|
Pentapolis
A pentapolis (from Greek ''penta-'', 'five' and ''polis'', 'city') is a geographic and/or institutional grouping of five cities. Cities in the ancient world probably formed such groups for political, commercial and military reasons, as happened later with the Cinque Ports in England. Significant historical cases * In the biblical Holy Land, describes the region where five cities — Sodom, Gomorrah, Zoara, Admah and Zeboim — united to resist the invasion of Chedorlaomer, and of which four were shortly after destroyed. * The Philistine Pentapolis: Ashkelon, Ashdod, Ekron, Gath, and Gaza, all combined to make Philistia. * The Doric – or Dorian Pentapolis: Kos, on the island of the same name in the Aegean Sea; Cnidus, in Caria on the west coast of Asia Minor; Lindus, Ialysus and Camirus, all three on Rhodes. * The Phrygian Pentapolis: Eucarpia, Hierapolis, Otrus, Bruzus, and Stectorium * The Pontic Pentapolis: Apollonia, Callatis, Mesembria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
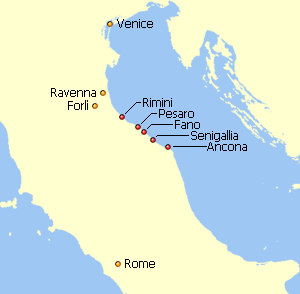
Pentapolis Within The Exarchate Of Ravenna
A pentapolis (from Greek ''penta-'', 'five' and ''polis'', 'city') is a geographic and/or institutional grouping of five cities. Cities in the ancient world probably formed such groups for political, commercial and military reasons, as happened later with the Cinque Ports in England. Significant historical cases * In the biblical Holy Land, describes the region where five cities — Sodom, Gomorrah, Zoara, Admah and Zeboim — united to resist the invasion of Chedorlaomer, and of which four were shortly after destroyed. * The Philistine Pentapolis: Ashkelon, Ashdod, Ekron, Gath, and Gaza, all combined to make Philistia. * The Doric – or Dorian Pentapolis: Kos, on the island of the same name in the Aegean Sea; Cnidus, in Caria on the west coast of Asia Minor; Lindus, Ialysus and Camirus, all three on Rhodes. * The Phrygian Pentapolis: Eucarpia, Hierapolis, Otrus, Bruzus, and Stectorium * The Pontic Pentapolis: Apollonia, Callatis, Mesembria, Ode ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phrygian Pentapolis
The Phrygian Pentapolis was an area of five cities (Greek ''pentapolis'', "five cities") in ancient Phrygia, now in Turkey. The five cities were: Eucarpia, Hierapolis Hierapolis (; grc, Ἱεράπολις, lit. "Holy City") was originally a Phrygian cult centre of the Anatolian mother goddess of Cybele and later a Greek city. Its location was centred upon the remarkable and copious hot springs in clas ..., Otrus, Bruzus, and Stectorium. References Ancient Greek geography Geography of Phrygia {{ancientPhrygia-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philistine
The Philistines ( he, פְּלִשְׁתִּים, Pəlīštīm; Koine Greek ( LXX): Φυλιστιείμ, romanized: ''Phulistieím'') were an ancient people who lived on the south coast of Canaan from the 12th century BC until 604 BC, when their polity, after having already been subjugated for centuries by the Neo-Assyrian Empire, was finally destroyed by King Nebuchadnezzar II of the Neo-Babylonian Empire. After becoming part of his empire and its successor, the Persian Empire, they lost their distinct ethnic identity and disappeared from the historical and archaeological record by the late 5th century BC.. The Philistines are known for their biblical conflict with the Israelites. Though the primary source of information about the Philistines is the Hebrew Bible, they are first attested to in reliefs at the Temple of Ramses III at Medinet Habu, in which they are called (accepted as cognate with Hebrew ); the parallel Assyrian term is , , or . Etymology The English ter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otrus
Otrus, or Otrous, was a town of ancient Phrygia located in the Phrygian Pentapolis, inhabited during Roman and Byzantine times. It was the seat of a bishop, a notable bishop was Zoticus of Otrous. No longer a residential bishopric, it remains a titular see of the Roman Catholic Church The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a .... Its site is located near Yanık Ören in Asiatic Turkey. References Populated places in Phrygia Former populated places in Turkey Roman towns and cities in Turkey Populated places of the Byzantine Empire History of Afyonkarahisar Province Catholic titular sees in Asia Sandıklı District {{Asia-RC-diocese-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hierapolis (Phrygian Pentapolis)
Hierapolis /ˌhaɪəˈræpəlɪs/ ( grc, Ιεράπολις ''Ierapolis'') was a town of the Phrygian Pentapolis in ancient Phrygia, inhabited during Roman and Byzantine The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ... times. Its site is located near Koçhisar in Asiatic Turkey. References Populated places in Phrygia Former populated places in Turkey Roman towns and cities in Turkey Populated places of the Byzantine Empire History of Afyonkarahisar Province Sandıklı District {{Afyonkarahisar-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philistia
Philistia (; Koine Greek (LXX): Γῆ τῶν Φυλιστιείμ, romanized: ''gê tôn Phulistieìm''), also known as the Philistine Pentapolis, was a confederation of cities in the Southwest Levant, which included the cities of Ashdod, Ashkelon, Ekron, Gath, Gaza, and for a time, Jaffa. The population, according to the most recent assessments, was, in all probability, formed basically from Canaanite stock going back to the Bronze Age,Benjamin M. Sulliva'In the Shadow of Phoenicia,' The Journal of Hellenic Studies, 2018, Vol. 138 pp.67-79 p.70 tinged with an Indo-European admixture of people from an Aegean background from roughly 1200 BCE onwards, and came to be known as ''Peleset'', or Philistines. At its maximum territorial expansion, its territory may have stretched along the Canaanite coast from Arish in the Sinai (today's Egypt) to the Yarkon River (today's Tel Aviv), and as far inland as Ekron and Gath. Nebuchadnezzar II invaded Philistia in 604 BC, burned Ashkelon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodom And Gomorrah
Sodom and Gomorrah () were two legendary biblical cities destroyed by God for their wickedness. Their story parallels the Genesis flood narrative in its theme of God's anger provoked by man's sin (see Genesis 19:1–28). They are mentioned frequently in the prophets and the New Testament as symbols of human wickedness and divine retribution, and the Quran also contains a version of the story about the two cities. The legend of their destruction may have originated as an attempt to explain the remains of third-millennium Bronze Age cities in the region, and subsequent Late Bronze Age collapse. Etymology The etymology of the names ''Sodom'' and ''Gomorrah'' is uncertain, and scholars disagree about them. They are known in Hebrew as hbo, , Səḏōm, label=none and hbo, , 'Ămōrā, label=none. In the Septuagint, these became grc, Σόδομα, Sódoma, label=none and grc, Γόμορρᾰ, Gómorrha, label=none; the Hebrew ghayn was absorbed by ayin sometime after the Septuagi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stectorium
Stectorium or Stektorion ( grc, Στεκτόριον) was a town of ancient Phrygia, in the Phrygian Pentapolis between Peltae and Synnada, inhabited during Roman and Byzantine times. Pausanias believed that Mygdon's tomb was located here. It was an episcopal see of a bishop; no longer a territorial diocese, it remains a Latin Church titular see of the Catholic Church The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwide . It is am .... Its site is located near Kocahüyük in Asiatic Turkey. References Populated places in Phrygia Former populated places in Turkey Roman towns and cities in Turkey Populated places of the Byzantine Empire History of Afyonkarahisar Province Catholic titular sees in Asia Sandıklı District {{Afyonkarahisar-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bruzus
Bruzus or Brouzos ( grc, Βροῦζος) was a town of ancient Phrygia, in the Phrygian Pentapolis, inhabited during Roman and Byzantine times. Druzon, which Ptolemy places among the cities of Phrygia Magna, should be Bruzon. It was the seat of a bishop; no longer a residential bishopric, it remains a titular see of the Roman Catholic Church The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a .... Its site is located near Karasandıklı in Asiatic Turkey. References Populated places in Phrygia Former populated places in Turkey Roman towns and cities in Turkey Populated places of the Byzantine Empire History of Afyonkarahisar Province Catholic titular sees in Asia Sandıklı District {{Afyonkarahisar-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ekron
Ekron (Philistine: 𐤏𐤒𐤓𐤍 ''*ʿAqārān'', he, עֶקְרוֹן, translit=ʿEqrōn, ar, عقرون), in the Hellenistic period known as Accaron ( grc-gre, Ακκαρων, Akkarōn}) was a Philistine city, one of the five cities of the Philistine Pentapolis, located in present-day Israel. In 1957 Ekron was first identified with the mound of Tel Miqne (Hebrew) or Khirbet el-Muqanna (Arabic), near the depopulated Palestinian village of 'Aqir, on the basis of the large size of the Iron Age archaeological remains; the judgement was strengthened by the discovery in 1996 of the Ekron inscription. The tell lies west of Jerusalem, and north of Tell es-Safi, the almost certain site of the Philistine city of Gath, on the grounds of Kibbutz Revadim on the eastern edge of the Israeli coastal plain. In the Bible In the Hebrew Bible, Ekron is mentioned initially in : :''This is the land that still remains: all the regions of the Philistines and all those of the Gesh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gath (city)
Gath or Gat ( he, גַּת, translit=Gaṯ, lit= wine press; la, Geth, Philistine: 𐤂𐤕 *''Gīt''), often referred to as Gath of the Philistines, was a major Philistine city and one of the five Philistine city-states during the Iron Age. It was located in northeastern Philistia, close to the border with Judah. Gath is often mentioned in the Hebrew Bible and its existence is confirmed by Egyptian inscriptions. Already of significance during the Bronze Age, the city is believed to be mentioned in the El-Amarna letters as Gimti/Gintu, ruled by the two Shuwardata and 'Abdi-Ashtarti. Another Gath, known as Ginti-kirmil (Gath of Carmel) also appears in the Amarna letters.Naʼaman, Nadav (2005), p207/ref> The site most favored as the location of Gath is the archaeological mound or tell known as Tell es-Safi in Arabic and Tel Zafit in Hebrew (sometimes written Tel Tzafit), located inside Tel Zafit National Park, but a stone inscription disclosing the name of the city has yet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polis
''Polis'' (, ; grc-gre, πόλις, ), plural ''poleis'' (, , ), literally means "city" in Greek. In Ancient Greece, it originally referred to an administrative and religious city center, as distinct from the rest of the city. Later, it also came to mean the body of citizens under a city's jurisdiction. In modern historiography, the term is normally used to refer to the ancient Greek city-states, such as Classical Athens and its contemporaries, and thus is often translated as "city-state". The ''poleis'' were not like other primordial ancient city-states like Tyre or Sidon, which were ruled by a king or a small oligarchy; rather, they were political entities ruled by their bodies of citizens. The Ancient Greek ''poleis'' developed during the Archaic period as the ancestor of the Ancient Greek city, state and citizenship and persisted (though with decreasing influence) well into Roman times, when the equivalent Latin word was '' civitas'', also meaning "citizenhood", w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |