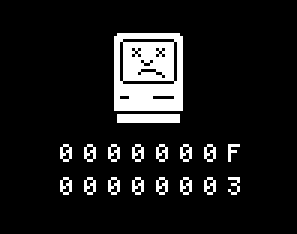|
Old World ROM
Old World ROM computers are the Macintosh (Mac) models that use a Macintosh Toolbox read-only memory (ROM) chip, usually in a socket (but soldered to the motherboard in some models). All Macs prior to the iMac, the iBook, the Blue and White Power Mac G3 and the Bronze Keyboard (Lombard) PowerBook G3 use Old World ROM, while said models, as well as all subsequent models until the introduction of the Intel-based EFI Models, are New World ROM machines. In particular, the Beige Power Mac G3 and all other beige and platinum-colored Power Macs are Old World ROM machines. In common use, the "Old World" designation usually applies to the early generations of PCI-based "beige" Power Macs (and sometimes the first NuBus-equipped models), but not the older Motorola 68000-based Macs; however, the Toolbox runs the same way on all three types of machines. Details PCI Power Macs with an Old World ROM contain an Open Firmware implementation, and a copy of the Macintosh Toolbox as an Open Fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mac 68K Emulator
The Mac 68k emulator is a software emulator built into all versions of the classic Mac OS for PowerPC. This emulator enabled running applications and system code that were originally written for the 680x0-based Macintosh models. With a few exceptions, notably Connectix's RAM Doubler, the emulator ran all software with no noticeable impact other than lower performance relative to the same program when compiled for PowerPC. Origins The first version was written by Gary Davidian, who had originally created it for use on the Motorola 88000 CPU, used in Apple's abortive first attempt at a RISC target platform. A later version, using dynamic recompilation, was developed by Eric Traut, who later worked on successful emulation projects at Connectix such as Virtual Game Station and Virtual PC. Prior to Traut's arrival there, Connectix had released Speed Doubler, which included an even faster PowerPC 68k emulator. Implementation All versions of this emulator emulated the "user" subset of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quik (boot Loader)
quik is a boot loader designed to start Linux on Apple Macintosh PowerPC systems based on the Old World ROM architecture. It was originally written by Paul Mackerras, and portions of its code were reused in all other Linux boot loaders for PowerPC, including the one known as BootX (not to be confused with the Mac OS X boot loader of the same name), which is dependent on the Mac OS. Quik's loader boots from Open Firmware and bypasses the Mac OS entirely. New World ROM systems use yaboot. It does not work on systems that do not have Open Firmware; older PowerPC hardware based on the NuBus architecture must boot into the Mac OS first and then use a separate boot loader. Quik is the only method of booting Linux on an Apple Network Server The Apple Network Server (ANS) was a line of PowerPC-based server computers designed, manufactured and sold by Apple Computer, Inc. from February 1996 to April 1997. It was codenamed "Shiner" and originally consisted of two models, the Network ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linux
Linux ( or ) is a family of open-source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically packaged as a Linux distribution, which includes the kernel and supporting system software and libraries, many of which are provided by the GNU Project. Many Linux distributions use the word "Linux" in their name, but the Free Software Foundation uses the name "GNU/Linux" to emphasize the importance of GNU software, causing some controversy. Popular Linux distributions include Debian, Fedora Linux, and Ubuntu, the latter of which itself consists of many different distributions and modifications, including Lubuntu and Xubuntu. Commercial distributions include Red Hat Enterprise Linux and SUSE Linux Enterprise. Desktop Linux distributions include a windowing system such as X11 or Wayland, and a desktop environment such as GNOME or KDE Plasma. Distributions inten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virtual Memory
In computing, virtual memory, or virtual storage is a memory management technique that provides an "idealized abstraction of the storage resources that are actually available on a given machine" which "creates the illusion to users of a very large (main) memory". The computer's operating system, using a combination of hardware and software, maps memory addresses used by a program, called '' virtual addresses'', into ''physical addresses'' in computer memory. Main storage, as seen by a process or task, appears as a contiguous address space or collection of contiguous segments. The operating system manages virtual address spaces and the assignment of real memory to virtual memory. Address translation hardware in the CPU, often referred to as a memory management unit (MMU), automatically translates virtual addresses to physical addresses. Software within the operating system may extend these capabilities, utilizing, e.g., disk storage, to provide a virtual address space tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A/UX
A/UX is Apple Computer's Unix-based operating system for Macintosh computers, integrated with System 7's graphical interface and application compatibility. Launched in 1988 and discontinued in 1995 with version 3.1.1, it is Apple's first official Unix-based operating system. A/UX requires select 68k-based Macintosh models with an FPU and a paged memory management unit (PMMU), including the Macintosh II, SE/30, Quadra, and Centris series. Described by ''InfoWorld'' as "an open systems solution with the Macintosh at its heart", the operating system is based on UNIX System V Release 2.2. It includes some additional features from System V Releases 3 and 4 and BSD versions 4.2 and 4.3. It is POSIX- and System V Interface Definition (SVID)-compliant and includes TCP/IP networking from version 2 onward. Having a Unix-compatible, POSIX-compliant operating system made it possible for Apple to bid for large contracts to supply computers to U.S. federal government institutes. Featu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BootX (Linux)
BootX is the name of a graphical bootloader developed by Benjamin Herrenschmidt, which runs as an application or an extension to Mac OS 8 and 9 that allows Old World Apple computers to boot Linux. It is no longer maintained by its original author, as it does not work with any current hardware, but it is still available, and further development may be possible. It is one of three Linux bootloaders which may be used on most Old World Apple computers, the others being miBoot (included, but also independently enhanced by Jeff Carr of LinuxPPC, Inc.), and quik. New World Macs use a different bootloader, yaboot Yaboot (yet another boot loader) is a bootloader for PowerPC-based hardware running Linux. History In 2009, maintenance by Paul Nasrat was handed over to Tony Breeds. Hardware support Support includes the New World ROM Macintosh and IBM RS/6 ..., for booting Linux. External links The BootX Bootloaderat penguinppc.org Boot loaders {{Linux-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boot Loader
A bootloader, also spelled as boot loader or called boot manager and bootstrap loader, is a computer program that is responsible for booting a computer. When a computer is turned off, its softwareincluding operating systems, application code, and dataremains stored on non-volatile memory. When the computer is powered on, it typically does not have an operating system or its loader in random-access memory (RAM). The computer first executes a relatively small program stored in read-only memory (ROM, and later EEPROM, NOR flash) along with some needed data, to initialize RAM (especially on x86 systems), to access the nonvolatile device (usually block device, eg NAND flash) or devices from which the operating system programs and data can be loaded into RAM. Some earlier computer systems, upon receiving a boot signal from a human operator or a peripheral device, may load a very small number of fixed instructions into memory at a specific location, initialize at least one CPU, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macintosh Startup
The classic Macintosh startup sequence includes hardware tests which may trigger the startup chime, Happy Mac, Sad Mac, and Chimes of Death. On Macs running macOS Big Sur or later the startup sound is enabled by default, but can be disabled by the user within System Preferences ( Big Sur or Monterey) or System Settings ( Ventura). Startup chime The Macintosh startup chime is played on power-up, before trying to boot an operating system. The sound indicates that diagnostic tests run immediately at startup have found no hardware or fundamental software problems. The specific sound differs depending on the ROM, which greatly varies depending on Macintosh model. The first sound version in the first three Macintosh models is a simple square-wave "beep", and all subsequent sounds are various chords. Mark Lentczner created the software that plays the arpeggiated chord in the Macintosh II. Variations of this sound were deployed until Jim Reekes created the startup chime in the Qua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sad Mac
The classic Macintosh startup sequence includes hardware tests which may trigger the startup chime, Happy Mac, Sad Mac, and Chimes of Death. On Macs running macOS Big Sur or later the startup sound is enabled by default, but can be disabled by the user within System Preferences ( Big Sur or Monterey) or System Settings ( Ventura). Startup chime The Macintosh startup chime is played on power-up, before trying to boot an operating system. The sound indicates that diagnostic tests run immediately at startup have found no hardware or fundamental software problems. The specific sound differs depending on the ROM, which greatly varies depending on Macintosh model. The first sound version in the first three Macintosh models is a simple square-wave "beep", and all subsequent sounds are various chords. Mark Lentczner created the software that plays the arpeggiated chord in the Macintosh II. Variations of this sound were deployed until Jim Reekes created the startup chime in the Quad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Icon (computing)
In computing, an icon is a pictogram or ideogram displayed on a computer screen in order to help the user navigate a computer system. The icon itself is a quickly comprehensible symbol of a software tool, function, or a data file, accessible on the system and is more like a traffic sign than a detailed illustration of the actual entity it represents. It can serve as an electronic hyperlink or file shortcut to access the program or data. The user can activate an icon using a mouse, pointer, finger, or recently voice commands. Their placement on the screen, also in relation to other icons, may provide further information to the user about their usage. In activating an icon, the user can move directly into and out of the identified function without knowing anything further about the location or requirements of the file or code. Icons as parts of the graphical user interface of the computer system, in conjunction with windows, menus and a pointing device (mouse), belong to the mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Happy Mac
The classic Macintosh startup sequence includes hardware tests which may trigger the startup chime, Happy Mac, Sad Mac, and Chimes of Death. On Macs running macOS Big Sur or later the startup sound is enabled by default, but can be disabled by the user within System Preferences ( Big Sur or Monterey) or System Settings ( Ventura). Startup chime The Macintosh startup chime is played on power-up, before trying to boot an operating system. The sound indicates that diagnostic tests run immediately at startup have found no hardware or fundamental software problems. The specific sound differs depending on the ROM, which greatly varies depending on Macintosh model. The first sound version in the first three Macintosh models is a simple square-wave "beep", and all subsequent sounds are various chords. Mark Lentczner created the software that plays the arpeggiated chord in the Macintosh II. Variations of this sound were deployed until Jim Reekes created the startup chime in the Qua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)
.png)