|
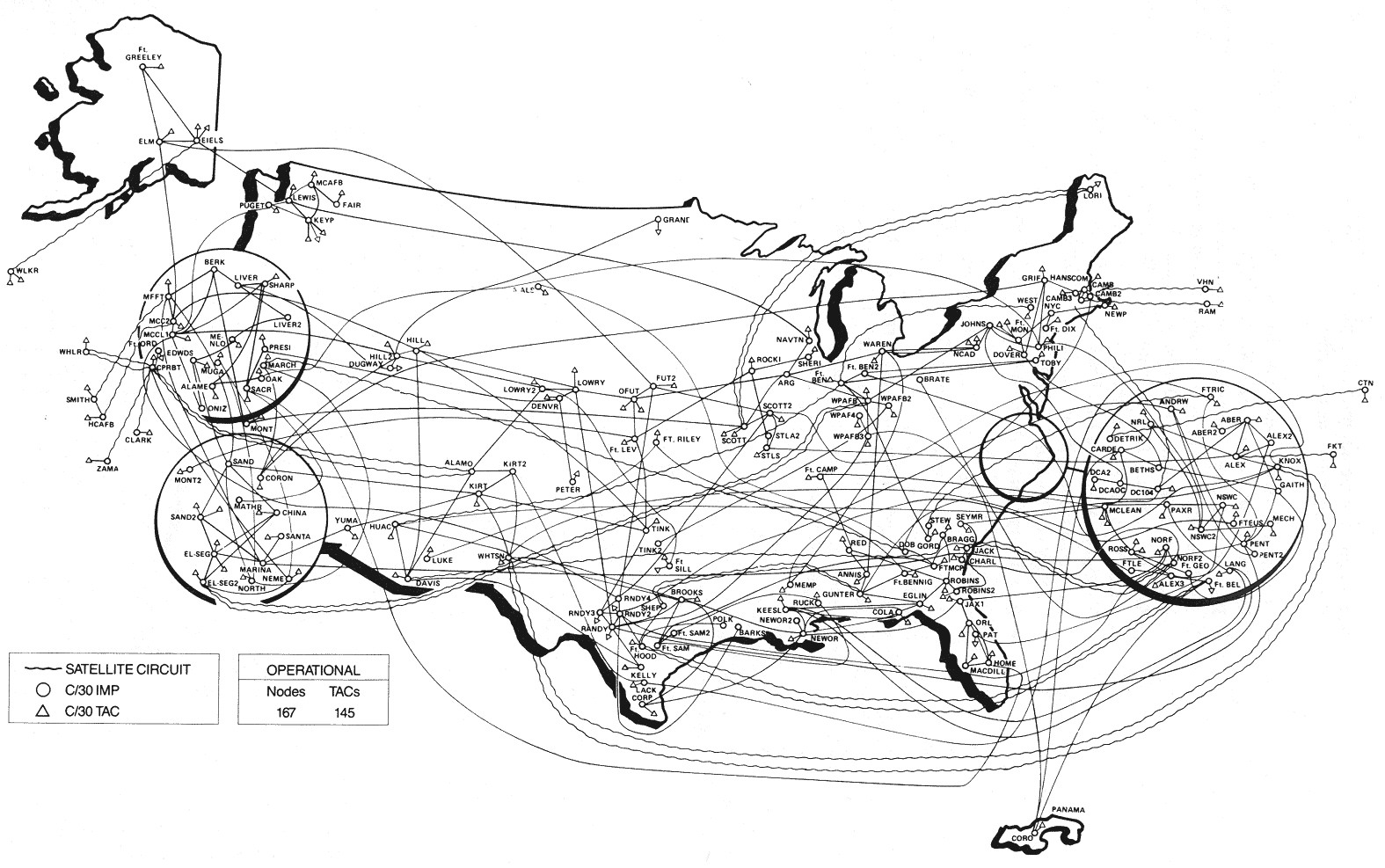
Milnet
In computer networking, MILNET (fully Military Network) was the name given to the part of the ARPANET internetwork designated for unclassified United States Department of Defense traffic.DEFENSE DATA NETWORK NEWSLETTEDDN-NEWS 26 6 May 1983 MILNET was physically separated from the ARPANET in 1983. The ARPANET remained in service for the academic research community, but direct connectivity between the networks was severed for security reasons. Gateways relayed electronic mail between the two networks. BBN Technologies built and managed both the MILNET and the ARPANET and the two networks used very similar technology. It is also known as "Military Net." During the 1980s the MILNET expanded as part of the Defense Data Network, a worldwide set of military networks running at different security levels. In the 1990s, MILNET became the NIPRNET The Non-classified Internet Protocol (IP) Router Network (NIPRNet) is an IP network used to exchange unclassified information, including info ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Defense Data Network
The Defense Data Network (DDN) was a computer networking effort of the United States Department of Defense from 1983 through 1995. It was based on ARPANET technology. History As an experiment, from 1971 to 1977, the Worldwide Military Command and Control System (WWMCCS) purchased and operated an ARPANET-type system from BBN Technologies for the Prototype WWMCCS Intercomputer Network (PWIN). The experiments proved successful enough that it became the basis of the much larger WIN system. Six initial WIN sites in 1977 increased to 20 sites by 1981. In 1975, the Defense Communication Agency (DCA) took over operation of the ARPANET as it became an operational tool in addition to an ongoing research project. At that time, the Automatic Digital Network (AUTODIN), carried most of the Defense Department's message traffic. Starting in 1972, attempts had been made to introduce some packet switching into its planned replacement, AUTODIN II. AUTODIN II development proved unsatisfactory, howe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ARPANET
The Advanced Research Projects Agency Network (ARPANET) was the first wide-area packet-switched network with distributed control and one of the first networks to implement the TCP/IP protocol suite. Both technologies became the technical foundation of the Internet. The ARPANET was established by the Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA) of the United States Department of Defense. Building on the ideas of J. C. R. Licklider, Bob Taylor initiated the ARPANET project in 1966 to enable access to remote computers. Taylor appointed Larry Roberts as program manager. Roberts made the key decisions about the network design. He incorporated Donald Davies' concepts and designs for packet switching, and sought input from Paul Baran. ARPA awarded the contract to build the network to Bolt Beranek & Newman who developed the first protocol for the network. Roberts engaged Leonard Kleinrock at UCLA to develop mathematical methods for analyzing the packet network technology. The first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BBN Technologies
Raytheon BBN (originally Bolt Beranek and Newman Inc.) is an American research and development company, based next to Fresh Pond in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States. In 1966, the Franklin Institute awarded the firm the Frank P. Brown Medal, in 1999 BBN received the IEEE Corporate Innovation Recognition, and on 1 February 2013, BBN was awarded the National Medal of Technology and Innovation, the highest honors that the U.S. government bestows upon scientists, engineers and inventors, by President Barack Obama. It became a wholly owned subsidiary of Raytheon in 2009. History BBN has its roots in an initial partnership formed on 15 October 1948 between Leo Beranek and Richard Bolt, professors at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. Bolt had won a commission to be an acoustic consultant for the new United Nations permanent headquarters to be built in New York City. Realizing the magnitude of the project at hand, Bolt had pulled in his MIT colleague Beranek for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NIPRNET
The Non-classified Internet Protocol (IP) Router Network (NIPRNet) is an IP network used to exchange unclassified information, including information subject to controls on distribution, among the private network's users. The NIPRNet also provides its users access to the Internet. It is one of the United States Department of Defense's three main networks. The others include SIPRNet and JWICS. History NIPRNet is composed of Internet Protocol routers owned by the United States Department of Defense (DOD). It was created in the 1980s and managed by the Defense Information Systems Agency (DISA) to supersede the earlier MILNET. Security improvements In the year leading up to 2010 NIPRNet has grown faster than the U.S. Department of Defense can monitor. DoD spent $10 million in 2010 to map out the current state of the NIPRNet, in an effort to analyze its expansion, and identify unauthorized users, who are suspected to have quietly joined the network. The NIPRNet survey, which use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internetwork
Internetworking is the practice of interconnecting multiple computer networks, such that any pair of hosts in the connected networks can exchange messages irrespective of their hardware-level networking technology. The resulting system of interconnected networks are called an ''internetwork'', or simply an ''internet''. The most notable example of internetworking is the Internet, a network of networks based on many underlying hardware technologies. The Internet is defined by a unified global addressing system, packet format, and routing methods provided by the Internet Protocol. The term ''internetworking'' is a combination of the components ''inter'' (between) and ''networking''. An earlier term for an internetwork is catenet, a short-form of ''(con)catenating networks''. Interconnection of networks Internetworking started as a way to connect disparate types of networking technology, but it became widespread through the developing need to connect two or more local area netw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Department Of Defense
The United States Department of Defense (DoD, USDOD or DOD) is an executive branch department of the federal government charged with coordinating and supervising all agencies and functions of the government directly related to national security and the United States Armed Forces. The DoD is the largest employer in the world, with over 1.34 million active-duty service members (soldiers, marines, sailors, airmen, and guardians) as of June 2022. The DoD also maintains over 778,000 National Guard and reservists, and over 747,000 civilians bringing the total to over 2.87 million employees. Headquartered at the Pentagon in Arlington, Virginia, just outside Washington, D.C., the DoD's stated mission is to provide "the military forces needed to deter war and ensure our nation's security". The Department of Defense is headed by the secretary of defense, a cabinet-level head who reports directly to the president of the United States. Beneath the Department of Defense are t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Security
Computer security, cybersecurity (cyber security), or information technology security (IT security) is the protection of computer systems and networks from attack by malicious actors that may result in unauthorized information disclosure, theft of, or damage to hardware, software, or data, as well as from the disruption or misdirection of the services they provide. The field has become of significance due to the expanded reliance on computer systems, the Internet, and wireless network standards such as Bluetooth and Wi-Fi, and due to the growth of smart devices, including smartphones, televisions, and the various devices that constitute the Internet of things (IoT). Cybersecurity is one of the most significant challenges of the contemporary world, due to both the complexity of information systems and the societies they support. Security is of especially high importance for systems that govern large-scale systems with far-reaching physical effects, such as power distrib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gateway (telecommunications)
A gateway is a piece of networking hardware or software used in telecommunications networks that allows data to flow from one discrete network to another. Gateways are distinct from routers or switches in that they communicate using more than one protocol to connect multiple networks and can operate at any of the seven layers of the open systems interconnection model (OSI). The term gateway can also loosely refer to a computer or computer program configured to perform the tasks of a gateway, such as a default gateway or router, and in the case of HTTP, gateway is also often used as a synonym for reverse proxy. Network gateway A network gateway provides a connection between networks and contains devices, such as protocol translators, impedance matchers, rate converters, fault isolators, or signal translators. A network gateway requires the establishment of mutually acceptable administrative procedures between the networks using the gateway. Network gateways, known as prot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronic Mail
Electronic mail (email or e-mail) is a method of exchanging messages ("mail") between people using electronic devices. Email was thus conceived as the electronic (digital) version of, or counterpart to, mail, at a time when "mail" meant only physical mail (hence '' e- + mail''). Email later became a ubiquitous (very widely used) communication medium, to the point that in current use, an email address is often treated as a basic and necessary part of many processes in business, commerce, government, education, entertainment, and other spheres of daily life in most countries. ''Email'' is the medium, and each message sent therewith is also called an ''email.'' The term is a mass noun. Email operates across computer networks, primarily the Internet, and also local area networks. Today's email systems are based on a store-and-forward model. Email servers accept, forward, deliver, and store messages. Neither the users nor their computers are required to be online simulta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |