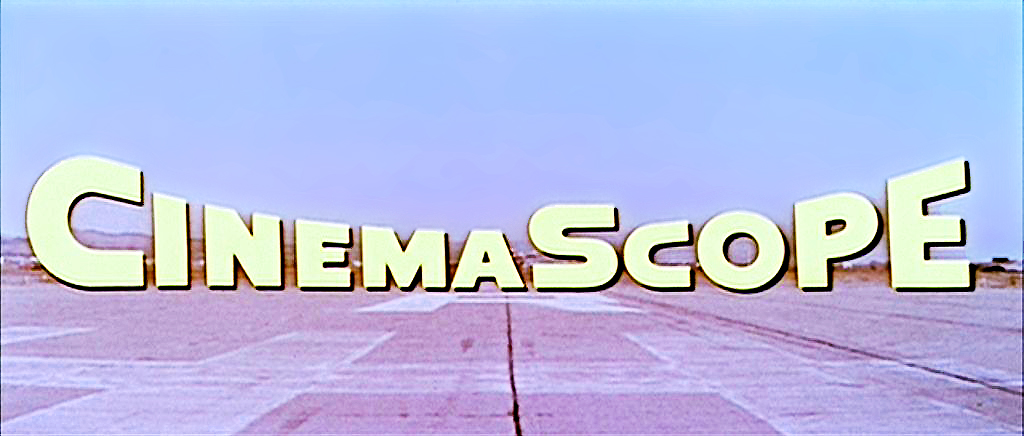|
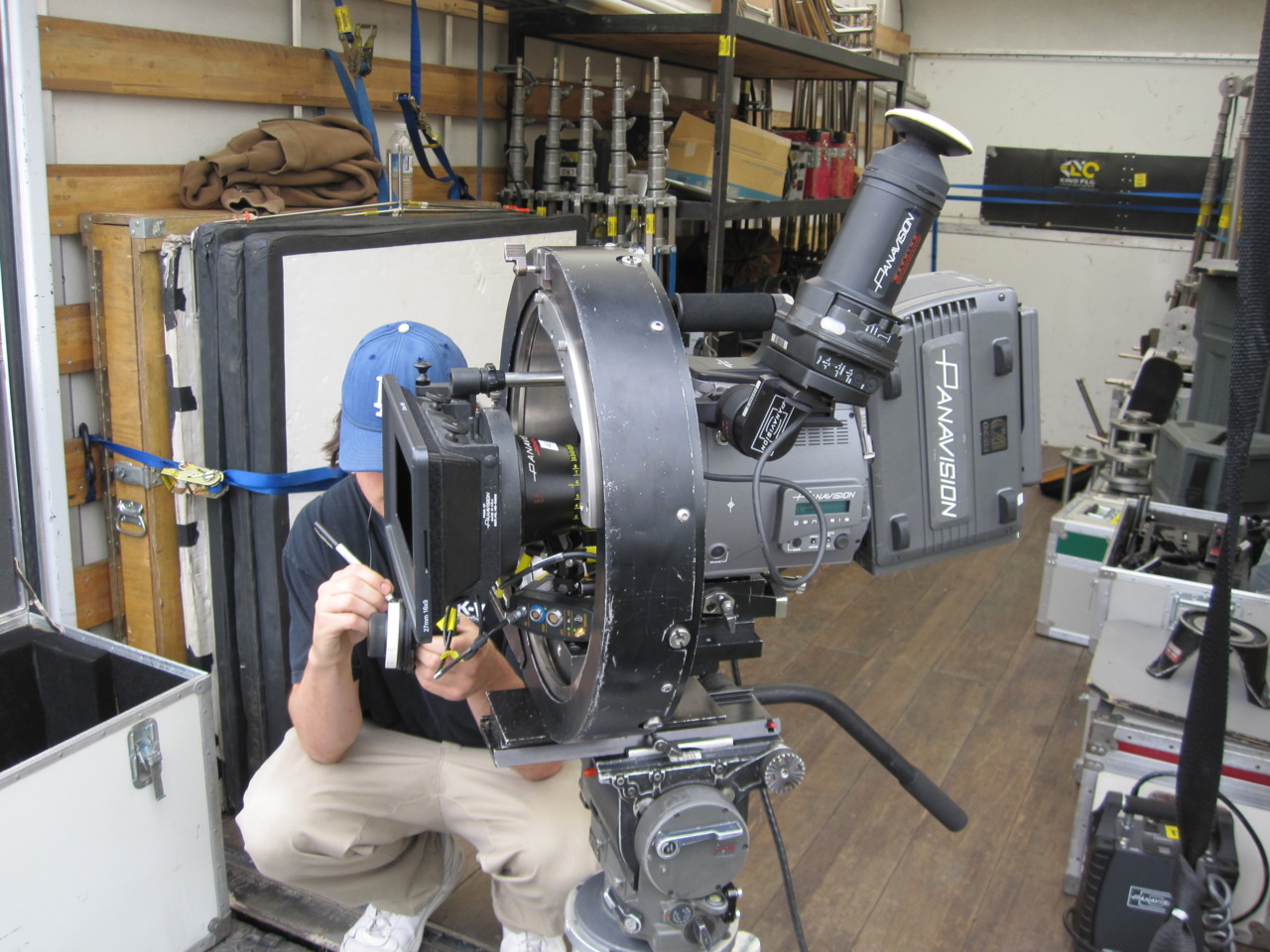
Panavision
Panavision is an American motion picture equipment company founded in 1953 specializing in cameras and lenses, based in Woodland Hills, California. Formed by Robert Gottschalk as a small partnership to create anamorphic projection lenses during the widescreen boom in the 1950s, Panavision expanded its product lines to meet the demands of modern filmmakers. The company introduced its first products in 1954. Originally a provider of CinemaScope accessories, the company's line of anamorphic widescreen lenses soon became the industry leader. In 1972, Panavision helped revolutionize filmmaking with the lightweight Panaflex 35 mm movie camera. The company has introduced other cameras such as the Millennium XL (1999) and the digital video Genesis (2004). Panavision operates exclusively as a rental facility—the company owns its entire inventory, unlike most of its competitors. Early history Robert Gottschalk founded Panavision in late 1953, in partnership with Richard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
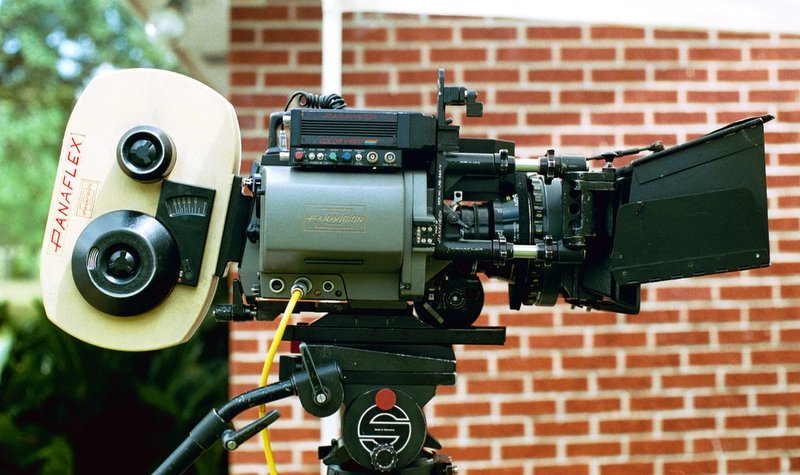
Panavision Cameras
Panavision has been a manufacturer of cameras for the motion picture industry since the 1950s, beginning with anamorphic widescreen lenses. The lightweight Panaflex is credited with revolutionizing filmmaking. Other influential cameras include the Millennium XL and the digital video Genesis. Panavision Silent Reflex * Panavision Silent Reflex (1967) * Panavision Super PSR (R-200 or Super R-200) Panaflex ; Panaflex (1972): ; Panaflex-X (1974): ; Panaflex Lightweight (1975): The Panaflex Lightweight is a sync-sound 35 mm motion picture camera, stripped of all components not essential for work with "floating camera" systems such as the Steadicam. Contemporary cameras such as the Panavision Gold II can weigh as much as depending on configuration. The Panaflex Lightweight II (1993) is crystal-controlled in one-frame increments between four and 36 frames per second, and has a fixed focal-plane shutter. 200°, 180°, 172.8° or 144° shutters can be installed by Panavision pri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panaflex
Panavision has been a manufacturer of cameras for the motion picture industry since the 1950s, beginning with anamorphic widescreen lenses. The lightweight Panaflex is credited with revolutionizing filmmaking. Other influential cameras include the Millennium XL and the digital video Genesis. Panavision Silent Reflex * Panavision Silent Reflex (1967) * Panavision Super PSR (R-200 or Super R-200) Panaflex ; Panaflex (1972): ; Panaflex-X (1974): ; Panaflex Lightweight (1975): The Panaflex Lightweight is a sync-sound 35 mm motion picture camera, stripped of all components not essential for work with "floating camera" systems such as the Steadicam. Contemporary cameras such as the Panavision Gold II can weigh as much as depending on configuration. The Panaflex Lightweight II (1993) is crystal-controlled in one-frame increments between four and 36 frames per second, and has a fixed focal-plane shutter. 200°, 180°, 172.8° or 144° shutters can be installed by Panavision pri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genesis (camera)
The Genesis is a discontinued high-end digital movie camera developed by Panavision, and was available solely by rental. It is based on a proprietary Super 35 1.78:1 (16:9) aspect ratio, 12.4-megapixel, RGB filtered CCD sensor. It was first used by a feature crew to shoot Bryan Singer's ''Superman Returns,'' and was shortly followed up thereafter by the World War I film '' Flyboys''. However, the computer effect-heavy nature of these two movies meant that ultimately the comedy ''Scary Movie 4'' was the first theatrically released feature primarily shot with the Genesis. It was discontinued in 2012 and succeeded by the Millennium DXL line developed with Red Digital Cinema. Background Unlike the 2/3" 3-CCD imaging system used in Sony's HDW-F900 CineAlta camera (used in ''Attack of the Clones''), the Genesis uses a single 12.4 megapixel CCD chip with the same width as a Super 35 mm film frame. The "Panavized" CineAltas did not use Panavision's existing range of 35 mm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anamorphic Format
Anamorphic format is the cinematography technique of shooting a widescreen picture on standard 35 mm film or other visual recording media with a non-widescreen native aspect ratio. It also refers to the projection format in which a distorted image is "stretched" by an anamorphic projection lens to recreate the original aspect ratio on the viewing screen (not to be confused with anamorphic widescreen, a different video encoding concept that uses similar principles but different means). The word ''anamorphic'' and its derivatives stem from the Greek ''anamorphoun'' ("to transform"), compound of ''morphé'' ("form, shape") with the prefix ''aná'' ("back, against"). In the late 1990s and 2000s, anamorphic lost popularity in comparison to "flat" (or "spherical") formats such as Super 35 with the advent of digital intermediates; however, in the years since digital cinema cameras and projectors have become commonplace, anamorphic has experienced a considerable resurgence of populari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Gottschalk
Robert Gottschalk (March 12, 1918 – June 3, 1982) was an American camera technician, inventor, and co-founder of Panavision. Early life Born to Gustav and Anna Gottschalk in Chicago, Illinois. His father was an architect who built several hotels in the city. Gustav's success left the family well-off financially and influenced Gottschalk's interest in film. In 1939, Gottschalk graduated with a degree in theater and arts from Carleton College in Minnesota. He then moved to California to open a camera shop with a long-term goal of becoming a filmmaker. Panavision He bought an interest in a camera shop and later got to know a nearby outfit that made underwater filming equipment for Jacques-Yves Cousteau. Equipment restrictions at the time made wide-angle filming difficult, and Gottschalk began experimenting with anamorphic lens equipment patented by Henri Chrétien. In 1953, the CinemaScope process, based on Chrétien's patents, was purchased and named by 20th Century Stu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CinemaScope
CinemaScope is an anamorphic lens series used, from 1953 to 1967, and less often later, for shooting widescreen films that, crucially, could be screened in theatres using existing equipment, albeit with a lens adapter. Its creation in 1953 by Spyros P. Skouras, the president of 20th Century Fox, marked the beginning of the modern anamorphic format in both principal 2.55:1, almost twice as wide as the previously common Academy format's 1.37:1 ratio. Although the technology behind the CinemaScope lens system was made obsolete by later developments, primarily advanced by Panavision, CinemaScope's anamorphic format has continued to this day. In film-industry jargon, the shortened form, 'Scope, is still widely used by both filmmakers and projectionists, although today it generally refers to any 2.35:1, 2.39:1, 2.40:1, or 2.55:1 presentation or, sometimes, the use of anamorphic lensing or projection in general. Bausch & Lomb won a 1954 Oscar for its development of the CinemaScope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Moore (cinematographer)
Richard Moore (October 4, 1925 - August 16, 2009) was an American cinematographer. In 1953, Moore teamed with Robert Gottschalk to co-found Panavision. Early life Moore was born in Jacksonville, Illinois, on October 4, 1925. He received a bachelor's degree in cinema from the University of Southern California. Following graduation, Moore began working on travelogues and documentaries. Career Moore collaborated with Robert Gottschalk in 1953 to co-found Panavision, a motion picture equipment company specializing in cameras and lenses. Among the company's innovations, Panavision developed a specific camera lens for use in widescreen format which is called Cinemascope. In 1972 the Panaflex lightweight silent reflex camera adaptable to either handheld or studio conditions was introduced. In a 2005 interview with ''Daily Variety'', Moore explained that his connections with Panavision seemed to him to be purely by chance, "Becoming a cameraman and becoming part of Panavision was stric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Widescreen
Widescreen images are displayed within a set of aspect ratios (relationship of image width to height) used in film, television and computer screens. In film, a widescreen film is any film image with a width-to-height aspect ratio greater than the standard 1.37:1 Academy aspect ratio provided by 35 mm film. For television, the original screen ratio for broadcasts was in fullscreen 4:3 (1.33:1). Largely between the 1990s and early 2000s, at varying paces in different nations, 16:9 (1.78:1) widescreen TV displays came into increasingly common use. They are typically used in conjunction with high-definition television (HDTV) receivers, or Standard-Definition (SD) DVD players and other digital television sources. With computer displays, aspect ratios wider than 4:3 are also referred to as widescreen. Widescreen computer displays were previously made in a 16:10 aspect ratio (e.g. 1680 × 1050), but now are usually 16:9 (e.g. 1920 × 1080). Film History Widescreen was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
35 Mm Movie Film
35 mm film is a film gauge used in filmmaking, and the film standard. In motion pictures that record on film, 35 mm is the most commonly used gauge. The name of the gauge is not a direct measurement, and refers to the nominal width of the 35 mm format photographic film, which consists of strips wide. The standard image exposure length on 35 mm for movies ("single-frame" format) is four perforations per frame along both edges, which results in 16 frames per foot of film. A variety of largely proprietary gauges were devised for the numerous camera and projection systems being developed independently in the late 19th century and early 20th century, as well as a variety of film feeding systems. This resulted in cameras, projectors, and other equipment having to be calibrated to each gauge. The 35 mm width, originally specified as inches, was introduced around 1890 by William Kennedy Dickson and Thomas Edison, using 120 film stock supplied by George Eastman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Movie Projector
A movie projector is an opto-mechanical device for displaying motion picture film by projecting it onto a screen. Most of the optical and mechanical elements, except for the illumination and sound devices, are present in movie cameras. Modern movie projectors are specially built video projectors. (see also digital cinema) Many projectors are specific to a particular film gauge and not all movie projectors are film projectors since the use of film is required. Predecessors The main precursor to the movie projector was the magic lantern. In its most common setup it had a concave mirror behind a light source to help direct as much light as possible through a painted glass picture slide and a lens, out of the lantern onto a screen. Simple mechanics to have the painted images moving were probably implemented since Christiaan Huygens introduced the apparatus around 1659. Initially candles and oil lamps were used, but other light sources, such as the argand lamp and lime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meredith Merle Nicholson
Meredith Merle Nicholson (March 11, 1913 – August 18, 2005) was an American cinematographer. He worked behind the camera on low-budget films of the 1950s, hit television series in the 1960s, and comedies, dramas, and made-for-TV movies in the 1970s and 1980s. In 1953, Nicholson, along with his two sons and three other partners, created the company Panavision. While working as an administrator there, he was able to take occasional quick jobs as a cameraman. He was eventually forced out of Panavision in 1960, and devoted the rest of his career to filming. Nicholson's first job as cinematographer was working for his friend Richard Cunha on Cunha's second film '' She Demons'' in 1958. This was followed by work on Cunha’s '' Frankenstein's Daughter'' (also in 1958), and ''Missile to the Moon'' in 1959. Nicholson is credited with achieving amazing results on these films, despite severe budget and time limitations. Each of these films was shot in eight days or fewer. This al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerberus Capital Management
Cerberus Capital Management, L.P. is an American private equity firm,Leaders Magazine"Providing Economic Opportunity: An Interview with The Honorable Dan Quayle, Chairman, Cerberus Global Investments, LLC". specializing in distressed investing. The firm is based in New York City, and run by Steve Feinberg, who co-founded Cerberus in 1992, with William L. Richter, who serves as a senior managing director. The firm has affiliate and advisory offices in the United States, Europe and Asia. Cerberus has around US$55 billion under management in funds and accounts. The company is a U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission Registered Investment Adviser. Investors include government and private sector pension and retirement funds, charitable foundations, university endowments, insurance companies, family savings and sovereign wealth funds. History Cerberus is named after the mythological three-headed dog that guarded the gates of Hell. Feinberg has stated that while the Cerberus n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_(14929131291).jpg)