in 1946. The ordinal scale is distinguished from the nominal scale by having a ''ranking''. It also differs from the interval scale and ratio scale by not having category widths that represent equal increments of the underlying attribute. Examples of ordinal data A well-known example of ordinal data is the Likert scale. An example of a Likert scale is: Examples of ordinal data are often found in questionnaires: for example, the survey question "Is your general health poor, reasonable, good, or excellent?" may have those answers coded respectively as 1, 2, 3, and 4. Sometimes data on an interval scale or ratio scale are grouped onto an ordinal scale: for example, individuals whose income is known might be grouped int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Percentage
In mathematics, a percentage (from la, per centum, "by a hundred") is a number or ratio expressed as a fraction of 100. It is often denoted using the percent sign, "%", although the abbreviations "pct.", "pct" and sometimes "pc" are also used. A percentage is a dimensionless number (pure number); it has no unit of measurement. Examples For example, 45% (read as "forty-five per cent") is equal to the fraction , the ratio 45:55 (or 45:100 when comparing to the total rather than the other portion), or 0.45. Percentages are often used to express a proportionate part of a total. (Similarly, one can also express a number as a fraction of 1,000, using the term "per mille" or the symbol "".) Example 1 If 50% of the total number of students in the class are male, that means that 50 out of every 100 students are male. If there are 500 students, then 250 of them are male. Example 2 An increase of $0.15 on a price of $2.50 is an increase by a fraction of = 0.06. Expressed as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Median
In statistics and probability theory, the median is the value separating the higher half from the lower half of a data sample, a population, or a probability distribution. For a data set, it may be thought of as "the middle" value. The basic feature of the median in describing data compared to the mean (often simply described as the "average") is that it is not skewed by a small proportion of extremely large or small values, and therefore provides a better representation of a "typical" value. Median income, for example, may be a better way to suggest what a "typical" income is, because income distribution can be very skewed. The median is of central importance in robust statistics, as it is the most resistant statistic, having a breakdown point of 50%: so long as no more than half the data are contaminated, the median is not an arbitrarily large or small result. Finite data set of numbers The median of a finite list of numbers is the "middle" number, when those numbers are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cumulative Distribution Function
In probability theory and statistics, the cumulative distribution function (CDF) of a real-valued random variable X, or just distribution function of X, evaluated at x, is the probability that X will take a value less than or equal to x. Every probability distribution supported on the real numbers, discrete or "mixed" as well as continuous, is uniquely identified by an ''upwards continuous'' ''monotonic increasing'' cumulative distribution function F : \mathbb R \rightarrow ,1/math> satisfying \lim_F(x)=0 and \lim_F(x)=1. In the case of a scalar continuous distribution, it gives the area under the probability density function from minus infinity to x. Cumulative distribution functions are also used to specify the distribution of multivariate random variables. Definition The cumulative distribution function of a real-valued random variable X is the function given by where the right-hand side represents the probability that the random variable X takes on a value less th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)


.jpg)
