|
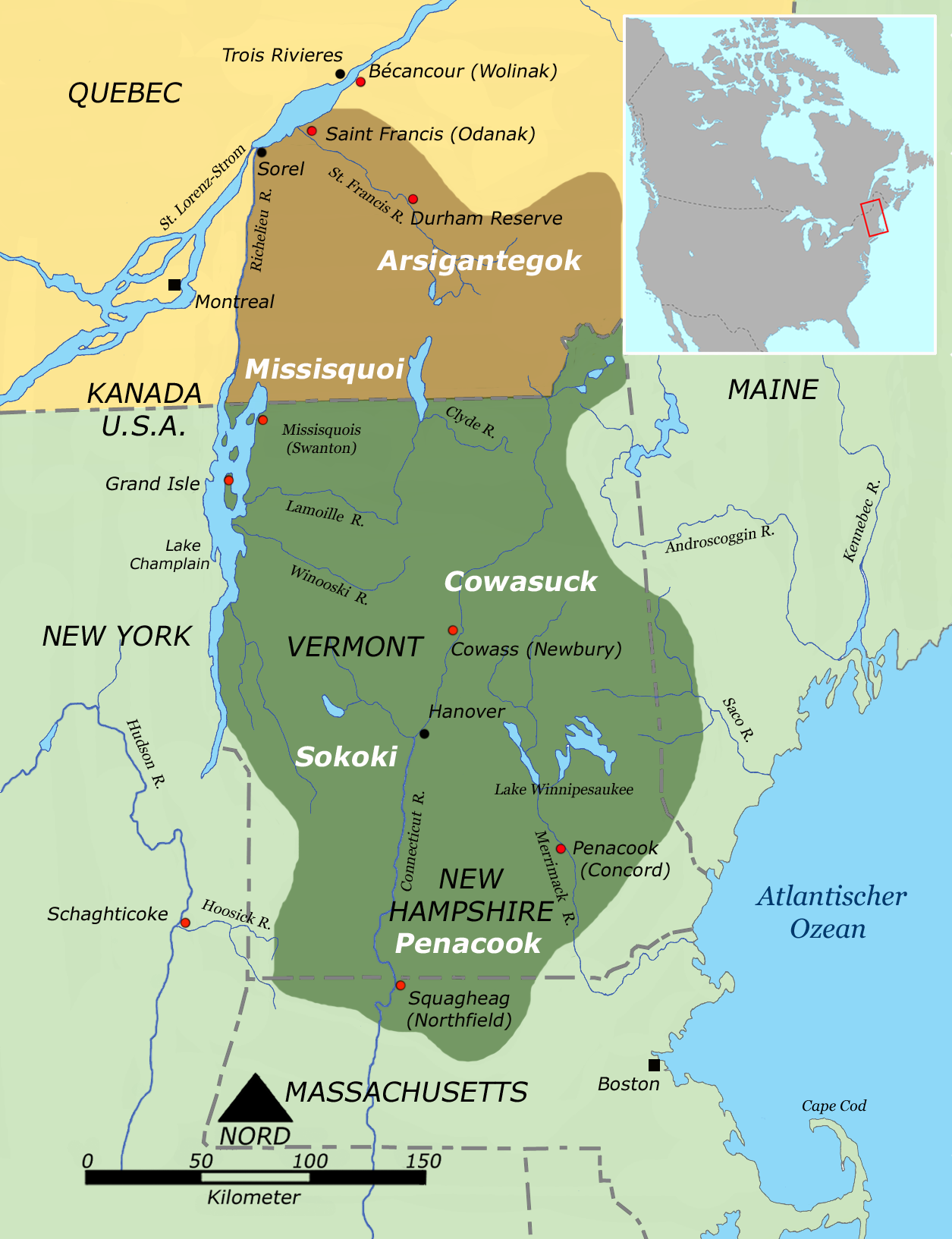
Odanak
Odanak is an Abenaki First Nations reserve in the Central Quebec region, Quebec, Canada. The mostly First Nations population as of the Canada 2021 Census was 481. The territory is located near the mouth of the Saint-François River at its confluence with the St. Lawrence River. It is partly within the limits of Pierreville and across the river from Saint-François-du-Lac. ''Odanak'' is an Abenaki word meaning "in the village". History Beginning about 1000 CE, Iroquoian-speaking people settled along the St. Lawrence River, where they practised agriculture along with hunting and fishing. Archeological surveys have revealed that by 1300, they built fortified villages similar to those seen and described by French explorer Jacques Cartier in the mid-16th century, when he visited Hochelaga and Stadacona. By 1600, however, the villages and people were gone. Since the 1950s, historians and anthropologists have used archeological and linguistic evidence to develop a consensus that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abenaki
The Abenaki ( Abenaki: ''Wαpánahki'') are an Indigenous peoples of the Northeastern Woodlands of Canada and the United States. They are an Algonquian-speaking people and part of the Wabanaki Confederacy. The Eastern Abenaki language was predominantly spoken in Maine, while the Western Abenaki language was spoken in Quebec, Vermont, and New Hampshire. While Abenaki peoples have shared cultural traits, they did not historically have a centralized government. They came together as a post-contact community after their original tribes were decimated by colonization, disease, and warfare. Names The word ''Abenaki'' and its syncope, ''Abnaki,'' are both derived from ''Wabanaki'', or ''Wôbanakiak,'' meaning "People of the Dawn Land" in the Abenaki language. While the two terms are often confused, the Abenaki are one of several tribes in the Wabanaki Confederacy. The name is spelled several ways including Abnaki, Abinaki, and Alnôbak. ''Wôbanakiak'' is derived from ''wôban ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint-François-du-Lac, Quebec
Saint-François-du-Lac () is a community in the Nicolet-Yamaska Regional County Municipality of Quebec, Canada. The population as of the Canada 2011 Census was 1,957. It is located at the confluence of the Saint Lawrence and Saint-François rivers, at the edge of Lac Saint-Pierre (hence its name, "Saint-François of the lake"). Saint-François-du-Lac faces the town of Pierreville across the Saint-François River. Quebec routes 132 and 143 intersect in the community and connect it to others. History Saint-François-du-Lac was founded as a French Jesuit mission village for converted Abenaki and other native peoples during the colonial years. The community was called St.-Francois-de-Sales, after a French saint, or Odanak, the Abenaki name. Indians in the community included Abenaki and refugees from other tribes and the wars with English colonists in eastern New England. Particularly in the aftermath of King Philip's War, which devastated southern coastal tribes, warriors from O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abenaki Language
Abenaki (''Eastern: Alənαpαtəwéwαkan, Western: Alnôbaôdwawôgan'') is an endangered Algonquian language of Quebec and the northern states of New England. The language has Eastern and Western forms which differ in vocabulary and phonology and are sometimes considered distinct languages. Eastern Abenaki languages are spoken by several peoples, including the Miꞌkmaq, Maliseet, Passamaquoddy, and Penobscot of coastal Maine. The last known natively fluent speaker of Penobscot, Madeline Shay, died in 1993. However, several Penobscot elders still speak Penobscot, and there is an ongoing effort to preserve it and teach it in the local schools; much of the language was preserved by Frank Siebert. Other dialects of Eastern Abenaki such as Caniba and Aroosagunticook are documented in French-language materials from the colonial period. In 2006, five speakers of Western Abenaki were recorded. History In '' Reflections in Bullough's Pond'', historian Diana Muir argues that Abena ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pierreville, Quebec
Pierreville () is a municipality in Nicolet-Yamaska Regional County Municipality, Quebec, located at the confluence of the Saint Lawrence and Saint-François rivers, at the edge of Lac Saint-Pierre. The population as of the Canada 2011 Census was 2,176. Pierreville faces the town of Saint-François-du-Lac across the Saint-François river, and lies at the junction of Route 132 and Route 226. Part of the Abenaki Indian reserve of Odanak is an enclave within the city limits of Pierreville. The limits of the reserve begin only a short walk away from the town's main street. History On 21 August 1991, an F3 tornado, the ''"tornade de Maskinongé"'', touched down in Notre-Dame-de-Pierreville (today part of Pierreville), destroying a number of summer homes in the area and injuring 15 people. On June 13, 2001, the parish municipalities of Notre-Dame-de-Pierreville and Saint-Thomas-de-Pierreville merged with the village municipality of Pierreville to form the new municipality of Pier ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint-François River
The Saint-François River is a right tributary of the St. Lawrence River in Quebec, Canada. Its source is Lake Saint-François in Chaudière-Appalaches, southeast of Thetford Mines. It flows southwest towards Sherbrooke, where it changes course northwest towards Drummondville, and finally empties into the Saint Lawrence River near Pierreville. Its total length is 135 miles. Etymology The river is named after Saint Francis Xavier (1506–1552) by the Jesuits, who explored the region under the French regime, and after François de Lauzon.François de Lauzon (1635-1647 or 1648), son of Jean de Lauzon Geography Its course is also unusual, as it flows from northeast to southwest to branch off, halfway through, and continue its course from southeast to northwest. The Saint-François River has its origins in the lake Saint-François and heads southwest towards Sherbrooke. Along the way, it crosses the lakes Lake Aylmer and Lake Louise as well as many municipalities. In Sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicolet-Bécancour (provincial Electoral District)
Nicolet-Bécancour is a provincial electoral district in the Centre-du-Québec region of Quebec, Canada that elects members to the National Assembly of Quebec. It notably includes the municipalities of Bécancour, Nicolet, Saint-Léonard-d'Aston, Daveluyville, Pierreville, Saint-François-du-Lac, Saint-Guillaume, Saint-Pierre-les-Becquets and Saint-Wenceslas. It was created for the 2012 election from parts of the former Nicolet-Yamaska and Lotbinière electoral districts. Members of the National Assembly Election results , align="left" colspan=3 bgcolor="#FFFFFF", Coalition Avenir Québec notional gain from Parti Québécois , align="right" bgcolor="#FFFFFF", Swing Swing or swinging may refer to: Apparatus * Swing (seat), a hanging seat that swings back and forth * Pendulum, an object that swings * Russian swing, a swing-like circus apparatus * Sex swing, a type of harness for sexual intercourse * Swing ri ... , alig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Area Code 450
Area codes 450, 579 and 354 are telephone area codes in the North American Numbering Plan in the Canadian province of Quebec, encompassing the off-island suburbs of Montreal, as well as the rest of the Montérégie region southward to the border with New York state. Among the cities in the numbering plan area are Laval, Longueuil, Terrebonne, Saint-Jean-sur-Richelieu, Brossard, Repentigny, Saint-Jérôme, Granby, Blainville and Saint-Hyacinthe. Area code 450 is also shared by several small communities in an adjacent part of Ontario: some landline customers in Chute-à-Blondeau (East Hawkesbury), near Pointe-Fortune have +1-450-451-xxxx numbers from the Rigaud exchange. History Area code 514 served the entire Montreal area for over half-a-century. However, by the mid-1990s, it was on the verge of exhaustion because of Montreal's rapid growth and Canada's inefficient system of number allocation. All competitive local exchange carriers in Canada are allocated blocks of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centre-du-Québec
Centre-du-Québec (, ''Central Quebec'') is a region of Quebec, Canada. The main centres are Drummondville, Victoriaville, and Bécancour. It has a land area of and a 2016 Census population of 242,399 inhabitants. Description The Centre-du-Québec region was established as an independent administrative region of Quebec on July 30, 1997 (in effect August 20 upon publication in the Gazette officielle du Québec); prior to this date, it formed the southern portion of the Mauricie–Bois-Francs region (the northern part of which is now known simply as Mauricie). Centre-du-Québec is not located in the geographic centre of Quebec, though it is approximately located in the centre of the southern portion of the province. Some consider the name Bois-Francs to be synonymous with the Centre-du-Québec region; others see it as being synonymous with Arthabaska Regional County Municipality, with its main city Victoriaville earning the title ''Capitale des Bois-Francs'' (capital of the B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iroquois
The Iroquois ( or ), officially the Haudenosaunee ( meaning "people of the longhouse"), are an Iroquoian-speaking confederacy of First Nations peoples in northeast North America/ Turtle Island. They were known during the colonial years to the French as the Iroquois League, and later as the Iroquois Confederacy. The English called them the Five Nations, comprising the Mohawk, Oneida, Onondaga, Cayuga, and Seneca (listed geographically from east to west). After 1722, the Iroquoian-speaking Tuscarora people from the southeast were accepted into the confederacy, which became known as the Six Nations. The Confederacy came about as a result of the Great Law of Peace, said to have been composed by Deganawidah the Great Peacemaker, Hiawatha, and Jigonsaseh the Mother of Nations. For nearly 200 years, the Six Nations/Haudenosaunee Confederacy were a powerful factor in North American colonial policy, with some scholars arguing for the concept of the Middle Ground, in that Europe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stadacona
Stadacona was a 16th-century St. Lawrence Iroquoian village not far from where Quebec City was founded in 1608. History French explorer and navigator Jacques Cartier, while travelling and charting the Saint Lawrence River, reached the village of Stadacona in July 1534. At the time, the village chief was Donnacona, who showed Cartier five scalps taken in their war with the Toudaman (likely the Miꞌkmaq), a neighbouring people who had attacked one of their forts the previous spring, killing 200 inhabitants. Despite efforts by the people of the village, Cartier seized some inhabitants and their chief, but later released Donnacona, who agreed for his two sons, Taignoagny and Domagaya, to return with Cartier to France for a year. Cartier returned to Stadacona with Donnacona's sons on his next voyage in 1535–1536, where he recorded a word they had used to refer to their home: "They call a town, Kanata" (Canada). When he and his crew stayed over the winter, they were effectively sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hochelaga (village)
Hochelaga (pronunciation: ) was a St. Lawrence Iroquois 16th century fortified village on or near Mount Royal in present-day Montreal, Quebec, Canada. Jacques Cartier arrived by boat on October 2, 1535; he visited the village on the following day. He was greeted well by the Iroquois, and named the mountain he saw nearby ''Mount Royal''. Several names in and around Montreal and the Hochelaga Archipelago can be traced back to him. A stone marker commemorating the former village was placed in 1925 on land adjacent to McGill University. It is believed to be in the vicinity of the village visited by Cartier in 1535. The site of the marker is designated a National Historic Site of Canada. The name of the village survives in Hochelaga-Maisonneuve, the name of a neighbourhood of Montreal; a variant spelling survives in Montreal's contemporary Osheaga Festival. Etymology Most linguists accept the word ''Hochelaga'' as a French borrowing of an Iroquoian term either ''osekare'', meaning ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mohawk Nation
The Mohawk people ( moh, Kanienʼkehá꞉ka) are the most easterly section of the Haudenosaunee, or Iroquois Confederacy. They are an Iroquoian-speaking Indigenous people of North America, with communities in southeastern Canada and northern New York State, primarily around Lake Ontario and the St. Lawrence River. As one of the five original members of the Iroquois League, the Kanienʼkehá꞉ka are known as the Keepers of the Eastern Door – the traditional guardians of the Iroquois Confederation against invasions from the east. Historically, the Kanienʼkehá꞉ka people were originally based in the valley of the Mohawk River in present-day upstate New York, west of the Hudson River. Their territory ranged north to the St. Lawrence River, southern Quebec and eastern Ontario; south to greater New Jersey and into Pennsylvania; eastward to the Green Mountains of Vermont; and westward to the border with the Iroquoian Oneida Nation's traditional homeland territory ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |