|
Parareptiles
Parareptilia ("at the side of reptiles") is a subclass or clade of basal sauropsids ( reptiles), typically considered the sister taxon to Eureptilia (the group that likely contains all living reptiles and birds). Parareptiles first arose near the end of the Carboniferous period and achieved their highest diversity during the Permian period. Several ecological innovations were first accomplished by parareptiles among reptiles. These include the first reptiles to return to marine ecosystems (mesosaurs), the first bipedal reptiles ( bolosaurids such as ''Eudibamus''), the first reptiles with advanced hearing systems ( nycteroleterids and others), and the first large herbivorous reptiles (the pareiasaurs). The only parareptiles to survive into the Triassic period were the procolophonoids, a group of small generalists, omnivores, and herbivores. The largest family of procolophonoids, the procolophonids, rediversified in the Triassic, but subsequently declined and became extinct by t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nyctiphruretus Acudens
''Nyctiphruretus'' (meaning "Guardian of the Night") is an extinct genus of nyctiphruretid parareptile known from the Guadalupian series (middle Permian) of European Russia. Many fossils of the type species, ''N. acudens'', were found well preserved near the Mezen River of European Russia in various stages of growth. The dentition identified that ''Nyctiphruretus'' is a herbivore. Based on the large numbers of individuals found and the sediment that they were found in, it appears that their diet consisted of aquatic plants. Adults discovered averaged 36 cm in length with a 4.4 cm skull that was crushed but recognisable. ''Nyctiphruretus'' was first named by Efremov in 1938 and the type species is ''Nyctiphruretus acudens''. In 2002, a second species was named by V. V. Bulanov. ''N. optabilis'' is known from a single jaw, also from Russia, Eastern Europe. Lee (1997) named the order Nyctiphruretia and the family Nyctiphruretidae, to include ''Nyctiphruretus''. While the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nycteroleteridae
Nycteroleteridae is a family of procolophonian parareptilians (extinct early reptiles) from the Middle to Late Permian of Russia and North America. They are sometimes classified as a sister group to pareiasaurids (but see ''Classification)''. The group includes the genera ''Macroleter'', '' Bashkyroleter'', ''"Bashkyroleter" mesensis'', ''Nycteroleter'', ''Emeroleter'', and probably ''Rhipaeosaurus''. They were carnivorous, and occasionally ate insects. The group was most common in European Russia, with only a few fossils in North America. One fossil has also been found in Africa, but this is the only one from Gondwana. Classification Nycteroleteridae is sometimes considered a sister group to the Pareiasauridae, but Bayesian inference suggests that it was in fact paraphyletic, with ''Rhipaeosaurus'' a basal member of the Pareiasauridae and other members of the Nycteroleteridae as outgroups. This is supported by the appearance of ''Rhipaeosaurus skull and teeth - it had tricuspi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
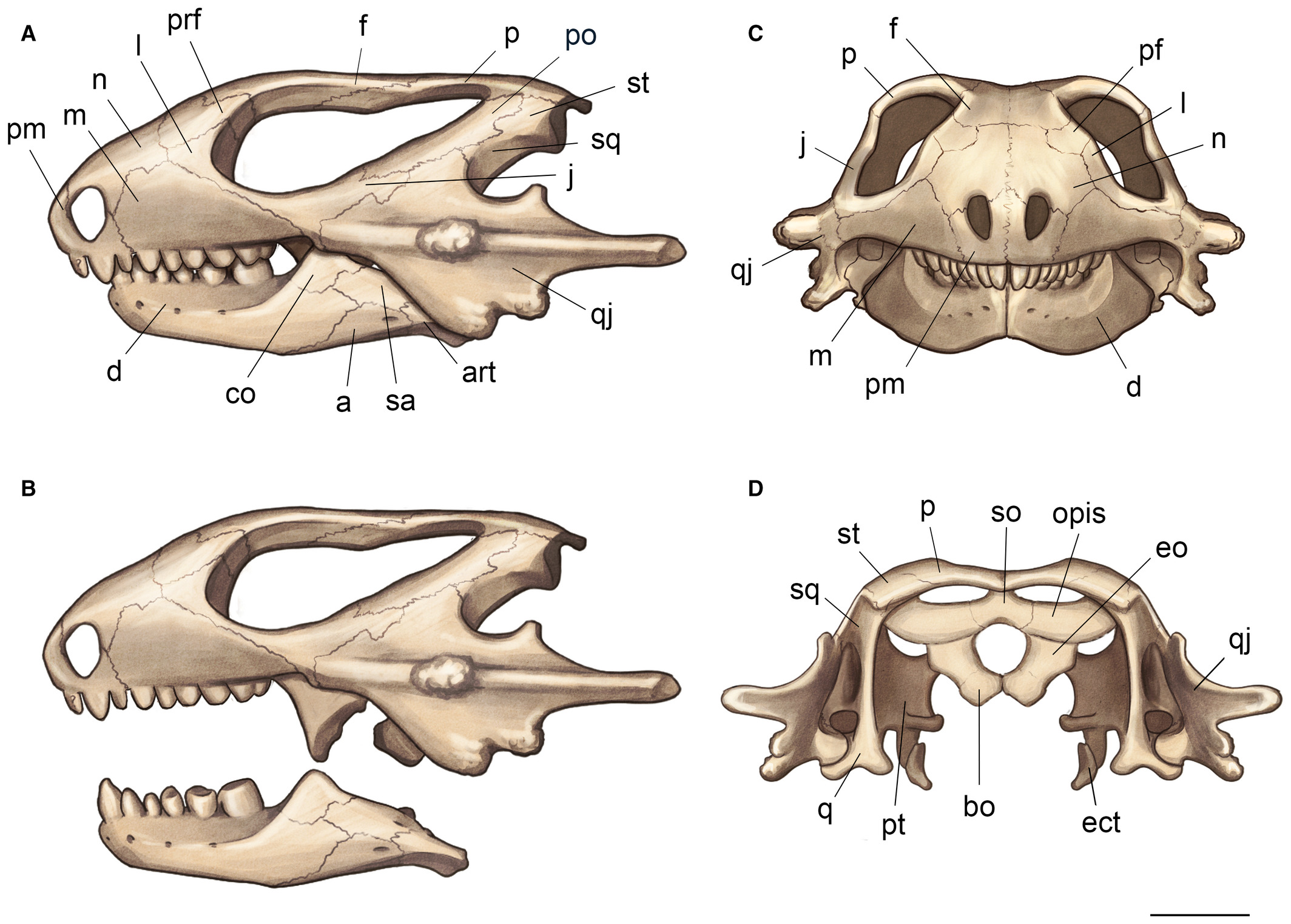
Millerosauria
Millerosauria is an order of Parareptiles that contains the families †Millerettidae and †Eunotosauridae. It is the sister group to the order Procolophonomorpha. It was named in 1957 by Watson. It was once considered a suborder of the disused group Captorhinida Fossil of '' Labidosaurus hamatus'' Captorhinida (older name: Cotylosauria) is a doubly paraphyletic grouping of early reptiles. Robert L. Carroll (1988) ranked it as an order in the subclass Anapsida, composed of the following suborders:R. L. Ca ... and was called Millerosauroidea. All members of this order are thought to be extinct. '' Eunotosaurus'' has been recovered as a stem-turtle in recent cladistic studies.Schoch RR, Sues HD (2015) A Middle Triassic stem-turtle and the evolution of the turtle body plan. Nature doi: 10.1038/nature14472. pub ahead of print/ref> References * Parareptiles Prehistoric animal orders Guadalupian first appearances Lopingian extinctions {{permian-reptile-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nyctiphruretid
Nyctiphruretidae is an extinct family of hallucicranian parareptiles known from the late Early to the late Middle Permian of European Russia and south-central United States. Nyctiphruretidae was named by Efremov in 1938. The type genus is ''Nyctiphruretus'' known from several Middle Permian locations in European Russia. Michael S. Y. Lee in 1997 placed the family in the larger clade Nyctiphruretia. The order was defined to include both nyctiphruretids and nycteroleterids. However, recent cladistic analyses suggest that nycteroleterids are more closely related to the Pareiasauria instead, thus making ''Nyctiphruretus'' the only genus of its order. In 2014, MacDougall & Reisz described and named a second genus of Nyctiphruretidae, ''Abyssomedon'', from the middle Leonardian stage of the late Early Permian of Comanche County, Oklahoma, south-central United States. It contains a single species, ''A. williamsi'', which represents the first nyctiphruretid known from North America, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesosaur
Mesosaurs ("middle lizards") were a group of small aquatic reptiles that lived during the early Permian period, roughly 299 to 270 million years ago. Mesosaurs were the first known aquatic reptiles, having apparently returned to an aquatic lifestyle from more terrestrial ancestors. It is uncertain which and how many terrestrial traits these ancestors displayed; recent research cannot establish with confidence if the first amniotes were fully terrestrial, or only amphibious. Most authors consider mesosaurs to have been aquatic, although adult animals may have been amphibious, rather than completely aquatic, as indicated by their moderate skeletal adaptations to a semiaquatic lifestyle.Pablo Nuñez Demarco et al. Was Mesosaurus a Fully Aquatic Reptile? Front. Ecol. Evol, published online July 27, 2018; doi: 10.3389/fevo.2018.00109 Similarly, their affinities are uncertain; they may have been among the most basal sauropsids or among the most basal parareptiles (in the case of which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Procolophonidae
Procolophonidae is an extinct family of small, lizard-like parareptiles known from the Late Permian to Late Triassic that were distributed across Pangaea, having been reported from Europe, North America, China, South Africa, South America, Antarctica and Australia. The most primitive procolophonids were likely insectiovous or omnivorous, more derived members of the clade developed bicusped molars, and were likely herbivorous feeding on high fiber vegetation or durophagous omnivores. Many members of the group are noted for spines projecting from the quadratojugal bone of the skull, which likely served a defensive purpose as well as possibly also for display. At least some taxa were likely fossorial burrowers. While diverse during the Early and Middle Triassic, they had very low diversity during the Late Triassic, and were extinct by the beginning of the Jurassic. Phylogeny Below is a cladogram A cladogram (from Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesosaur
Mesosaurs ("middle lizards") were a group of small aquatic reptiles that lived during the early Permian period, roughly 299 to 270 million years ago. Mesosaurs were the first known aquatic reptiles, having apparently returned to an aquatic lifestyle from more terrestrial ancestors. It is uncertain which and how many terrestrial traits these ancestors displayed; recent research cannot establish with confidence if the first amniotes were fully terrestrial, or only amphibious. Most authors consider mesosaurs to have been aquatic, although adult animals may have been amphibious, rather than completely aquatic, as indicated by their moderate skeletal adaptations to a semiaquatic lifestyle.Pablo Nuñez Demarco et al. Was Mesosaurus a Fully Aquatic Reptile? Front. Ecol. Evol, published online July 27, 2018; doi: 10.3389/fevo.2018.00109 Similarly, their affinities are uncertain; they may have been among the most basal sauropsids or among the most basal parareptiles (in the case of which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acleistorhinid
Acleistorhinidae is an extinct family of Late Carboniferous and Early Permian-aged (Moscovian to Kungurian stage) parareptiles. Acleistorhinids are most diverse from the Richards Spur locality of the Early Permian of Oklahoma. Richards Spur acleistorhinids include ''Acleistorhinus'', ''Colobomycter'', and possibly ''Delorhynchus'' and ''Feeserpeton''. Other taxa include '' Carbonodraco'' from the Late Carboniferous of Ohio and '' Karutia'' from the Early Permian of Brazil. Acleistorhinidae is commonly considered a subgroup of lanthanosuchoids, related to taxa such as '' Chalcosaurus'', '' Lanthaniscus'' and '' Lanthanosuchus''. However, a re-examination of parareptile phylogeny conducted by Cisneros ''et al.'' (2021) argued that lanthanosuchids were not closely related to acleistorhinids. The phylogenetic analysis conducted by these authors recovered acleistorhinids as the sister group of the clade Procolophonia, while lanthanosuchids were recovered within the procolophonian subgr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Procolophonomorpha
Procolophonomorpha is an order or clade containing most parareptiles. Many papers have applied various definitions to the name, though most of these definitions have since been considered synonymous with modern parareptile clades such as Ankyramorpha and Procolophonia. The current definition of Procolophonomorpha, as defined by Modesto, Scott, & Reisz (2009), is that of as a stem-based group containing ''Procolophon'' and all taxa more closely related to it than to '' Milleretta''. It constitutes a diverse assemblage that includes a number of lizard-like forms, as well as more diverse types such as the pareiasaurs. Lee 1995, 1996, 1997 argues that turtles evolved from pareiasaurs, but this view is no longer considered likely. Rieppel and deBraga 1996 and deBraga and Rieppel, 1997 argue that turtles evolved from sauropterygians, and there is both molecular and fossil (''Pappochelys'') evidence for the origin of turtles among diapsid reptiles. Classification The following cladogr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Procolophonid
Procolophonidae is an extinct family of small, lizard-like parareptiles known from the Late Permian to Late Triassic that were distributed across Pangaea, having been reported from Europe, North America, China, South Africa, South America, Antarctica and Australia. The most primitive procolophonids were likely insectiovous or omnivorous, more derived members of the clade developed bicusped molars, and were likely herbivorous feeding on high fiber vegetation or durophagous omnivores. Many members of the group are noted for spines projecting from the quadratojugal bone of the skull, which likely served a defensive purpose as well as possibly also for display. At least some taxa were likely fossorial burrowers. While diverse during the Early and Middle Triassic, they had very low diversity during the Late Triassic, and were extinct by the beginning of the Jurassic. Phylogeny Below is a cladogram A cladogram (from Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bolosauridae
Bolosauridae is an extinct family of ankyramorph parareptiles known from the latest Carboniferous (Gzhelian) or earliest Permian (Asselian) to the early Guadalupian epoch (latest Roadian stage) of North America, China, Germany, Russia and France. The bolosaurids were unusual for their time period by being bipedal, the oldest known tetrapods to have been so. Their teeth suggest that they were herbivores. The bolosaurids were a rare group and died out without any known descendants. The following cladogram shows the phylogenetic In biology, phylogenetics (; from Greek φυλή/ φῦλον [] "tribe, clan, race", and wikt:γενετικός, γενετικός [] "origin, source, birth") is the study of the evolutionary history and relationships among or within groups ... position of the Bolosauridae, from Johannes Müller, Jin-Ling Li and Robert R. Reisz, 2008. References Procolophonomorphs Permian reptiles Paleozoic reptiles of Asia Paleozoic reptiles of Europe Pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Permian
The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.9 Mya. It is the last period of the Paleozoic Era; the following Triassic Period belongs to the Mesozoic Era. The concept of the Permian was introduced in 1841 by geologist Sir Roderick Murchison, who named it after the Perm Governorate, region of Perm in Russia. The Permian witnessed the diversification of the two groups of amniotes, the synapsids and the Sauropsida, sauropsids (reptiles). The world at the time was dominated by the supercontinent Pangaea, which had formed due to the collision of Euramerica and Gondwana during the Carboniferous. Pangaea was surrounded by the superocean Panthalassa. The Carboniferous rainforest collapse left behind vast regions of desert within the continental interior. Amniotes, which could better cope with these drier conditi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |