|
Mifepristone
Mifepristone, also known as RU-486, is a medication typically used in combination with misoprostol to bring about a medical abortion during pregnancy and manage early miscarriage. This combination is 97% effective during the first 63 days of pregnancy. It is also effective in the second trimester of pregnancy. Effectiveness should be verified two weeks after use. It is taken by mouth. Common side effects include abdominal pain, feeling tired, and vaginal bleeding. Serious side effects may include heavy vaginal bleeding, bacterial infection, and birth defects if the pregnancy does not end. If used, appropriate follow up care needs to be available. Mifepristone is an antiprogestogen. It works by blocking the effects of progesterone, making both the cervix and uterine vessels dilate and causing uterine contraction. Mifepristone was developed in 1980 and came into use in France in 1987. It became available in the United States in 2000. It is on the WHO Model List of Essential Me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Abortion
A medical abortion, also known as medication abortion, occurs when drugs (medication) are used to bring about an abortion. Medical abortions are an alternative to surgical abortions such as vacuum aspiration or dilation and curettage. Medical abortions are more common than surgical abortions in most places, including Europe, India, China, and the United States. Medical abortions are typically performed by administering a two-drug combination: mifepristone followed by misoprostol. When mifepristone is not available, misoprostol alone may be used in some situations. Medical abortion is both safe and effective throughout a range of gestational ages, including the second and third trimester. In the United States, the mortality rate for medical abortion is 14 times lower than the mortality rate for childbirth, and the rate of serious complications requiring hospitalization or blood transfusion is less than 0.4%. Medical abortion can be administered safely by the patient at home, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Misoprostol
Misoprostol is a synthetic prostaglandin medication used to prevent and treat stomach and duodenal ulcers, induce labor, cause an abortion, and treat postpartum bleeding due to poor contraction of the uterus. Misoprostol is taken by mouth when used to prevent gastric ulcers in persons taking NSAIDs. For abortions it is used by itself and with mifepristone or methotrexate. By itself, effectiveness for abortion is between 66% and 90%. For labor induction or abortion, it is taken by mouth, dissolved in the mouth, or placed in the vagina. For postpartum bleeding it may also be used rectally. Common side effects include diarrhea and abdominal pain. It is pregnancy category X meaning that it is known to result in negative outcomes for the fetus if taken during pregnancy. In rare cases, uterine rupture may occur. It is a prostaglandin analogue—specifically, a synthetic prostaglandin E1 (PGE1). Misoprostol was developed in 1973. It is on the World Health Organization's List of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiprogestogen
Antiprogestogens, or antiprogestins, also known as progesterone antagonists or progesterone blockers, are a class of drugs which prevent progestogens like progesterone from mediating their biological effects in the body. They act by receptor antagonist, blocking the progesterone receptor (PR) and/or steroidogenesis inhibitor, inhibiting or antigonadotropin, suppressing progestogen biosynthesis, production. Antiprogestogens are one of three types of sex-hormonal agent, sex hormone antagonists, the others being antiestrogens and antiandrogens. Antiprogestogens are used as abortifacients and emergency contraception, emergency contraceptives and in the treatment of uterine fibroids. They are also being studied in the treatment of breast cancer. Examples of antiprogestogens include the progesterone receptor weak partial agonist mifepristone, the selective progesterone receptor modulator (SPRM) ulipristal acetate, and the silent antagonist aglepristone. For medical abortion, mifepristone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiglucocorticoid
An antiglucocorticoid is a drug which reduces glucocorticoid activity in the body. They include direct glucocorticoid receptor antagonists such as mifepristone and synthesis inhibitors such as metyrapone, ketoconazole, and aminoglutethimide. They are used to treat Cushing's syndrome. Antiglucocorticoids could be effective antidepressants for a subset of specific mood disorders, but their use is limited by side effects. See also * Corticosteroid * Antimineralocorticoid An antimineralocorticoid, also known as a mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist (MRA or MCRA) or aldosterone antagonist, is a diuretic drug which antagonizes the action of aldosterone at mineralocorticoid receptors. This group of drugs is ofte ... References Antiglucocorticoids {{pharmacology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emergency Contraception
Emergency contraception (EC) is a birth control measure, used after sexual intercourse to prevent pregnancy. There are different forms of EC. Emergency contraceptive pills (ECPs), sometimes simply referred to as emergency contraceptives (ECs), or the morning-after pill, are medications intended to disrupt or delay ovulation or fertilization, which are necessary for pregnancy. p. 121: Intrauterine devices (IUDs)usually used as a primary contraceptive methodare sometimes used as the most effective form of emergency contraception. However, the use of IUDs for emergency contraception is relatively rare. Definition Emergency contraception is a birth control measure taken to reduce the risk of pregnancy following unprotected sexual intercourse or when other regular contraceptive measures have not worked properly or have not been used correctly. It is intended to be used occasionally and is not the same as medical abortion. Emergency contraception is offered to women who do not wish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiprogestogen
Antiprogestogens, or antiprogestins, also known as progesterone antagonists or progesterone blockers, are a class of drugs which prevent progestogens like progesterone from mediating their biological effects in the body. They act by receptor antagonist, blocking the progesterone receptor (PR) and/or steroidogenesis inhibitor, inhibiting or antigonadotropin, suppressing progestogen biosynthesis, production. Antiprogestogens are one of three types of sex-hormonal agent, sex hormone antagonists, the others being antiestrogens and antiandrogens. Antiprogestogens are used as abortifacients and emergency contraception, emergency contraceptives and in the treatment of uterine fibroids. They are also being studied in the treatment of breast cancer. Examples of antiprogestogens include the progesterone receptor weak partial agonist mifepristone, the selective progesterone receptor modulator (SPRM) ulipristal acetate, and the silent antagonist aglepristone. For medical abortion, mifepristone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
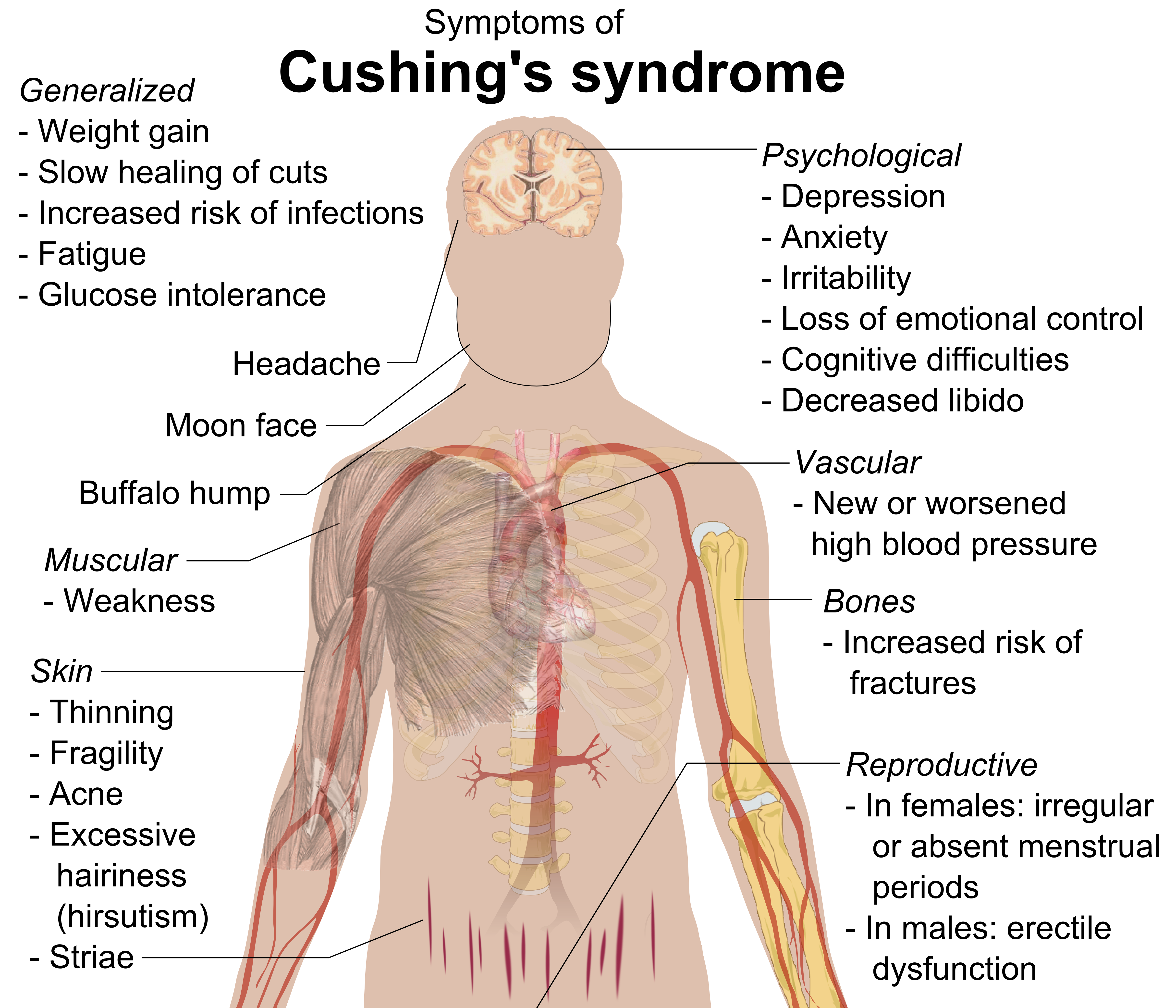
Cushing's Syndrome
Cushing's syndrome is a collection of signs and symptoms due to prolonged exposure to glucocorticoids such as cortisol. Signs and symptoms may include high blood pressure, abdominal obesity but with thin arms and legs, reddish stretch marks, a round red face, a fat lump between the shoulders, weak muscles, weak bones, acne, and fragile skin that heals poorly. Women may have more hair and irregular menstruation. Occasionally there may be changes in mood, headaches, and a chronic feeling of tiredness. Cushing's syndrome is caused by either excessive cortisol-like medication, such as prednisone, or a tumor that either produces or results in the production of excessive cortisol by the adrenal glands. Cases due to a pituitary adenoma are known as Cushing's disease, which is the second most common cause of Cushing's syndrome after medication. A number of other tumors, often referred to as ectopic due to their placement outside the pituitary, may also cause Cushing's. Some of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Pregnancy Loss
Miscarriage, also known in medical terms as a spontaneous abortion and pregnancy loss, is the death of an embryo or fetus before it is able to survive independently. Miscarriage before 6 weeks of gestation is defined by ESHRE as biochemical loss. Once ultrasound or histological evidence shows that a pregnancy has existed, the used term is clinical miscarriage, which can be ''early'' before 12 weeks and ''late'' between 12-21 weeks. Fetal death after 20 weeks of gestation is also known as a stillbirth. The most common symptom of a miscarriage is vaginal bleeding with or without pain. Sadness, anxiety, and guilt may occur afterwards. Tissue and clot-like material may leave the uterus and pass through and out of the vagina. Recurrent miscarriage (also referred to medically as Recurrent Spontaneous Abortion or RSA) may also be considered a form of infertility. Risk factors for miscarriage include being an older parent, previous miscarriage, exposure to tobacco smoke, obesity, diab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WHO Model List Of Essential Medicines
The WHO Model List of Essential Medicines (aka Essential Medicines List or EML), published by the World Health Organization (WHO), contains the medications considered to be most effective and safe to meet the most important needs in a health system. The list is frequently used by countries to help develop their own local lists of essential medicines. , more than 155 countries have created national lists of essential medicines based on the World Health Organization's model list. This includes both developed and developing countries. The list is divided into core items and complementary items. The core items are deemed to be the most cost-effective options for key health problems and are usable with little additional health care resources. The complementary items either require additional infrastructure such as specially trained health care providers or diagnostic equipment or have a lower cost–benefit ratio. About 25% of items are in the complementary list. Some medicatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abortifacient
An abortifacient ("that which will cause a miscarriage" from Latin: ''abortus'' "miscarriage" and '' faciens'' "making") is a substance that induces abortion. This is a nonspecific term which may refer to any number of substances or medications, ranging from herbs to prescription medications. Common abortifacients used in performing medical abortions include mifepristone, which is typically used in conjunction with misoprostol in a two-step approach. Synthetic oxytocin, which is routinely used safely during term labor, is also commonly used to induce abortion in the second or third trimester. For thousands of years writers in many parts of the world have described and recommended herbal abortifacients to women who seek to terminate a pregnancy, although their use may carry risks to the health of the woman. Medications Because "abortifacient" is a broad term used to describe a substance's effects on pregnancy, there is a wide range of drugs that can be described as abortifac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Congress Of Obstetricians And Gynecologists
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) is a professional association of physicians specializing in obstetrics and gynecology in the United States. Several Latin American countries are also represented within Districts of the organization. It is a 501(c)(3) organization with a membership of more than 60,000 obstetrician-gynecologists and women's health care professionals. It was founded in 1951. __TOC__ Background A companion 501(c)(6) organization, the American ''Congress'' of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, was founded in 2008 and became operational in 2010. The two organizations coexist, and member individuals automatically belong to both. Both are not-for-profit. The College as a 501(c)(3) focuses on education (with limited political work), whereas the Congress as a 501(c)(6) is allowed to advocate for members' interests in terms of the business of medicine (BOM) through lobbying and other political work. Their main advocacy focuses on women's reprod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Blood Sugar
Hyperglycemia is a condition in which an excessive amount of glucose circulates in the blood plasma. This is generally a blood sugar level higher than 11.1 mmol/L (200 mg/dL), but symptoms may not start to become noticeable until even higher values such as 13.9–16.7 mmol/L (~250–300 mg/dL). A subject with a consistent range between ~5.6 and ~7 mmol/L (100–126 mg/dL) (American Diabetes Association guidelines) is considered slightly hyperglycemic, and above 7 mmol/L (126 mg/dL) is generally held to have diabetes. For diabetics, glucose levels that are considered to be too hyperglycemic can vary from person to person, mainly due to the person's renal threshold of glucose and overall glucose tolerance. On average, however, chronic levels above 10–12 mmol/L (180–216 mg/dL) can produce noticeable organ damage over time. Signs and symptoms The degree of hyperglycemia can change over time depending on the metabolic cause, for example, impaired glucos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |