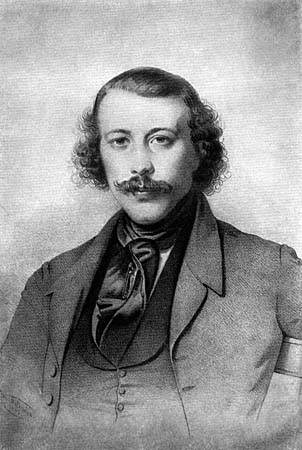|
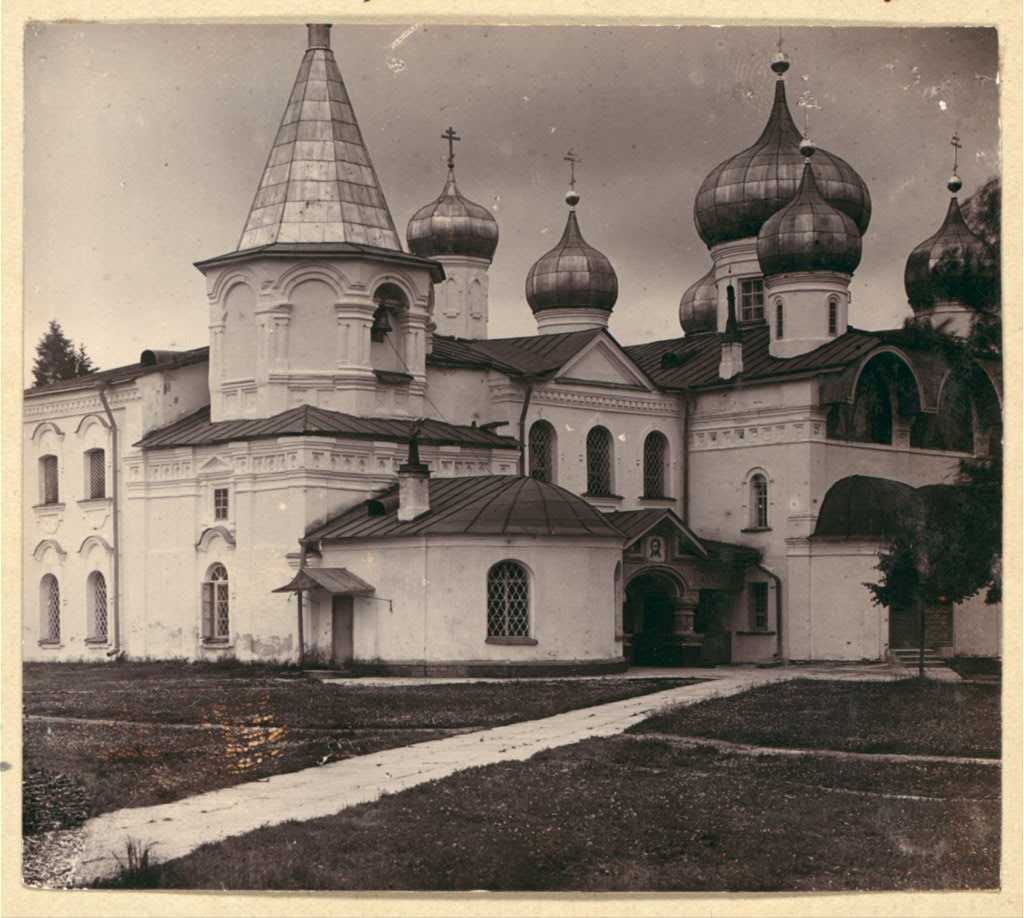
Olonets
Olonets (russian: Оло́нец; krl, Anus, olo, Anuksenlinnu; fi, Aunus, Aunuksenkaupunki or Aunuksenlinna) is a town and the administrative center of Olonetsky District of the Republic of Karelia, Russia, located on the Olonka River to the east of Lake Ladoga. Population: History Olonets is the oldest documented settlement in Karelia, mentioned by Novgorodian sources as early as 1137. Its history is obscure until 1649, when a fortress was built there to protect the Grand Duchy of Moscow against the Swedes. The same year it was granted town privileges. Until the Great Northern War, Olonets developed as a principal market for Russian trade with Sweden. To the south from the town, there sprawled a belt of fortified abbeys, of which the Alexander-Svirsky Monastery was the most important. In the 18th century, Olonets' importance shifted from trade to ironworking industries. In 1773, it was made the seat of Olonets Governorate. Eleven years later, however, the seat was move ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olonets Governorate
The Olonets Governorate or Government of Olonets was a '' guberniya'' (governorate) of north-western Imperial Russia, extending from Lake Ladoga almost to the White Sea, bounded west by Finland, north and east by Arkhangelsk and Vologda, and south by Novgorod and Saint Petersburg. The area was 57,422 m², of which 6,794 m² were covered by lakes. Geology Its north-western portion belonged orographically and geologically to the Finland region; it is thickly dotted with hills reaching 1,000 ft. in altitude, and diversified by numberless smaller ridges and hollows running from northwest to south-east. The rest of the governorate was a flat plateau sloping towards the marshy lowlands of the south. The geological structure was very varied. Granites, syenites, and diorites, covered with Laurentian metamorphic slates, occurred extensively in the north-west. Near Lake Onega they were overlain with Devonian sandstones and limestones, yielding marble and sandstone for buil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olonetsky District
{{Geodis ...
Olonetsky (masculine), Olonetskaya (feminine), or Olonetskoye (neuter) may refer to: * Olonetsky District, a district of the Republic of Karelia, Russia *Olonetskoye Urban Settlement, a municipal formation incorporating the town of Olonets and eight rural localities in Olonetsky District of the Republic of Karelia, Russia *Olonets Governorate (''Olonetskaya guberniya''), a governorate of the Russian Empire *Olonets Viceroyalty (''Olonetskoye namestnichestvo''), a viceroyalty of the Russian Empire bordering Vologda Viceroyalty * Olonets Oblast (''Olonetskaya oblast''), a division of the Russian Empire, originally in Novgorod Viceroyalty Novgorod Viceroyalty (russian: Новгоро́дское наме́стничество) was an administrative division (a '' namestnichestvo'') of the Russian Empire, which existed in 1776–1796. The seat of the Viceroyalty was located in Novg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Republic Of Karelia
The Republic of Karelia (russian: Респу́блика Каре́лия, Respublika Kareliya; ; krl, Karjalan tašavalta; ; fi, Karjalan tasavalta; vep, Karjalan Tazovaldkund, Ludic: ''Kard’alan tazavald''), also known as just Karelia (russian: Каре́лия, Ка́рьяла; krl, Karjala), is a republic of Russia situated in Northwest Russia. The republic is a part of the Northwestern Federal District, and covers an area of , with a population of 603,067 residents. Its capital is Petrozavodsk. The modern Karelian Republic was founded as an autonomous republic within the Russian SFSR by the Resolution of the Presidium of the All-Russian Central Executive Committee (VTsIK) on 27 June 1923 and by the Decree of the VTsIK and the Council of People's Commissars of 25 July 1923, from the Karelian Labour Commune. From 1940 to 1956, it was known as the Karelo-Finnish Soviet Socialist Republic, one of the union republics in the Soviet Union. In 1956, it was once again mad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Witold Pilecki
Witold Pilecki (13 May 190125 May 1948; ; codenames ''Roman Jezierski, Tomasz Serafiński, Druh, Witold'') was a Polish World War II cavalry officer, intelligence agent, and resistance leader. As a youth, Pilecki joined Polish underground scouting, and in the aftermath of World War I, Polish militia and later, the Polish Army. He participated in the Polish-Soviet War which ended in 1921. In 1939 he participated in the unsuccessful defense of Poland against the German invasion and shortly afterward, joined the Polish resistance, co-founding the Secret Polish Army resistance movement. In 1940 Pilecki volunteered to allow himself to be captured by the occupying Germans in order to infiltrate the Auschwitz concentration camp. At Auschwitz he organized a resistance movement that eventually included hundreds of inmates, and he secretly drew up reports detailing German atrocities at the camp, which were smuggled out to Home Army headquarters and shared with the Western Allies. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olonka River
The Olonka (russian: Олонка) is a river in the Republic of Karelia, Russia. It gave the name to the town of Olonets by the river and eventually to the surrounding territory (Olonets Governorate, Olonets Krai, now Olonetsky District Olonetsky (masculine), Olonetskaya (feminine), or Olonetskoye (neuter) may refer to: * Olonetsky District, a district of the Republic of Karelia, Russia *Olonetskoye Urban Settlement, a municipal formation incorporating the town of Olonets and eight ...). It flows out of the reservoir Utozero and discharges into Lake Ladoga. It is long, and has a drainage basin of . The 1906 Russian ''Brockhaus and Efron Encyclopedic Dictionary'' writes that Olonka flows from Lake Topornoye, through lakes Vagvozero, Utozero and Torosozero, and eventually to Lake Ladoga. This section is now referred to as Topornaya (Топорная). The highest point of this drainage chain is Kaskozero, which overspills into Lake Pyyre Järvi ( Pyureyarvi, Пюреярв ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petrozavodsk
Petrozavodsk (russian: Петрозаводск, p=pʲɪtrəzɐˈvotsk; Karelian, Vepsian and fi, Petroskoi) is the capital city of the Republic of Karelia, Russia, which stretches along the western shore of Lake Onega for some . The population of the city was 280,890 as of 2022. Etymology The name of the city is a combination of words Peter ( Peter the Great) and ''zavod'' (meaning factory). It was previously known as ''Shuysky Zavod'' (1703–1704) and ''Petrovskaya Sloboda'' (1704–1777), which was the first name of the city related to Peter the Great. It was renamed to Petrozavodsk after Catherine the Great granted the settlement the status of a city. An ancient Swedish name was ''Onegaborg'', known from a map from 1592 of the Flemish cartographer Abraham Ortelius, and hence translated to Finnish as ''Äänislinna'', a name used during the occupation of Eastern Karelia by Finnish forces during the Continuation War (1941–1944) in the context of World War II. History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karelians
Karelians ( krl, karjalaižet, karjalazet, karjalaiset, Finnish: , sv, kareler, karelare, russian: Карелы) are a Finnic ethnic group who are indigenous to the historical region of Karelia, which is today split between Finland and Russia. Karelians living in Russian Karelia are considered a distinct ethnic group closely related to Finnish Karelians, who are considered a subset of Finns. This distinction historically arose from Karelia having been fought over and eventually split between Sweden and Novgorod, resulting in Karelians being under different cultural spheres. In Russia, Karelians mostly live in the Republic of Karelia, where they are the designated ethnic group, and in other adjacent north-western parts of the country. They traditionally speak the Karelian language and are Eastern Orthodox Christians. There are also significant Karelian enclaves in the Tver and Novgorod oblasts, as some Karelians migrated to those areas after the Russo-Swedish War of 165 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander-Svirsky Monastery
Alexander-Svirsky Monastery (Александро-Свирский монастырь) is a Russian Orthodox monastery situated deep in the woods of the Leningrad Oblast, just south from its border with the Republic of Karelia. The golden age of this cloister was in the 17th century. It boasts one of the few preserved three-tented belfries and medieval clock towers in Russia. The abbey was founded in 1487, when a monk of the Valaam Monastery, named Alexander, settled between Roshchinsky and Holy lakes, 20 km to the east from Lake Ladoga and 6 km from the Svir River. During his life in the woods, he had a vision of the Holy Trinity who ordered him to build two oaken chapels dedicated to the Trinity and the Saviour's Transfiguration. These churches gave birth to the twin Trinity and the Transfiguration cloisters, collectively known as the Alexander Svirsky Monastery. The monastery's founder died on August 30, 1533, and was buried at the Transfiguration cloister, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karelia
Karelia ( Karelian and fi, Karjala, ; rus, Каре́лия, links=y, r=Karélija, p=kɐˈrʲelʲɪjə, historically ''Korjela''; sv, Karelen), the land of the Karelian people, is an area in Northern Europe of historical significance for Russia (including the Soviet era), Finland, and Sweden. It is currently divided between northwestern Russia (specifically the federal subjects of the Republic of Karelia and Leningrad Oblast) and Finland (the regions of South Karelia, North Karelia, and the eastern portion of modern-day Kymenlaakso). Use of name Various subdivisions may be called Karelia. Finnish Karelia was a historical province of Finland, and is now divided between Finland and Russia, often called just ''Karjala'' in Finnish. The eastern part of this chiefly Lutheran area was ceded to Russia after the Winter War of 1939–40. The Republic of Karelia is a Russian federal subject, including East Karelia with a chiefly Russian Orthodox population. Within pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walery Mroczkowski
Walery Karłowicz Mroczkowski (6 April 1840 – 1 October 1889) was a Polish insurgent in the 1863 January Uprising. He was arrested and imprisoned by the Prussian authorities. Upon release in 1865, he was sent into exile and travelled to Italy, Switzerland, London and finally settled in France. While in Florence he met Mikhail Bakunin and became an anarchist and a member of the latter's close circle. He is also known as a portrait photographer in France, working under the pseudonym, "Ostroga" or "Valerien Ostroga". Early life Nothing is known, at present, of Mroczkowski's family background or childhood. As the earliest written record, the diary of his uprising colleague Szymon Kotylla published in 1907, indicates that he was a student at the Medical Academy in Warsaw (1860–1861), he would have had access to funds for his interrupted studies and for travel to Italy for military training. As a convinced patriot he went to Cuneo in Italy to attend the Polish military cadet schoo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mikhail Bakunin
Mikhail Alexandrovich Bakunin (; 1814–1876) was a Russian revolutionary anarchist, socialist and founder of collectivist anarchism. He is considered among the most influential figures of anarchism and a major founder of the revolutionary socialist and social anarchist tradition. Bakunin's prestige as a revolutionary also made him one of the most famous ideologues in Europe, gaining substantial influence among radicals throughout Russia and Europe. Bakunin grew up in Pryamukhino, a family estate in Tver Governorate. From 1840, he studied in Moscow, then in Berlin hoping to enter academia. Later in Paris, he met Karl Marx and Pierre-Joseph Proudhon, who deeply influenced him. Bakunin's increasing radicalism ended hopes of a professorial career. He was expelled from France for opposing The Russian Empire's occupation of Poland. In 1849, he was arrested in Dresden for his participation in the Czech rebellion of 1848 and deported to Russian Empire, where he was imprisoned f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyrynsalmi
Hyrynsalmi is a municipality in Finland and is part of the Kainuu region. The municipality has a population of () and covers an area of of which is water. The population density is . The municipality is unilingually Finnish Finnish may refer to: * Something or someone from, or related to Finland * Culture of Finland * Finnish people or Finns, the primary ethnic group in Finland * Finnish language, the national language of the Finnish people * Finnish cuisine See also .... The world championships in swamp football is held annually in Hyrynsalmi. References External links Municipality of Hyrynsalmi– Official website Map of Hyrynsalmi(PDF file) Municipalities of Kainuu {{OuluProvince-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |