|
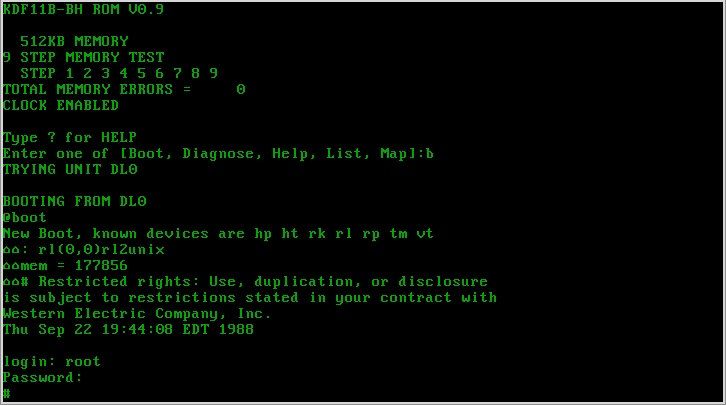
PDP-11
The PDP-11 is a series of 16-bit minicomputers sold by Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) from 1970 into the 1990s, one of a set of products in the Programmed Data Processor (PDP) series. In total, around 600,000 PDP-11s of all models were sold, making it one of DEC's most successful product lines. The PDP-11 is considered by some experts to be the most popular minicomputer. The PDP-11 included a number of innovative features in its instruction set and additional general-purpose registers that made it much easier to program than earlier models in the PDP series. Further, the innovative Unibus system allowed external devices to be easily interfaced to the system using direct memory access, opening the system to a wide variety of peripherals. The PDP-11 replaced the PDP-8 in many real-time computing applications, although both product lines lived in parallel for more than 10 years. The ease of programming of the PDP-11 made it very popular for general-purpose computing uses a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Equipment Corporation
Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC ), using the trademark Digital, was a major American company in the computer industry from the 1960s to the 1990s. The company was co-founded by Ken Olsen and Harlan Anderson in 1957. Olsen was president until forced to resign in 1992, after the company had gone into precipitous decline. The company produced many different product lines over its history. It is best known for the work in the minicomputer market starting in the mid-1960s. The company produced a series of machines known as the PDP line, with the PDP-8 and PDP-11 being among the most successful minis in history. Their success was only surpassed by another DEC product, the late-1970s VAX "supermini" systems that were designed to replace the PDP-11. Although a number of competitors had successfully competed with Digital through the 1970s, the VAX cemented the company's place as a leading vendor in the computer space. As microcomputers improved in the late 1980s, especially ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RSTS/E
RSTS () is a multi-user time-sharing operating system developed by Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC, now part of Hewlett-Packard) for the PDP-11 series of 16-bit minicomputers. The first version of RSTS (RSTS-11, Version 1) was implemented in 1970 by DEC software engineers that developed the TSS-8 time-sharing operating system for the PDP-8. The last version of RSTS (RSTS/E, Version 10.1) was released in September 1992. RSTS-11 and RSTS/E are usually referred to just as "RSTS" and this article will generally use the shorter form. RSTS-11 supports the BASIC programming language, an extended version called BASIC-PLUS, developed under contract by ''Evans Griffiths & Hart'' of Boston,. Starting with RSTS/E version 5B, DEC added support for additional programming languages by emulating the execution environment of the RT-11 and RSX-11 operating systems. Acronyms and abbreviations *BTSS (Basic Time Sharing System – never marketed) – The first name for RSTS. *CCL (Concise Comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RSX-11
RSX-11 is a discontinued family of multi-user real-time operating systems for PDP-11 computers created by Digital Equipment Corporation. In widespread use through the late 1970s and early 1980s, RSX-11 was influential in the development of later operating systems such as OpenVMS, VMS and Windows NT. As the original ''Real-Time System Executive'' name suggests, RSX was designed (and commonly used) for real time use, with process control a major use, thereof. It was also popular for program development and general computing. History Name and origins RSX-11 began as a port to the PDP-11 architecture of the earlier RSX-15 operating system for the PDP-15 minicomputer, first released in 1971. The main architect for RSX-15 (later renamed XVM/RSX) was Dennis “Dan” Brevik. Commenting on the ''RSX'' acronym, Brevik says: RSX-11D and IAS The porting effort first produced small paper tape based real-time executives (RSX-11A, RSX-11C) which later gained limited support for disks (RSX ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RT-11
RT-11 (Real-time 11) is a discontinued small, low-end, single-user real-time operating system for the full line of Digital Equipment Corporation PDP-11 16-bit computers. RT-11 was first implemented in 1970. It was widely used for real-time computing systems, process control, and data acquisition across all PDP-11s. It was also used for low-cost general-use computing. Features Multitasking RT-11 systems did not support preemptive multitasking, but most versions could run multiple simultaneous applications. All variants of the monitors provided a ''background job''. The FB, XM, and ZM monitors also provided a ''foreground job'', and six ''system jobs'' if selected via the SYSGEN system generation program. These tasks had fixed priorities, with the background job lowest and the foreground job highest. It was possible to switch between jobs from the system console user interface, and SYSGEN could generate a monitor that provided a single background job (the SB, XB and ZB variants). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Programmed Data Processor
Programmed Data Processor (PDP), referred to by some customers, media and authors as "Programmable Data Processor," is a term used by the Digital Equipment Corporation from 1957 to 1990 for several lines of minicomputers. The name 'PDP' intentionally avoids the use of the term 'computer'. At the time of the first PDPs, computers had a reputation of being large, complicated, and expensive machines. The venture capitalists behind Digital (especially Georges Doriot) would not support Digital's attempting to build a 'computer' and the term 'minicomputer' had not yet been coined. So instead, Digital used their existing line of logic modules to build a ''Programmed Data Processor'' and aimed it at a market that could not afford the larger computers. The various PDP machines can generally be grouped into families based on word length. Series Members of the PDP series include: ;PDP-1: The original PDP, an 18-bit 4-rack machine used in early time-sharing operating system work, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seventh Edition Unix
Seventh Edition Unix, also called Version 7 Unix, Version 7 or just V7, was an important early release of the Unix operating system. V7, released in 1979, was the last Bell Laboratories release to see widespread distribution before the commercialization of Unix by AT&T Corporation in the early 1980s. V7 was originally developed for Digital Equipment Corporation's PDP-11 minicomputers and was later ported to other platforms. Overview Unix versions from Bell Labs were designated by the edition of the user's manual with which they were accompanied. Released in 1979, the Seventh Edition was preceded by Sixth Edition, which was the first version licensed to commercial users. Development of the Research Unix line continued with the Eighth Edition, which incorporated development from 4.1BSD, through the Tenth Edition, after which the Bell Labs researchers concentrated on developing Plan 9. V7 was the first readily portable version of Unix. As this was the era of minicomputers, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2BSD
The History of the Berkeley Software Distribution begins in the 1970s. 1BSD (PDP-11) The earliest distributions of Unix from Bell Labs in the 1970s included the source code to the operating system, allowing researchers at universities to modify and extend Unix. The operating system arrived at Berkeley in 1974, at the request of computer science professor Bob Fabry who had been on the program committee for the Symposium on Operating Systems Principles where Unix was first presented. A PDP-11/45 was bought to run the system, but for budgetary reasons, this machine was shared with the mathematics and statistics groups at Berkeley, who used RSTS, so that Unix only ran on the machine eight hours per day (sometimes during the day, sometimes during the night). A larger PDP-11/70 was installed at Berkeley the following year, using money from the Ingres database project. Also in 1975, Ken Thompson took a sabbatical from Bell Labs and came to Berkeley as a visiting professor. He helped to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DEC BATCH-11/DOS-11
BATCH-11/DOS-11, also known simply as DOS-11, is a discontinued operating system by Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) of Maynard, Massachusetts. The first version of DOS-11 (V08-02) was released in 1970 and was the first operating system to run on the Digital PDP-11 minicomputer. DOS-11 was not known to be easy to use even in its day and became much less used in 1973 with the release of the RT-11 operating system. Features DOS-11 included: * DOS-Monitor * Edit-11 (text editor) * FORTRAN IV (programming language) * Libr-11 (librarian) * Link-11 (linker) * ODT-11R ( debugging program) * PAL-11R (assembler) * PIP (file utility package) DOS-11 came with XXDP, a diagnostics and monitor program for the PDP-11. Like other Digital operating systems, DOS-11 also had a FORTRAN-IV (Ansi-66) compiler. FORTRAN-IV was not supported on PDP-11 systems with less than 12K of memory. DOS-11 systems running in 8K and 12K configurations ran a limited version of the MACRO-11 Assembler (PAL-11R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MUMPS
MUMPS ("Massachusetts General Hospital Utility Multi-Programming System"), or M, is an imperative, high-level programming language with an integrated transaction processing key–value database. It was originally developed at Massachusetts General Hospital for managing hospital laboratory information systems. MUMPS technology has since expanded as the predominant database for health information systems and electronic health records in the United States. MUMPS-based information systems run over 40% of the hospitals in the U.S., run across all of the U.S. federal hospitals and clinics, and provide health information services for over 54% of patients across the U.S. A unique feature of the MUMPS technology is its integrated database language, allowing direct, high-speed read-write access to permanent disk storage. This provides tight integration of unlimited applications within a single database, and provides extremely high performance and reliability as an online transaction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultrix
Ultrix (officially all-caps ULTRIX) is the brand name of Digital Equipment Corporation's (DEC) discontinued native Unix operating systems for the PDP-11, VAX, MicroVAX and DECstations. History The initial development of Unix occurred on DEC equipment, notably DEC PDP-7 and PDP-11 (Programmable Data Processor) systems. Later DEC computers, such as their VAX, also offered Unix. The first port to VAX, UNIX/32V, was finished in 1978, not long after the October 1977 announcement of the VAX, for which – at that time – DEC only supplied its own proprietary operating system, VMS. DEC's Unix Engineering Group (UEG) was started by Bill Munson with Jerry Brenner and Fred Canter, both from DEC's Customer Service Engineering group, Bill Shannon (from Case Western Reserve University), and Armando Stettner (from Bell Labs). Other later members of UEG included Joel Magid, Bill Doll, and Jim Barclay recruited from DEC's marketing and product management groups. Under Canter's direction, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unibus
The Unibus was the earliest of several computer bus and backplane designs used with PDP-11 and early VAX systems manufactured by the Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) of Maynard, Massachusetts. The Unibus was developed around 1969 by Gordon Bell and student Harold McFarland while at Carnegie Mellon University. The name refers to the unified nature of the bus; Unibus was used both as a system bus allowing the central processing unit to communicate with main memory, as well as a peripheral bus, allowing peripherals to send and receive data. Unifying these formerly separate busses allowed external devices to easily perform direct memory access (DMA) and made the construction of device drivers easier as control and data exchange was all handled through memory-mapped I/O. Unibus was physically large, which led to the introduction of Q-bus, which multiplexed some signals to reduce pin count. Higher performance PDP systems used Fastbus, essentially two Unibusses in one. The sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DECtape
DECtape, originally called Microtape, is a magnetic tape data storage medium used with many Digital Equipment Corporation computers, including the PDP-6, PDP-8, LINC-8, PDP-9, PDP-10, PDP-11, PDP-12, and the PDP-15. On DEC's 32-bit systems, VAX/VMS support for it was implemented but did not become an official part of the product lineup. DECtapes are 3/4 inch (19 mm) wide, and formatted into blocks of data that can each be read or written individually. Each tape stores 184K 12-bit PDP-8 words or 144K 18-bit words. Block size is 128 12-bit words (for the 12-bit machines), or 256 18-bit words for the other machines (16, 18, 32, or 36 bit systems). From a programming point of view, because the system is block-oriented and allows random seeking, DECtape behaves like a very slow disk drive. Origins DECtape has its origin in the LINCtape tape system, which was originally designed by Wesley Clark at the MIT Lincoln Laboratory as an integral part of the LINC computer. There a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)