|
Outline Of The Ottoman Empire
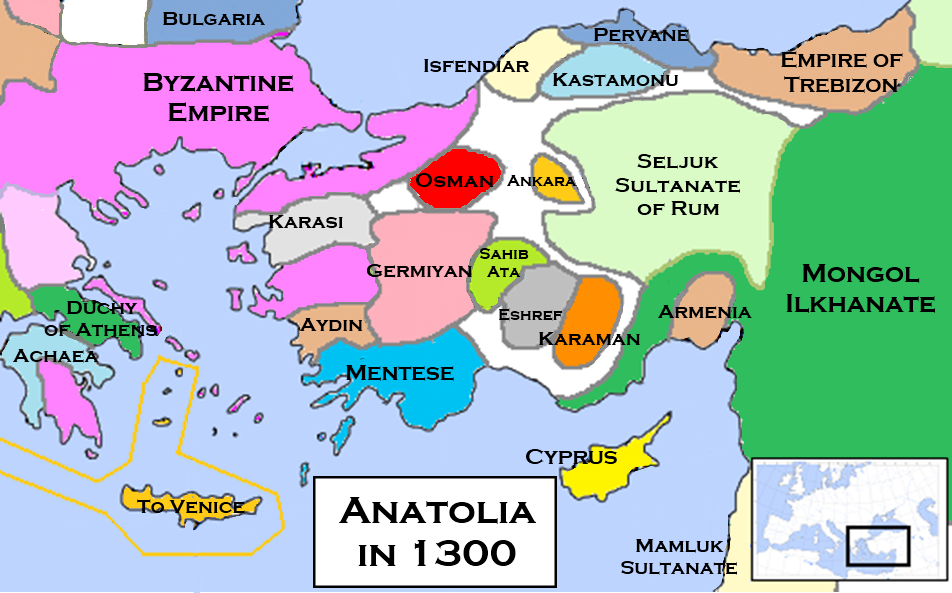
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to the Ottoman Empire: The Ottoman Empire was a Muslim empire that lasted from c. 1299 to 1922. It was also known by its European contemporaries as the Turkish Empire or Turkey after the principal ethnic group. At its zenith from the sixteenth to eighteenth centuries it controlled Southeast Europe, Southwest Asia and North Africa. General history Main periods * Rise of the Ottoman Empire * Classical Age of the Ottoman Empire * Transformation of the Ottoman Empire * Territorial evolution of the Ottoman Empire * Ottoman ancien régime * Decline and modernization of the Ottoman Empire * Defeat and dissolution of the Ottoman Empire * Partition Subperiods * Ottoman Interregnum * Sultanate of Women * Köprülü era * Tulip period * Tanzimat era * 1st Constitutional Era * 2nd Constitutional Era Historiography * Ottoman Decline Thesis * Ghaza thesis * Renegade thesis * Historiography of the fall of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tulip Period
The Tulip Period, or Tulip Era (Ottoman Turkish: لاله دورى, tr, Lâle Devri), is a period in Ottoman history from the Treaty of Passarowitz on 21 July 1718 to the Patrona Halil Revolt on 28 September 1730. This was a relatively peaceful period, during which the Ottoman Empire began to orient itself outwards. The name of the period derives from the tulip craze among the Ottoman court society. Cultivating this culturally ambiguous emblem had become a celebrated practice. The tulip period illustrated the conflicts brought by early modern consumer culture. During this period the elite and high-class society of the Ottoman period had established an immense fondness for the tulip, which were utilized in various occasions. Tulips defined nobility and privilege, both in terms of goods and leisure time. The Tulip Period, an era of relative peace and prosperity, saw a rebirth of Ottoman art and architecture (see Tulip Period architecture). During this period, Ottoman public ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demographics Of The Ottoman Empire
This article is about the demographics of the Ottoman Empire, including population density, ethnicity, education level, religious affiliations and other aspects of the population. Lucy Mary Jane Garnett Lucy Mary Jane Garnett (1849–1934) was a folklorist and traveller. She is best known for her work in Turkey. She also translated Greek folk poetry. See also *''Turkey of the Ottomans ''Turkey of the Ottomans'' is an anthropological boo ... stated in the 1904 book ''Turkish Life in Town and Country'', published in 1904, that "No country in the world, perhaps, contains a population so heterogeneous as that of Turkey."Lucy Garnett, Garnett, Lucy Mary Jane. ''Turkish Life in Town and Country''. G.P. Putnam's Sons, 1904. p1 Census Demographic data for most of the history of the Ottoman Empire is not quite precise. For most of the five centuries of its existence, the empire did not have easily computable valid data except figures for the number of employed citizens. Unti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoman Turkish Language
Ottoman Turkish ( ota, لِسانِ عُثمانى, Lisân-ı Osmânî, ; tr, Osmanlı Türkçesi) was the standardized register of the Turkish language used by the citizens of the Ottoman Empire (14th to 20th centuries CE). It borrowed extensively, in all aspects, from Arabic and Persian, and its speakers used the Ottoman Turkish alphabet for written communication. During the peak of Ottoman power (), words of foreign origin in Turkish literature in the Ottoman Empire heavily outnumbered native Turkish words, with Arabic and Persian vocabulary accounting for up to 88% of the Ottoman vocabulary in some texts.''Persian Historiography & Geography''Pustaka Nasional Pte Ltd p 69 Consequently, Ottoman Turkish was largely unintelligible to the less-educated lower-class and to rural Turks, who continued to use ("raw/vulgar Turkish"; compare Vulgar Latin and Demotic Greek), which used far fewer foreign loanwords and is the basis of the modern standard. The Tanzimât era (1839– ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Science And Technology In The Ottoman Empire
During its 600-year existence, the Ottoman Empire made significant advances in science and technology, in a wide range of fields including mathematics, astronomy and medicine. The Islamic Golden Age was traditionally believed to have ended in the thirteenth century, but has been extended to the fifteenth George Saliba (1994), ''A History of Arabic Astronomy: Planetary Theories During the Golden Age of Islam'', pp. 245, 250, 256–7, New York University Press, and sixteenthAhmad Y HassanFactors Behind the Decline of Islamic Science After the Sixteenth Century/ref> centuries by some, who have included continuing scientific activity in the Ottoman Empire in the west and in Persia and Mughal India in the east. Education Advancement of madrasah The madrasah education institution, which first originated during the Seljuk period, reached its highest point during the Ottoman reign.İnalcık, Halil. 1973. "Learning, the Medrese, and the Ulema." In ''The Ottoman Empire: The Cla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Culture Of The Ottoman Empire
Ottomans culture evolved over several centuries as the ruling administration of the Turks absorbed, adapted and modified the various native cultures of conquered lands and their peoples. There was influence from the customs and languages of Islamic societies, while Persian culture had a significant contribution through the Seljuq Turks, the Ottomans' predecessors. Despite newer added amalgamations, the Ottoman dynasty, like their predecessors in the Sultanate of Rum and the Seljuk Empire were influenced by Persian culture, language, habits and customs. Throughout its history, the Ottoman Empire had substantial subject populations of Orthodox subjects, Armenians, Jews and Assyrians, who were allowed a certain amount of autonomy under the ''millet'' system of Ottoman government, and whose distinctive cultures were adopted and adapted by the Ottoman state. As the Ottoman Empire expanded it assimilated the culture of numerous regions under its rule and beyond, being particularly in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Structure In The Ottoman Empire
There is considerable controversy regarding social status in the Ottoman Empire. Social scientists have developed class models on the socio-economic stratification of Ottoman society which feature more or less congruent theories. Albert Hourani described the Ottoman Empire as "a bureaucratic state, holding different regions within a single administrative and fiscal system". The Ottoman Empire lasted for over six hundred years (1299–1923) and encompassed present-day Turkey, the Balkans and the Fertile Crescent. Thus the Empire included an extremely diverse population ranging from the Muslim majority (Turks, Arabs, Bosniaks, Albanians, etc) to various minority populations, specifically Christians and Jews, whom Muslims referred to as "People of the Book". As an imperial/colonial enterprise, the Ottoman system allowed some Greeks, Tatars, Italians, Albanians, Serbs, Hungarians, Georgians, Bulgarians, Ruthenians and Circassians The Circassians (also referred to as Cherk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State Organization Of The Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire developed over the years as a despotism with the Sultan as the supreme ruler of a centralized government that had an effective control of its provinces, officials and inhabitants. Wealth and rank could be inherited but were just as often earned. Positions were perceived as titles, such as viziers and ''aghas''. Military service was a key to many problems. The expansion of the Empire called for a systematic administrative organization that developed into a dual system of military ("Central Government") and civil administration ("Provincial System") and developed a kind of separation of powers: higher executive functions were carried out by the military authorities and judicial and basic administration were carried out by civil authorities. Outside this system were various types of vassal and tributary states. Most of the areas ruled by the Ottomans were explicitly mentioned in the official full style of the sultan, including various lofty titles adopted to e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economic History Of The Ottoman Empire
The economic history of the Ottoman Empire covers the period 1299–1923. Trade, agriculture, transportation, and religion make up the Ottoman Empire's economy. The Ottomans saw military expansion of currency, more emphasis on manufacturing and industry in the wealth-power-wealth equation, and moving towards capitalist economics comprising expanding industries and markets. They continued along the trajectory of territorial expansion, traditional monopolies, cats, buildings, and agriculture. Transportation 16th, 17th, and 18th centuries Trade has always been an important aspect of an economy. It was no different in the 17th century. As the Ottoman Empire expanded, it started gaining control of important trade routes. The capture of Constantinople (1453) to the Ottoman Turks was a key event. Along with their victory, they now had significant control of the Silk Road, which European countries used to trade with Asia. Many sources state that the Ottoman Empire “blocked” the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Historiography Of The Fall Of The Ottoman Empire
The historiography of the Ottoman Empire refers to the studies, sources, critical methods and interpretations used by scholars to develop a history of the Ottoman Dynasty's empire. Scholars have long studied the Empire, looking at the causes for its formation (such as the Ghaza thesis), its relations to the Great Powers (such as Sick man of Europe) and other empires (such as Transformation of the Ottoman Empire), and the kinds of people who became imperialists or anti-imperialists (such as the Young Turks), together with their mindsets. The history of the breakdown of the Empire (such as Ottoman decline thesis) has attracted scholars of the histories of the Middle East (such as Partition of the Ottoman Empire), and Greece (Rise of nationalism in the Ottoman Empire). New Themes Western understanding of the Ottoman History. Ottoman history has been rewritten for political and cultural advantage and speculative theories rife with inconsistent research, ahistorical assumption ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ghaza Thesis
The Ghaza or Ghazi thesis (from ota, غزا, ''ġazā'', "holy war," or simply "raid") is a historical paradigm first formulated by Paul Wittek which has been used to interpret the nature of the Ottoman Empire during the earliest period of its history, the fourteenth century, and its subsequent history. The thesis addresses the question of how the Ottomans were able to expand from a small principality on the frontier of the Byzantine Empire into a centralized, intercontinental empire. According to the Ghaza thesis, the Ottomans accomplished this by attracting recruits to fight for them in the name of Islamic holy war against the non-believers. Such a warrior was known in Ottoman Turkish as a '' ghazi'', and thus this thesis sees the early Ottoman state as a "Ghazi State," defined by an ideology of holy war. The Ghaza Thesis dominated early Ottoman historiography throughout much of the twentieth century before coming under increasing criticism beginning in the 1980s. Histori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoman Decline Thesis
The Ottoman decline thesis or Ottoman decline paradigm ( tr, Osmanlı Gerileme Tezi) is an obsolete * * * * * Leslie Peirce, "Changing Perceptions of the Ottoman Empire: the Early Centuries," ''Mediterranean Historical Review'' 19/1 (2004): 22. * Cemal Kafadar, "The Question of Ottoman Decline," ''Harvard Middle Eastern and Islamic Review'' 4/1–2 (1997–98), pp. 30–75. * M. Fatih Çalışır, "Decline of a 'Myth': Perspectives on the Ottoman 'Decline'," ''The History School'' 9 (2011): 37–60. * Donald Quataert, "Ottoman History Writing and Changing Attitudes towards the Notion of 'Decline,'" ''History Compass'' 1 (2003) historical narrative which once played a dominant role in the study of the history of the Ottoman Empire. According to the decline thesis, following a golden age associated with the reign of Sultan Suleiman the Magnificent (r. 1520–1566), the empire gradually entered into a period of all-encompassing stagnation and decline from which it was never ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)


.jpg)