|
Mauer 1
The Mauer 1 mandible is the oldest-known specimen of the genus ''Homo'' in Germany. It was found in 1907 in a sand quarry in the community Mauer, around south-east of Heidelberg. The Mauer 1 mandible is the type specimen of the species ''Homo heidelbergensis''. Some European researchers have classified the find as ''Homo erectus heidelbergensis'', regarding it as a subspecies of ''Homo erectus''. In 2010 the mandible's age was for the first time exactly determined to be 609,000 ± 40,000 years.Günther A. Wagner et al.: ''Radiometric dating of the type-site for ''Homo heidelbergensis'' at Mauer, Germany.'' In: ''Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.'' vol. 107, no. 46, 2010, pp. 19726–19730 . Previously, specialist literature had referred to an age of either 600,000 or 500,000 years on the basis of less accurate dating methods. Discovery On October 21, 1907, Daniel Hartmann, a worker at a sand mine in the Grafenrain open-field system of the Mauer community uneart ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homo Heidelbergensis
''Homo heidelbergensis'' (also ''H. sapiens heidelbergensis''), sometimes called Heidelbergs, is an extinct species or subspecies of archaic human which existed during the Middle Pleistocene. It was subsumed as a subspecies of '' H. erectus'' in 1950 as ''H. e. heidelbergensis'', but towards the end of the century, it was more widely classified as its own species. It is debated whether or not to constrain ''H. heidelbergensis'' to only Europe or to also include African and Asian specimens, and this is further confounded by the type specimen (Mauer 1) being a jawbone, because jawbones feature few diagnostic traits and are generally missing among Middle Pleistocene specimens. Thus, it is debated if some of these specimens could be split off into their own species or a subspecies of ''H. erectus''. Because the classification is so disputed, the Middle Pleistocene is often called the "muddle in the middle." ''H. heidelbergensis'' is regarded as a chronospecies, evolving from an Afr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Paleontology is the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are usually considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years old to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online before print. The observation in the 19th century that certain fossils were associated with certain rock strata led to the recognition of a geological timescale and the relative ages of different fossils. The development of radiometric dating techniques in the early 20th century allowed scientists to quantitatively measure the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleontology
Paleontology (), also spelled palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of life that existed prior to, and sometimes including, the start of the Holocene epoch (roughly 11,700 years before present). It includes the study of fossils to classify organisms and study their interactions with each other and their environments (their paleoecology). Paleontological observations have been documented as far back as the 5th century BC. The science became established in the 18th century as a result of Georges Cuvier's work on comparative anatomy, and developed rapidly in the 19th century. The term itself originates from Greek (, "old, ancient"), (, (gen. ), "being, creature"), and (, "speech, thought, study"). Paleontology lies on the border between biology and geology, but differs from archaeology in that it excludes the study of anatomically modern humans. It now uses techniques drawn from a wide range of sciences, including biochemistry, mathematics, and engineeri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleoanthropology
Paleoanthropology or paleo-anthropology is a branch of paleontology and anthropology which seeks to understand the early development of anatomically modern humans, a process known as hominization, through the reconstruction of evolutionary kinship lines within the family Hominidae, working from biological evidence (such as petrified skeletal remains, bone fragments, footprints) and cultural evidence (such as stone tools, artifacts, and settlement localities). The field draws from and combines primatology, paleontology, biological anthropology, and cultural anthropology. As technologies and methods advance, genetics plays an ever-increasing role, in particular to examine and compare DNA structure as a vital tool of research of the evolutionary kinship lines of related species and genera. Etymology The term paleoanthropology derives from Greek palaiós (παλαιός) "old, ancient", ánthrōpos (ἄνθρωπος) "man, human" and the suffix -logía (-λογία) "study of". ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
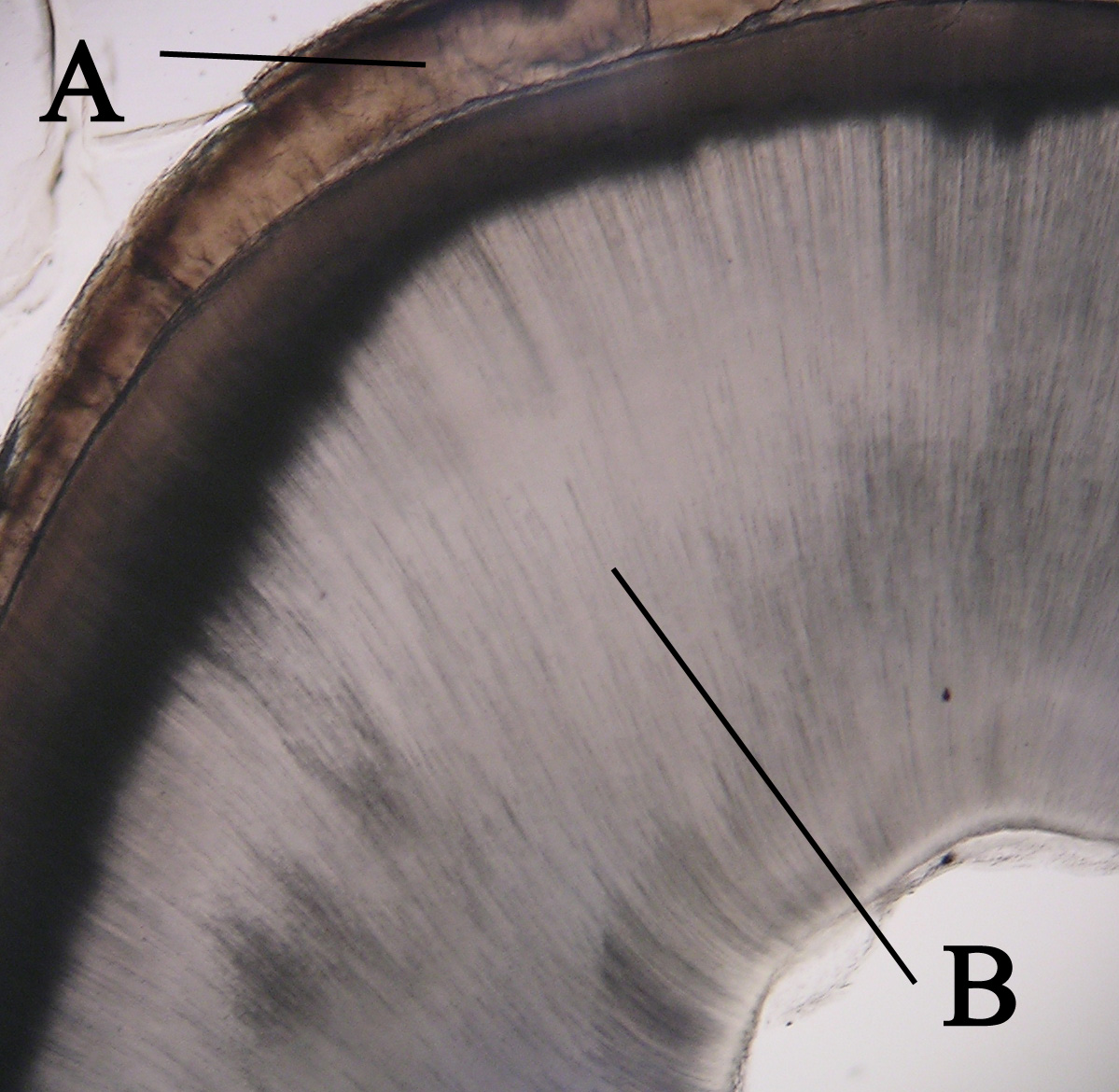
Dentin
Dentin () (American English) or dentine ( or ) (British English) ( la, substantia eburnea) is a calcified tissue of the body and, along with enamel, cementum, and pulp, is one of the four major components of teeth. It is usually covered by enamel on the crown and cementum on the root and surrounds the entire pulp. By volume, 45% of dentin consists of the mineral hydroxyapatite, 33% is organic material, and 22% is water. Yellow in appearance, it greatly affects the color of a tooth due to the translucency of enamel. Dentin, which is less mineralized and less brittle than enamel, is necessary for the support of enamel. Dentin rates approximately 3 on the Mohs scale of mineral hardness. There are two main characteristics which distinguish dentin from enamel: firstly, dentin forms throughout life; secondly, dentin is sensitive and can become hypersensitive to changes in temperature due to the sensory function of odontoblasts, especially when enamel recedes and dentin channels bec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Premolar
The premolars, also called premolar teeth, or bicuspids, are transitional teeth located between the canine and molar teeth. In humans, there are two premolars per quadrant in the permanent set of teeth, making eight premolars total in the mouth. They have at least two cusps. Premolars can be considered transitional teeth during chewing, or mastication. They have properties of both the canines, that lie anterior and molars that lie posterior, and so food can be transferred from the canines to the premolars and finally to the molars for grinding, instead of directly from the canines to the molars. Human anatomy The premolars in humans are the maxillary first premolar, maxillary second premolar, mandibular first premolar, and the mandibular second premolar. Premolar teeth by definition are permanent teeth distal to the canines, preceded by deciduous molars. Morphology There is always one large buccal cusp, especially so in the mandibular first premolar. The lower seco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wisdom Tooth
A third molar, commonly called wisdom tooth, is one of the three molars per quadrant of the human dentition. It is the most posterior of the three. The age at which wisdom teeth come through ( erupt) is variable, but this generally occurs between late teens and early twenties. Most adults have four wisdom teeth, one in each of the four quadrants, but it is possible to have none, fewer, or more, in which case the extras are called supernumerary teeth. Wisdom teeth may get stuck ( impacted) against other teeth if there is not enough space for them to come through normally. Impacted wisdom teeth are still sometimes removed for orthodontic treatment, believing that they move the other teeth and cause crowding, though this is not held anymore as true. Impacted wisdom teeth may suffer from tooth decay if oral hygiene becomes more difficult. Wisdom teeth which are partially erupted through the gum may also cause inflammation and infection in the surrounding gum tissues, termed pericor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homo Sapiens
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, and language. Humans are highly social and tend to live in complex social structures composed of many cooperating and competing groups, from families and kinship networks to political states. Social interactions between humans have established a wide variety of values, social norms, and rituals, which bolster human society. Its intelligence and its desire to understand and influence the environment and to explain and manipulate phenomena have motivated humanity's development of science, philosophy, mythology, religion, and other fields of study. Although some scientists equate the term ''humans'' with all members of the genus ''Homo'', in common usage, it generally refers to ''Homo sapiens'', the only extant member. Anatomically mod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dentition
Dentition pertains to the development of teeth and their arrangement in the mouth. In particular, it is the characteristic arrangement, kind, and number of teeth in a given species at a given age. That is, the number, type, and morpho-physiology (that is, the relationship between the shape and form of the tooth in question and its inferred function) of the teeth of an animal. Animals whose teeth are all of the same type, such as most non-mammalian vertebrates, are said to have '' homodont'' dentition, whereas those whose teeth differ morphologically are said to have '' heterodont'' dentition. The dentition of animals with two successions of teeth (deciduous, permanent) is referred to as '' diphyodont'', while the dentition of animals with only one set of teeth throughout life is ''monophyodont''. The dentition of animals in which the teeth are continuously discarded and replaced throughout life is termed ''polyphyodont''. The dentition of animals in which the teeth are set in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hermann Klaatsch
Hermann Klaatsch (10 March 1863 – 5 January 1916) was a German physician, anatomist, physical anthropologist, evolutionist, and professor at the University of Heidelberg from 1890, and at the University of Breslau (Wrocław) until 1916.Hermann Klaatsch " (biography), Aaron Possis, , , 2003. Klaatsch studied |
Species Description
A species description is a formal description of a newly discovered species, usually in the form of a scientific paper. Its purpose is to give a clear description of a new species of organism and explain how it differs from species that have been described previously or are related. In order for species to be validly described, they need to follow guidelines established over time. Zoological naming requires adherence to the ICZN code, plants, the ICN, viruses ICTV, and so on. The species description often contains photographs or other illustrations of type material along with a note on where they are deposited. The publication in which the species is described gives the new species a formal scientific name. Some 1.9 million species have been identified and described, out of some 8.7 million that may actually exist. Millions more have become extinct throughout the existence of life on Earth. Naming process A name of a new species becomes valid (available in z ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homo Heidelbergensis (Erstbeschreibung) 01
''Homo heidelbergensis'' (also ''H. sapiens heidelbergensis'') is an extinct species or subspecies of archaic human which existed during the Middle Pleistocene. It was subsumed as a subspecies of ''H. erectus'' in 1950 as ''H. e. heidelbergensis'', but towards the end of the century, it was more widely classified as its own species. It is debated whether or not to constrain ''H. heidelbergensis'' to only Europe or to also include African and Asian specimens, and this is further confounded by the type specimen (Mauer 1) being a jawbone, because jawbones feature few diagnostic traits and are generally missing among Middle Pleistocene specimens. Thus, it is debated if some of these specimens could be split off into their own species or a subspecies of ''H. erectus''. Because the classification is so disputed, the Middle Pleistocene is often called the "muddle in the middle." ''H. heidelbergensis'' is regarded as a chronospecies, evolving from an African form of ''H. erectus'' (somet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_01.jpg)








.jpg)