|
Palmatolepidae
Palmatolepidae is an extinct conodont family. It is part of the clade Prioniodontida, also known as the "complex conodonts".Conodonts Meet Cladistics: Recovering Relationships and Assessing the Completeness of the Conodont Fossil Record. Philip C J Donoghue, Palaeontology, 44(1), pages 65-93, November 2003, References External links Palmatolepidaeat fossilworks Fossilworks is a portal which provides query, download, and analysis tools to facilitate access to the Paleobiology Database, a large relational database assembled by hundreds of paleontologists from around the world. History Fossilworks was crea ....org (retrieved 30 April 2016) Ozarkodinida families {{Conodont-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polygnathacea
Polygnathacea is an extinct superfamily of conodonts. Families Families are, * † Cavusgnathidae Clark ''et al.'', 1981 * †Palmatolepidae Müller, 1956 * †Polygnathidae Polygnathidae is an extinct family of conodonts. References External links * Polygnathidaeat fossilworks Fossilworks is a portal which provides query, download, and analysis tools to facilitate access to the Paleobiology Database, a la ... Bassler, 1925 References * Ontogeny and trophic types of some Tournaisian Polygnathacea (Conodonta). AV Zhuravlev - Courier Forschungsinstitut Senckenberg, 1995 * Variation in the outline and distribution of epithelial cell imprints on the surface of polygnathacean conodont elements. AV Zhuravlev - Lethaia, 2001 - Wiley Online Library * The architecture and function of Carboniferous polygnathacean conodont apparatuses. RJ Aldridge, MP Smith, RD Norby… - Palaeobiology of …, 1987 - Halsted Press External links * Polygnathaceaat fossilworks.org (ret ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palmatolepis
''Palmatolepis'' is an extinct conodont genus in the family Palmatolepidae. It was the most abundant genus of conodonts of the Late Devonian, disappearing during the Devonian/Carboniferous crisis. Species * †''Palmatolepis glabra'' * †''Palmatolepis hassi''Locality and horizon: Upper part of the Grey Member, Ferques Formation, La Parisienne quarry (now flooded), Pas-de-Calais, France. Specimen from lowermost Ag. triangularis Conodont Zone, equivalent to late Palmatolepis hassi Zone (ca. 373 Ma, Frasnian). * †''Palmatolepis khaensis'' Savage 2013 * †''Palmatolepis marki'' Savage 2013 * †''Palmatolepis spallettae'' * †''Palmatolepis subperlobata'' ** †''Palmatolepis subperlobata lapoensis'' Savage 2013 * †''Palmatolepis triangularis'' * †''Palmatolepis unicornis'' Use in stratigraphy The Famennian (372.2 ± 1.6 mya) is defined by a GSSP Golden Spike located at Coumiac quarry, Montagne Noire, France where there is a biologic abundant occurrence of ''Palmatol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
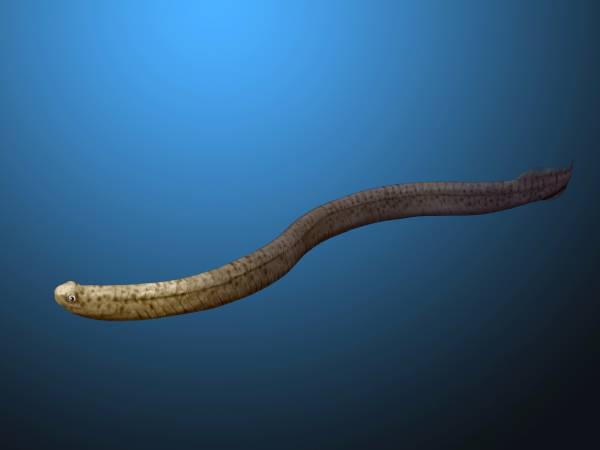
Conodont
Conodonts ( Greek ''kōnos'', " cone", + ''odont'', "tooth") are an extinct group of agnathan (jawless) vertebrates resembling eels, classified in the class Conodonta. For many years, they were known only from their tooth-like oral elements, which are usually found in isolation and are now called conodont elements. Knowledge about soft tissues remains limited. They existed in the world's oceans for over 300 million years, from the Cambrian to the beginning of the Jurassic. Conodont elements are widely used as index fossils, fossils used to define and identify geological periods. The animals are also called Conodontophora (conodont bearers) to avoid ambiguity. Discovery and understanding of conodonts The teeth-like fossils of the conodont were first discovered by Heinz Christian Pander and the results published in Saint Petersburg, Russia, in 1856. The name ''pander'' is commonly used in scientific names of conodonts. It was only in the early 1980s that the first fossil eviden ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ozarkodinida
Ozarkodinida is an extinct conodont order. It is part of the clade Prioniodontida, also known as the "complex conodonts". Name Ozarkodinida is named after the Ozark Mountains of Missouri Missouri is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. Ranking 21st in land area, it is bordered by eight states (tied for the most with Tennessee): Iowa to the north, Illinois, Kentucky and Tennessee to the east, Arkansas t ..., United States. Elements The feeding apparatus of ozarkodinids is composed at the front of an axial Sa element, flanked by two groups of four close-set elongate Sb and Sc elements which were inclined obliquely inwards and forwards. Above these elements lay a pair of arched and inward pointing (makellate) M elements. Behind the S-M array lay transversely oriented and bilaterally opposed (pectiniform, i.e. comb-shaped) Pb and Pa elements. References External links * * Prehistoric jawless fish orders {{Conodont-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prioniodontida
Prioniodontida, also known as the "complex conodonts", is a large clade of conodonts that includes two major evolutionary grades; the Prioniodinina and the Ozarkodinina. It includes many of the more famous conodonts, such as the giant ordovician ''Promissum'' (Prioniodinina) from the Soom Shale and the Carboniferous specimens from the Granton Shrimp bed (Ozarkodinina). They are euconodonts, in that their elements are composed of two layers; the crown and the basal body, and are assumed to be a clade A clade (), also known as a monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that are monophyletic – that is, composed of a common ancestor and all its lineal descendants – on a phylogenetic tree. Rather than the English ter .... Phylogeny This is a recent cladogram of the Prioniodontida, simplified from Donoghue ''et al.'', (2008). Notes References {{Taxonbar, from=Q6581502 Vertebrate unranked clades ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conodont
Conodonts ( Greek ''kōnos'', " cone", + ''odont'', "tooth") are an extinct group of agnathan (jawless) vertebrates resembling eels, classified in the class Conodonta. For many years, they were known only from their tooth-like oral elements, which are usually found in isolation and are now called conodont elements. Knowledge about soft tissues remains limited. They existed in the world's oceans for over 300 million years, from the Cambrian to the beginning of the Jurassic. Conodont elements are widely used as index fossils, fossils used to define and identify geological periods. The animals are also called Conodontophora (conodont bearers) to avoid ambiguity. Discovery and understanding of conodonts The teeth-like fossils of the conodont were first discovered by Heinz Christian Pander and the results published in Saint Petersburg, Russia, in 1856. The name ''pander'' is commonly used in scientific names of conodonts. It was only in the early 1980s that the first fossil eviden ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Kingdom (biology), biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals Heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, are Motility, able to move, can Sexual reproduction, reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage in which their body consists of a hollow sphere of Cell (biology), cells, the blastula, during Embryogenesis, embryonic development. Over 1.5 million Extant taxon, living animal species have been Species description, described—of which around 1 million are Insecta, insects—but it has been estimated there are over 7 million animal species in total. Animals range in length from to . They have Ecology, complex interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as zoology. Most living animal species are in Bilateria, a clade whose members have a Symmetry in biology#Bilate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |