|
Mylar
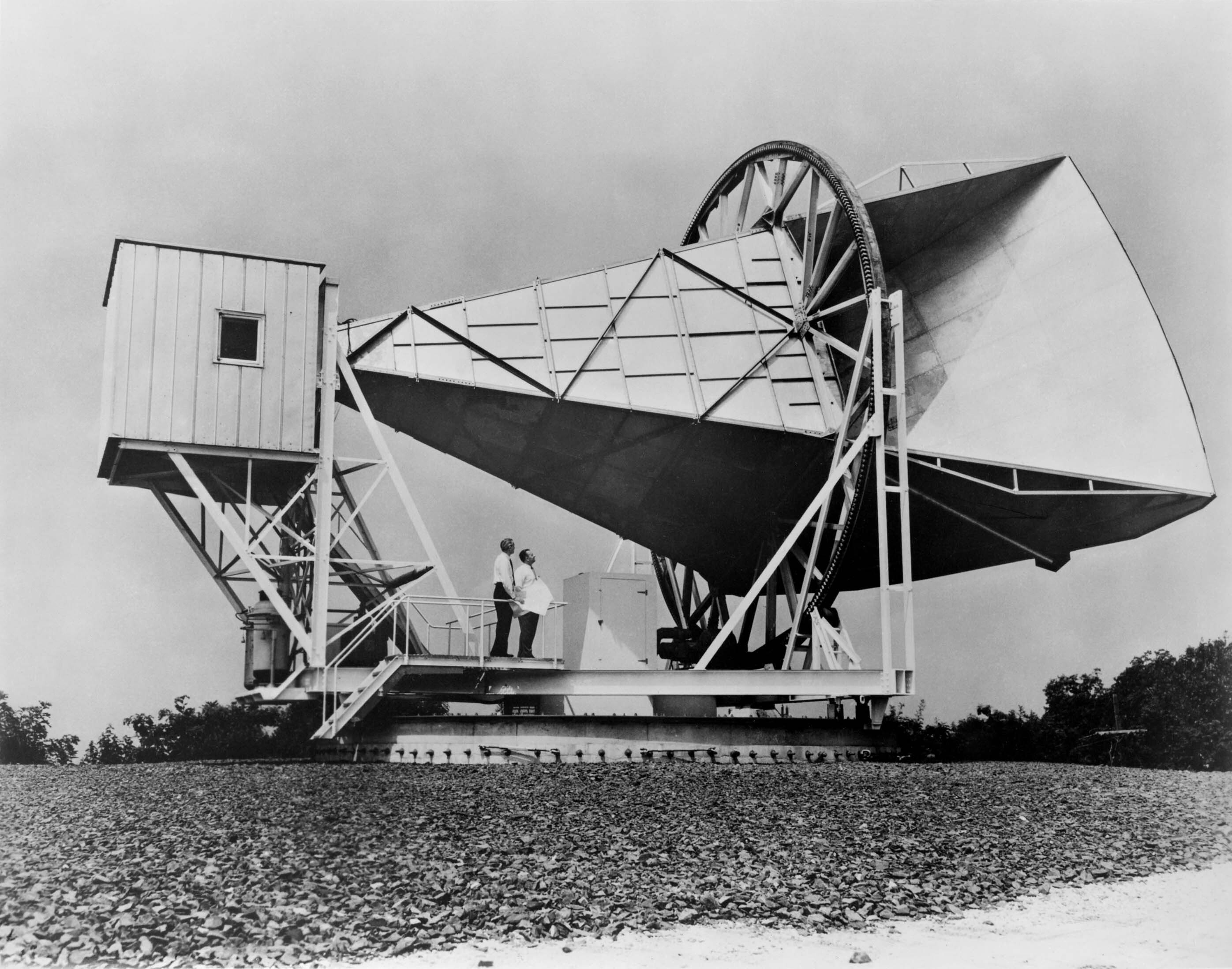
BoPET (biaxially-oriented polyethylene terephthalate) is a polyester film made from stretched polyethylene terephthalate (PET) and is used for its high tensile strength, chemical and dimensional stability, transparency, reflectivity, gas and aroma barrier properties, and electrical insulation. A variety of companies manufacture boPET and other polyester films under different brand names. In the UK and US, the best-known trade names are Mylar, Melinex, and Hostaphan. History BoPET film was developed in the mid-1950s,Izard, Emmette Farr"Production of polyethylene terephthalate" U.S. patent no. 2,534,028 (filed: 1948 May 13; issued: 1950 December 12). originally by DuPont, Imperial Chemical Industries (ICI), and Hoechst. In 1955 Eastman Kodak used Mylar as a support for photographic film and called it "ESTAR Base". The very thin and tough film allowed reels to be exposed on long-range U-2 reconnaissance flights. In 1964, NASA launched Echo II, a diameter balloon constr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Project Echo
Project Echo was the first passive communications satellite experiment. Each of the two American spacecraft, launched in 1960 and 1964, were metalized balloon satellites acting as passive reflectors of microwave signals. Communication signals were transmitted from one location on Earth and bounced off the surface of the satellite to another Earth location. The first transmissions using Echo were sent from Goldstone, California to Holmdel, New Jersey on 12 August 1960. The last Echo satellite deorbited and burned up in the atmosphere on 7 June 1969.Astronautix.com, ''Echo'' Background The concept of using orbital satellites to relay communications predated space travel, first being advanced by |
Polyethylene Terephthalate
Polyethylene terephthalate (or poly(ethylene terephthalate), PET, PETE, or the obsolete PETP or PET-P), is the most common thermoplastic polymer resin of the polyester family and is used in fibres for clothing, containers for liquids and foods, and thermoforming for manufacturing, and in combination with glass fibre for engineering resins. In 2016, annual production of PET was 56 million tons. The biggest application is in fibres (in excess of 60%), with bottle production accounting for about 30% of global demand. In the context of textile applications, PET is referred to by its common name, polyester, whereas the acronym ''PET'' is generally used in relation to packaging. Polyester makes up about 18% of world polymer production and is the fourth-most-produced polymer after polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP) and polyvinyl chloride (PVC). PET consists of repeating (C10H8O4) units. PET is commonly recycled, and has the digit 1 (♳) as its resin identification code (RIC) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyethylene Terephthalate
Polyethylene terephthalate (or poly(ethylene terephthalate), PET, PETE, or the obsolete PETP or PET-P), is the most common thermoplastic polymer resin of the polyester family and is used in fibres for clothing, containers for liquids and foods, and thermoforming for manufacturing, and in combination with glass fibre for engineering resins. In 2016, annual production of PET was 56 million tons. The biggest application is in fibres (in excess of 60%), with bottle production accounting for about 30% of global demand. In the context of textile applications, PET is referred to by its common name, polyester, whereas the acronym ''PET'' is generally used in relation to packaging. Polyester makes up about 18% of world polymer production and is the fourth-most-produced polymer after polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP) and polyvinyl chloride (PVC). PET consists of repeating (C10H8O4) units. PET is commonly recycled, and has the digit 1 (♳) as its resin identification code (RIC) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DuPont (1802–2017)
DuPont de Nemours, Inc., commonly shortened to DuPont, is an American multinational chemical company first formed in 1802 by French-American chemist and industrialist Éleuthère Irénée du Pont de Nemours. The company played a major role in the development of Delaware and first arose as a major supplier of gunpowder. DuPont developed many polymers such as Vespel, neoprene, nylon, Corian, Teflon, Mylar, Kapton, Kevlar, Zemdrain, M5 fiber, Nomex, Tyvek, Sorona, Corfam and Lycra in the 20th century, and its scientists developed many chemicals, most notably Freon (chlorofluorocarbons), for the refrigerant industry. It also developed synthetic pigments and paints including ChromaFlair. In 2015, DuPont and the Dow Chemical Company agreed to a reorganization plan in which the two companies would merge and split into three. As a merged entity, DuPont simultaneously acquired Dow and renamed itself to DowDuPont on August 31, 2017, and after 18 months spin off the merged entity's m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metallised Film
Metallised films (or metallized films) are polymer films coated with a thin layer of metal, usually aluminium. They offer the glossy metallic appearance of an aluminium foil at a reduced weight and cost. Metallised films are widely used for decorative purposes and food packaging, and also for specialty applications including insulation and electronics. Manufacture Metallisation is performed using a physical vapor deposition process. Aluminium is the most common metal used for deposition, but other metals such as nickel and chromium are also used. The metal is heated and evaporated under vacuum. This condenses on the cold polymer film, which is unwound near the metal vapour source. This coating is much thinner than a metal foil could be made, in the range of 0.5 micrometres.Hanlon, J. (1992). 1st ed. ''Handbook of Package Engineering'', Lancaster, PA, Technomic Publishing: . Chapter 4 Coatings and Laminations This coating will not fade or discolour over time. While oriented polypro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Insulation
An electrical insulator is a material in which electric current does not flow freely. The atoms of the insulator have tightly bound electrons which cannot readily move. Other materials—semiconductors and conductors—conduct electric current more easily. The property that distinguishes an insulator is its resistivity; insulators have higher resistivity than semiconductors or conductors. The most common examples are non-metals. A perfect insulator does not exist because even insulators contain small numbers of mobile charges (charge carriers) which can carry current. In addition, all insulators become electrically conductive when a sufficiently large voltage is applied that the electric field tears electrons away from the atoms. This is known as the breakdown voltage of an insulator. Some materials such as glass, paper and PTFE, which have high resistivity, are very good electrical insulators. A much larger class of materials, even though they may have lower bulk resistivit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plastics Extrusion
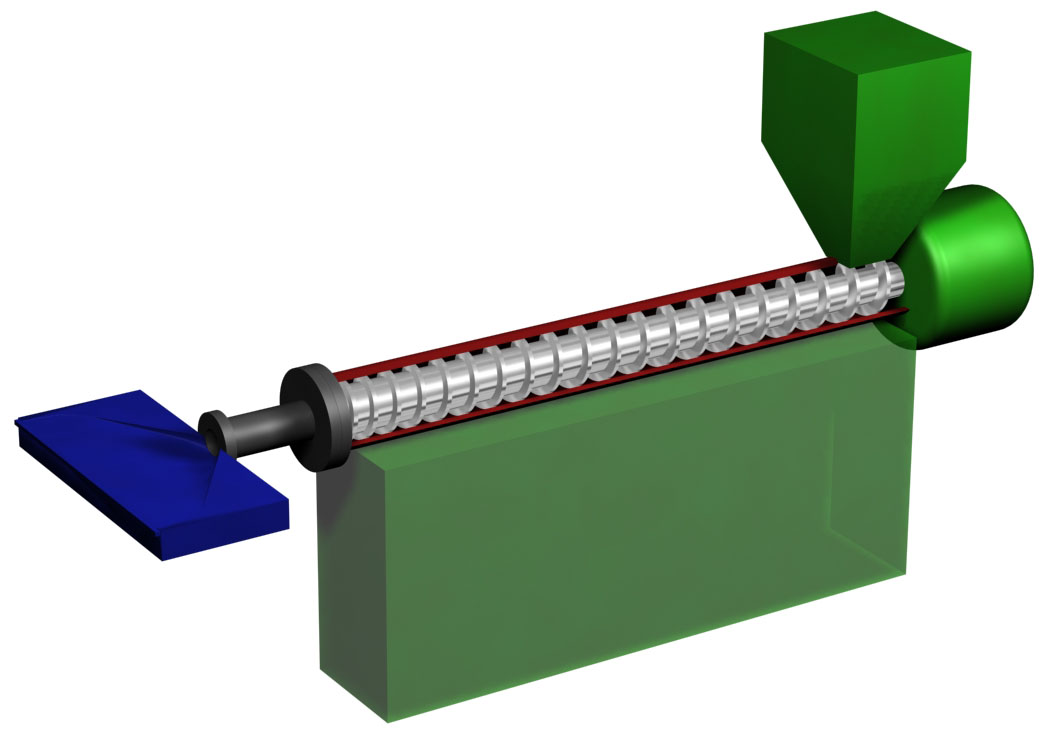
Plastics extrusion is a high-volume manufacturing process in which raw plastic is melted and formed into a continuous profile. Extrusion produces items such as pipe/tubing, weatherstripping, fencing, deck railings, window frames, plastic films and sheeting, thermoplastic coatings, and wire insulation. This process starts by feeding plastic material (pellets, granules, flakes or powders) from a hopper into the barrel of the extruder. The material is gradually melted by the mechanical energy generated by turning screws and by heaters arranged along the barrel. The molten polymer is then forced into a die, which shapes the polymer into a shape that hardens during cooling. History The first precursors to the modern extruder were developed in the early 19th century. In 1820, Thomas Hancock invented a rubber "masticator" designed to reclaim processed rubber scraps, and in 1836 Edwin Chaffee developed a two-roller machine to mix additives into rubber. The first thermoplastic extr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drawing (manufacturing)
Drawing is a metalworking process that uses tensile forces to stretch (elongate) metal, glass, or plastic. As the metal is drawn (pulled), it stretches to become thinner, to achieve a desired shape and thickness. Drawing is classified into two types: sheet metal drawing and wire, bar, and tube drawing. Sheet metal drawing is defined as a plastic deformation over a curved axis. For wire, bar, and tube drawing, the starting stock is drawn through a die to reduce its diameter and increase its length. Drawing is usually performed at room temperature, thus classified as a cold working process; however, drawing may also be performed at elevated temperatures to hot work large wires, rods or hollow sections in order to reduce forces.Degarmo, p. 432.Kalpakjian, pp. 415–419. Drawing differs from rolling in that the pressure of drawing is not transmitted through the turning action of the mill but instead depends on force applied locally near the area of compression. This means the am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthogonality
In mathematics, orthogonality is the generalization of the geometric notion of '' perpendicularity''. By extension, orthogonality is also used to refer to the separation of specific features of a system. The term also has specialized meanings in other fields including art and chemistry. Etymology The word comes from the Ancient Greek ('), meaning "upright", and ('), meaning "angle". The Ancient Greek (') and Classical Latin ' originally denoted a rectangle. Later, they came to mean a right triangle. In the 12th century, the post-classical Latin word ''orthogonalis'' came to mean a right angle or something related to a right angle. Mathematics Physics * In optics, polarization states are said to be orthogonal when they propagate independently of each other, as in vertical and horizontal linear polarization or right- and left-handed circular polarization. * In special relativity, a time axis determined by a rapidity of motion is hyperbolic-orthogonal to a space axis o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heat Set
Heat setting is a term used in the textile industry to describe a thermal process usually taking place in either a steam atmosphere or a dry heat environment. The effect of the process gives fibers, yarns or fabric dimensional stability and, very often, other desirable attributes like higher volume, wrinkle resistance or temperature resistance. Very often, heat setting is also used to improve attributes for subsequent processes. Heat setting can eliminate the tendency of undesirable torquing. At the winding, twisting, weaving, tufting and knitting processes, the increased tendency to torquing can cause difficulties in processing the yarn. When using heat setting for carpet yarns, desirable results include not only the diminishing of torquing but also the stabilization or fixing of the fiber thread. Both twist stabilization and stabilization of frieze effect are results of the heat setting process. Heat setting benefits staple yarns as well as bulked continuous filament (BCF) y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research. NASA was established in 1958, succeeding the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA), to give the U.S. space development effort a distinctly civilian orientation, emphasizing peaceful applications in space science. NASA has since led most American space exploration, including Project Mercury, Project Gemini, the 1968-1972 Apollo Moon landing missions, the Skylab space station, and the Space Shuttle. NASA supports the International Space Station and oversees the development of the Orion spacecraft and the Space Launch System for the crewed lunar Artemis program, Commercial Crew spacecraft, and the planned Lunar Gateway space station. The agency is also responsible for the Launch Services Program, which provides oversight of launch operations and countdow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |