|
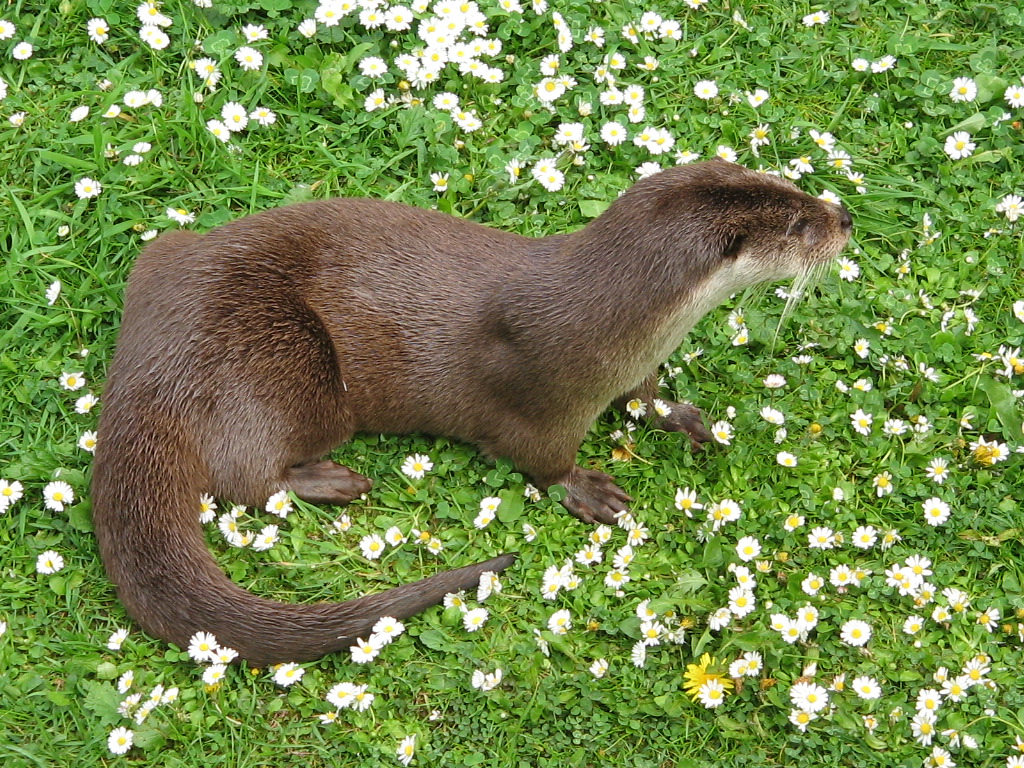
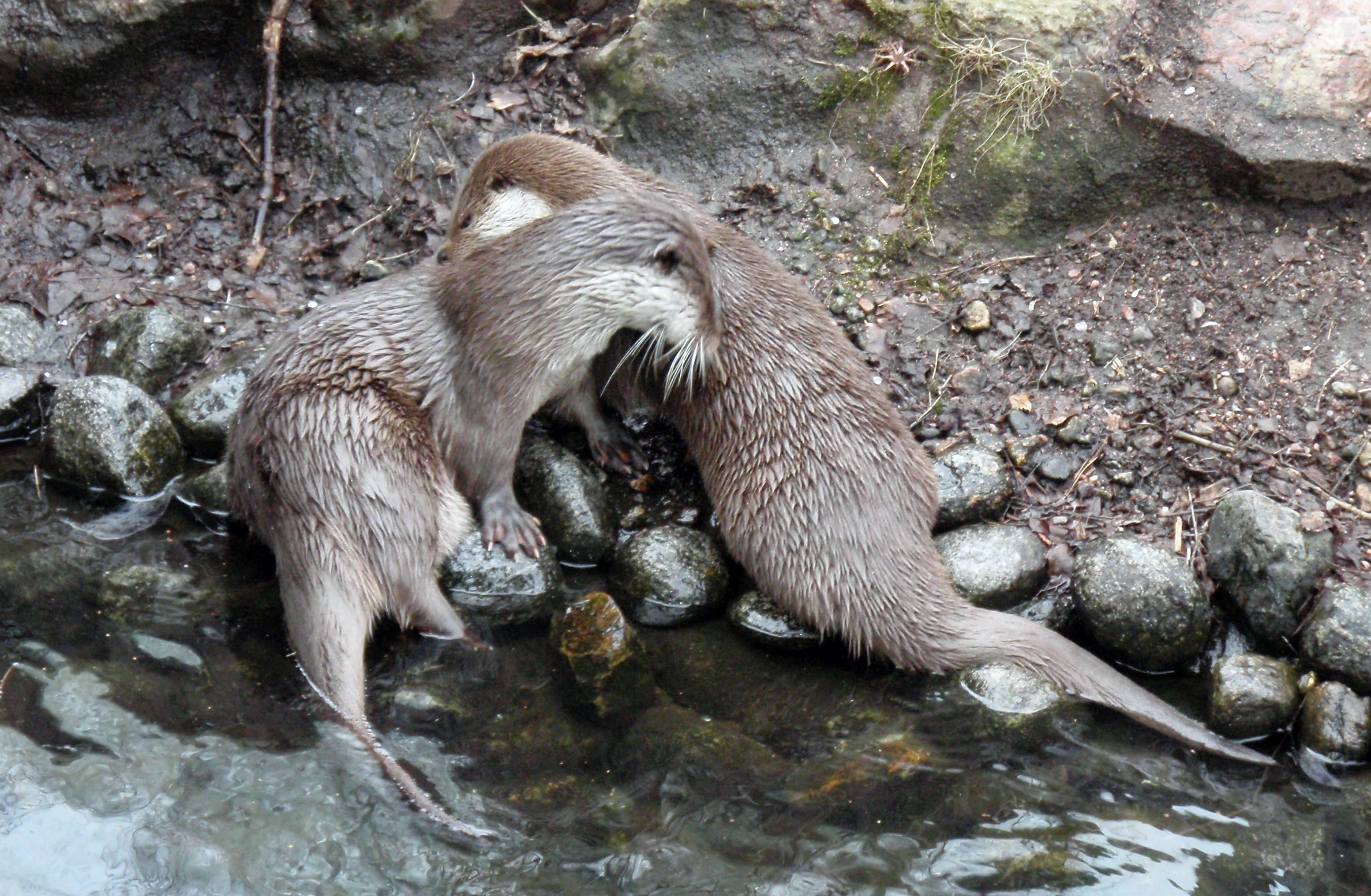
Otter
Otters are carnivorous mammals in the subfamily Lutrinae. The 13 extant otter species are all semiaquatic, aquatic, or marine, with diets based on fish and invertebrates. Lutrinae is a branch of the Mustelidae family, which also includes weasels, badgers, mink, and wolverines, among other animals. Etymology The word ''otter'' derives from the Old English word or . This, and cognate words in other Indo-European languages, ultimately stem from the Proto-Indo-European language root , which also gave rise to the English word "water". Terminology An otter's den is called a holt or couch. Male otters are called dogs or boars, females are called bitches or sows, and their offspring are called pups or cubs. The collective nouns for otters are bevy, family, lodge, romp (being descriptive of their often playful nature) or, when in water, raft. The feces of otters are typically identified by their distinctive aroma, the smell of which has been described as ranging from freshly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pteronura
The giant otter or giant river otter (''Pteronura brasiliensis'') is a South American carnivorous mammal. It is the longest member of the weasel family, Mustelidae, a globally successful group of predators, reaching up to . Atypical of mustelids, the giant otter is a social species, with family groups typically supporting three to eight members. The groups are centered on a dominant breeding pair and are extremely cohesive and cooperative. Although generally peaceful, the species is territorial, and aggression has been observed between groups. The giant otter is diurnal, being active exclusively during daylight hours. It is the noisiest otter species, and distinct vocalizations have been documented that indicate alarm, aggression, and reassurance. The giant otter ranges across north-central South America; it lives mostly in and along the Amazon River and in the Pantanal. Its distribution has been greatly reduced and is now discontinuous. Decades of poaching for its velvety ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eurasian Otter
The Eurasian otter (''Lutra lutra''), also known as the European otter, Eurasian river otter, common otter, and Old World otter, is a semiaquatic mammal native to Eurasia. The most widely distributed member of the otter subfamily (Lutrinae) of the weasel family (Mustelidae), it is found in the waterways and coasts of Europe, many parts of Asia, and parts of northern Africa. The Eurasian otter has a diet mainly of fish, and is strongly territorial. It is endangered in some parts of its range, but is recovering in others. Description The Eurasian otter is a typical species of the otter subfamily. Brown above and cream below, these long, slender creatures are well-equipped for their aquatic habits. Their bones show osteosclerosis, increasing their density to reduce buoyancy. This otter differs from the North American river otter by its shorter neck, broader visage, the greater space between the ears and its longer tail. However, the Eurasian otter is the only otter in much of its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
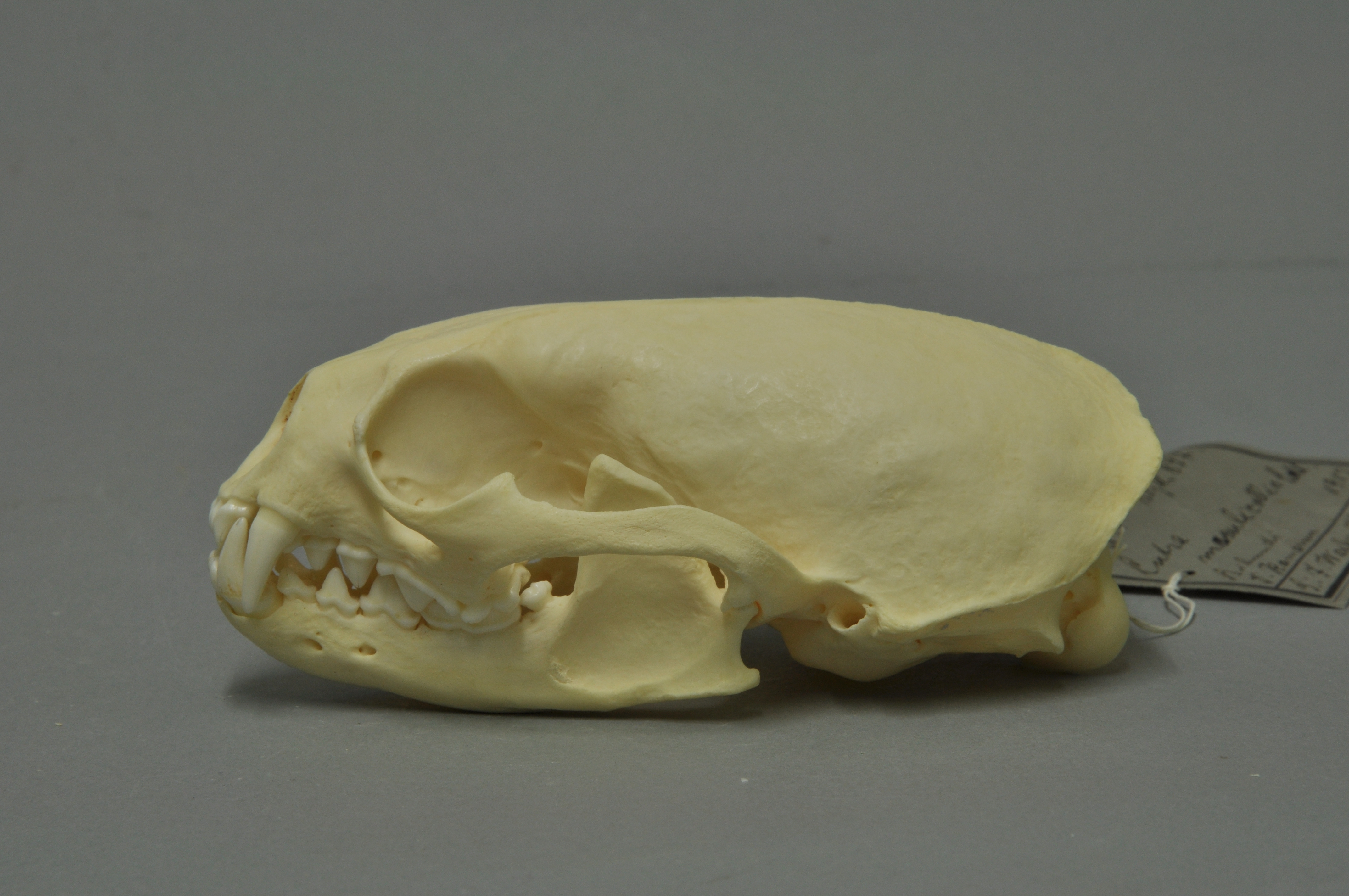
Aonyx
''Aonyx'' is a genus of otters, containing three species, the African clawless otter, the Congo clawless otter, and the Asian small-clawed otter. The word ''aonyx'' means "clawless", derived from the prefix '' a-'' ("without") and ''onyx'' ("claw/hoof"). Species Three species are currently recognised: Zoologists differ as to whether or not to include the Asian small-clawed otter in this genus, or in its own genus '' Amblonyx''. They also differ as to whether the Congo clawless otter is a species, or is conspecific Biological specificity is the tendency of a characteristic such as a behavior or a biochemical variation to occur in a particular species. Biochemist Linus Pauling stated that "Biological specificity is the set of characteristics of living organis ... with the African clawless otter. Notes References External links * * Mammal genera Otters Taxa named by René Lesson {{Carnivora-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrictis
The spotted-necked otter (''Hydrictis maculicollis''), or speckle-throated otter, is an otter native to sub-Saharan Africa. Description The spotted-necked otter is a relatively small species, with males measuring from nose to rump, and weighing , while females are and . The tail is long and muscular, measuring in both sexes. (2011). Like many other otters, it is sleek and has webbed paws for swimming. Females have two pairs of s, and while males have a large , the is hidden beneath the skin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enhydriodon
''Enhydriodon'' is an extinct genus of typically large otters that lived in what is now Kenya, Ethiopia, Uganda, Chad, South Africa, Pakistan, and India from the late Miocene up to early Pleistocene. The otter is thought to be a relative of modern-day sea otters. ''E. omoensis'' and ''E. dikikae'' are described as the largest mustelids to have ever existed, though only fragments of the genus have been found such as the skull, femur, and dental remains in Ethiopia. Multiple estimates put them at about while ''E. omoensis'' was described to be lion-sized, making them the largest mustelids described so far. Most species of the ''Enhydriodon'' genus are presumed to be semi-aquatic given most of the fossil isotope values being similar to fossilized semi-aquatic animals like hippopotamuses. The largest species, ''Enhydriodon omoensis'', however, was determined to be a terrestrial predator, capable of hunting herbivorous terrestrial prey. ''Enhydriodon'' is part of the bunodont otters g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megalenhydris
''Megalenhydris barbaricina'' is a Late Pleistocene giant otter from Sardinia. It is known from a single skeleton, discovered in the ''Grotta di Ispinigoli'' near Dorgali, and was described in 1987. The species is one of four extinct otter species from Sardinia and Corsica. The others are ''Algarolutra majori'', '' Lutra castiglionis''Pereira, E., and M. Salotti. "Cyrnolutra castiglionis, a new otter (Mustelidae, Lutrinae) from the Middle Pleistocene'Castiglione 3CG'deposit (Oletta, Corsica)." Comptes Rendus de l'Académie des Sciences, Séries IIA 331.1 (2000): 45-52/ref> and '' Sardolutra, Sardolutra ichnusae''. This otter was large, possibly even larger than the extant '' Pteronura'', which can reach two meters in length. The structure of the teeth points to a diet of shellfish and/or crustaceans. A special characteristic of the species is the flattening of the first few caudal vertebrae The spinal column, a defining synapomorphy shared by nearly all vertebrates,Hagfish ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mustelidae
The Mustelidae (; from Latin ''mustela'', weasel) are a family of carnivorous mammals, including weasels, badgers, otters, ferrets, martens, minks and wolverines, among others. Mustelids () are a diverse group and form the largest family in the suborder Caniformia of the order Carnivora. They comprise about 66 to 70 species in nine subfamilies. Variety Mustelids vary greatly in size and behaviour. The smaller variants of the least weasel can be under in length, while the giant otter of Amazonian South America can measure up to and sea otters can exceed in weight. Wolverines can crush bones as thick as the femur of a moose to get at the marrow, and have been seen attempting to drive bears away from their kills. The sea otter uses rocks to break open shellfish to eat. Martens are largely arboreal, while European badgers dig extensive tunnel networks, called setts. Only one mustelid has been domesticated; the ferret. Tayra are also kept as pets (although they requi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enhydritherium
''Enhydritherium terraenovae'' is an extinct marine otter endemic to North America that lived during the Miocene through Pliocene epochs from ~9.1–4.9 Ma. ( AEO), existing for approximately . The ancestral lineage of ''Enhydritherium terraenova'' can be traced to Africa and Eurasia, but no clear route of migration can be determined according to Thompson et al. Taxonomy ''Enhydritherium terraenovae'' was named by Berta and Morgan in 1985 and is the genotype for this animal. Its type locality is the phosphate Palmetto Mine in Florida, which is in a Hemphillian marginal marine sandstone in the Upper Bone Valley Formation of Florida. Fossil distribution Fossil specimens were found in California (3 sites) and Florida (8 sites). In 2017, part of a jawbone was found in the Juchipila Basin, Zacatecas , image_map = Zacatecas in Mexico (location map scheme).svg , map_caption = State of Zacatecas within Mexico , coordinates = , coor_pinpoi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lutrogale
''Lutrogale'' was proposed as generic name by John Edward Gray in 1865 for otters with a convex forehead and nose, using the smooth-coated otter '' L. perspicillata'' as type species. The genus also contains the following extinct and fossil species: *''L. cretensis'' – Cretan otter The Cretan otter ''(Lutrogale cretensis)'' is an extinct otter that was endemic to Crete during the Pleistocene. Taxonomy It was a close relative of the smooth-coated otter ''(L. perspicillata)'', whom today lives only in southern Asia but had ... *''L. palaeoleptonyx'' *''L. robusta'' References {{Taxonbar, from=Q2899249 Otters Mammal genera Mammal genera with one living species Taxa named by John Edward Gray ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lutra
''Lutra'' is a genus of otters, one of seven in the subfamily Lutrinae. Taxonomy and evolution The genus includes these species: Extant species Extinct species *†'' Lutra affinis'' *†'' Lutra bressana '' *†'' Lutra bravardi'' *†'' Lutra castiglionis'' *†'' Lutra euxena'' *†'' Lutra fatimazohrae'' *†'' Lutra franconica'' *†'' Lutra palaeindica'' *†'' Lutra simplicidens'' *†'' Lutra trinacriae'' The genus most likely evolved in Asia during the late Pliocene epoch; the oldest fossil belonging to the genus is of the species ''L. palaeindica'', and dates from the late Pliocene. Habitat ''Lutra'' species are semiaquatic mammals, so they are well-adapted to both water and land. They prefer shallow, narrow areas of streams surrounded by mature trees and with rocks, especially where weirs reduce the flow of the water, as well as attract fishes. They seem to tolerate roads and residential and agricultural areas, but only moderate human interaction. They clearly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lontra
''Lontra'' is a genus of otters from the Americas. Species These species were previously included in the genus ''Lutra'', together with the Eurasian otter The Eurasian otter (''Lutra lutra''), also known as the European otter, Eurasian river otter, common otter, and Old World otter, is a semiaquatic mammal native to Eurasia. The most widely distributed member of the otter subfamily (Lutrinae) of th ..., but they have now been moved to a separate genus. The genus comprises four living and one known fossil species: Extant species Extinct species References Otters Mammal genera Taxa named by John Edward Gray {{Carnivora-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enhydra
''Enhydra'' is a genus of mustelid that contains the sea otter and two extinct relatives. It is the only extant genus of the bunodont otters group, referring to otters with non-blade carnassials with rounded cusps. Sea otters probably diverged from other otters during the Pliocene, approximately 5 mya. They probably arose from the closely related ''Enhydritherium'', a bunodont otter endemic to North America during the late Miocene and early Pliocene epochs. '' Enhydra reevei'', the oldest known species, has its origins in the Atlantic, suggesting this may have been where sea otters originated. Fossil evidence indicates the ''Enhydra'' lineage became isolated in the North Pacific The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the continen ... approximately 2 million years ago, giving rise to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)