|
Masculine
Masculinity (also called manhood or manliness) is a set of attributes, behaviors, and roles associated with men and boys. Masculinity can be theoretically understood as socially constructed, and there is also evidence that some behaviors considered masculine are influenced by both cultural factors and biological factors. To what extent masculinity is biologically or socially influenced is subject to debate. It is distinct from the definition of the biological male sex, as anyone can exhibit masculine traits. Standards of masculinity vary across different cultures and historical periods. Overview Masculine qualities and roles are considered typical of, appropriate for, and expected of boys and men. Standards of manliness or masculinity vary across different cultures, subcultures, ethnic groups and historical periods. Traits traditionally viewed as masculine in Western society include strength, courage, independence, leadership, and assertiveness.Thomas, R. Murray (20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leadership
Leadership, both as a research area and as a practical skill, encompasses the ability of an individual, group or organization to "lead", influence or guide other individuals, teams, or entire organizations. The word "leadership" often gets viewed as a contested term. Specialist literature debates various viewpoints on the concept, sometimes contrasting Eastern and Western approaches to leadership, and also (within the West) North American versus European approaches. U.S. academic environments define leadership as "a process of social influence in which a person can enlist the aid and support of others in the accomplishment of a common and ethical task". Basically, leadership can be defined as an influential power-relationship in which the power of one party (the "leader") promotes movement/change in others (the "followers"). Some have challenged the more traditional managerial views of leadership (which portray leadership as something possessed or owned by one individual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Androgynous
Androgyny is the possession of both masculine and feminine characteristics. Androgyny may be expressed with regard to biological sex, gender identity, or gender expression. When ''androgyny'' refers to mixed biological sex characteristics in humans, it often refers to intersex people, who are born with congenital variations that complicate assigning their sex at birth. In comparison, hermaphroditism is the possession of both male and female reproductive organs. Regarding gender identity, androgynous individuals may identify with non-binary identities. Others may identify as transgender. As a form of gender expression, androgyny has fluctuated in popularity in different cultures and throughout history. Physically, an androgynous appearance may be achieved through personal grooming, fashion, or hormone treatment. Etymology The term derives from grc, ἀνδρόγυνος, from , stem - (''anér, andro-'', meaning man) and (''gunē, gyné'', meaning woman) through the l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feminine
Femininity (also called womanliness) is a set of attributes, behaviors, and roles generally associated with women and girls. Femininity can be understood as socially constructed, and there is also some evidence that some behaviors considered feminine are influenced by both cultural factors and biological factors. To what extent femininity is biologically or socially influenced is subject to debate. It is conceptually distinct from both the female biological sex and from womanhood, as all humans can exhibit feminine and masculine traits, regardless of sex and gender. Traits traditionally cited as feminine include gracefulness, gentleness, empathy, humility, and sensitivity, though traits associated with femininity vary across societies and individuals, and are influenced by a variety of social and cultural factors. Overview and history Despite the terms ''femininity'' and ''masculinity'' being in common usage, there is little scientific agreement about what femininity and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beowulf And The Dragon
''Beowulf'' (; ang, Bēowulf ) is an Old English epic poem in the tradition of Germanic heroic legend consisting of 3,182 alliterative lines. It is one of the most important and most often translated works of Old English literature. The date of composition is a matter of contention among scholars; the only certain dating is for the manuscript, which was produced between 975 and 1025. Scholars call the anonymous author the "''Beowulf'' poet". The story is set in pagan Scandinavia in the 6th century. Beowulf, a hero of the Geats, comes to the aid of Hrothgar, the king of the Danes, whose mead hall in Heorot has been under attack by the monster Grendel. After Beowulf slays him, Grendel's mother attacks the hall and is then defeated. Victorious, Beowulf goes home to Geatland and becomes king of the Geats. Fifty years later, Beowulf defeats a dragon, but is mortally wounded in the battle. After his death, his attendants cremate his body and erect a tower on a headland ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World History Encyclopedia
World History Encyclopedia (formerly Ancient History Encyclopedia) is a nonprofit educational company created in 2009 by Jan van der Crabben. The organization publishes and maintains articles, images, videos, podcasts, and interactive educational tools related to history. All users may contribute content to the site, although submissions are reviewed by an editorial team before publication. In 2021, the organization was renamed from the Ancient History Encyclopedia to World History Encyclopedia to reflect its broadened scope, covering world history from all time periods, as opposed to just ancient history. Original articles are written in English and later translated into other languages, mainly French and Spanish. Organization history The Ancient History Encyclopedia was founded in 2009 by van der Crabben with the stated goal of improving history education worldwide by creating a freely accessible and reliable history source. The nonprofit organization is based in Godalming, Unit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germanicus
Germanicus Julius Caesar (24 May 15 BC – 10 October AD 19) was an ancient Roman general, known for his campaigns in Germania. The son of Nero Claudius Drusus and Antonia the Younger, Germanicus was born into an influential branch of the patrician ''gens Claudia''. The agnomen ''Germanicus'' was added to his full name in 9 BC when it was posthumously awarded to his father in honour of his victories in Germania. In AD 4, he was adopted by his paternal uncle Tiberius, who succeeded Augustus as Roman emperor a decade later. As a result, Germanicus became an official member of the ''gens Julia'', another prominent family, to which he was related on his mother's side. His connection to the Julii was further consolidated through a marriage between himself and Agrippina the Elder, a granddaughter of Augustus. He was also the father of Caligula, the maternal grandfather of Nero, and the older brother of Claudius. During the reign of Augustus, Germanicus enjoyed an accelerated p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
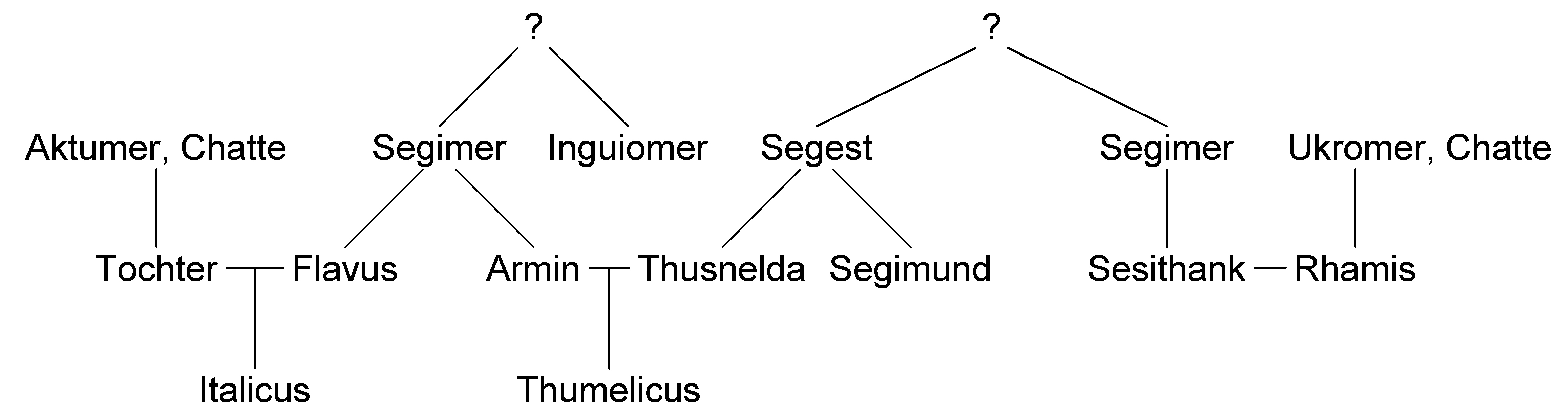
Thusnelda
Thusnelda (; 10 BC – after AD 17) was a Germanic Cheruscan noblewoman who was captured by the Roman general Germanicus during his invasion of Germania. She was the wife of Arminius. Tacitus and Strabo cite her capture as evidence of both the firmness and restraint of Roman arms. Biography Thusnelda was the daughter of the pro-Roman Cheruscan prince Segestes. In 9 AD, Arminius, Thusnelda's future husband, who had been given by his father to the Romans as a child and raised as a Roman military commander serving under Publius Quinctilius Varus, switched sides to the Germans, and led a coalition of Germanic tribes that defeated the legions of Varus at the Battle of the Teutoburg Forest. The conflict between the Roman Empire and the Germanic tribes continued after the Battle of the Teutoburg Forest, and Arminius abducted and impregnated Thusnelda circa 14 AD, likely as a result of a dispute with her pro-Roman father. In May 15 AD, Thusnelda was captured by Germanicus, who comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arminius
Arminius ( 18/17 BC – 21 AD) was a chieftain of the Germanic Cherusci tribe who is best known for commanding an alliance of Germanic tribes at the Battle of the Teutoburg Forest in 9 AD, in which three Roman legions under the command of general Publius Quinctilius Varus were destroyed. His victory at Teutoburg Forest would precipitate the Roman Empire's permanent strategic withdrawal from Germania Magna. Modern historians have regarded Arminius' victory as one of Rome's greatest defeats. As it prevented the Romanization of Germanic peoples east of the Rhine, it has also been considered one of the most decisive battles in history and a turning point in human history. Born a prince of the Cherusci tribe, Arminius was part of the Roman friendly faction of the tribe. He learned Latin and served in the Roman military, which gained him Roman citizenship and the rank of ''eques''. After serving with distinction in the Great Illyrian Revolt, he was sent to Germania to aid the lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germanic Tribes
The Germanic peoples were historical groups of people that once occupied Central Europe and Scandinavia during antiquity and into the early Middle Ages. Since the 19th century, they have traditionally been defined by the use of ancient and early medieval Germanic languages and are thus equated at least approximately with Germanic-speaking peoples, although different academic disciplines have their own definitions of what makes someone or something "Germanic". The Romans named the area belonging to North-Central Europe in which Germanic peoples lived '' Germania'', stretching East to West between the Vistula and Rhine rivers and north to south from Southern Scandinavia to the upper Danube. In discussions of the Roman period, the Germanic peoples are sometimes referred to as ''Germani'' or ancient Germans, although many scholars consider the second term problematic since it suggests identity with present-day Germans. The very concept of "Germanic peoples" has become the sub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tacitus
Publius Cornelius Tacitus, known simply as Tacitus ( , ; – ), was a Roman historian and politician. Tacitus is widely regarded as one of the greatest Roman historians by modern scholars. The surviving portions of his two major works—the ''Annals'' (Latin: ''Annales'') and the ''Histories'' (Latin: ''Historiae'')—examine the reigns of the emperors Tiberius, Claudius, Nero, and those who reigned in the Year of the Four Emperors (69 AD). These two works span the history of the Roman Empire from the death of Augustus (14 AD) to the death of Domitian (96 AD), although there are substantial lacunae in the surviving texts. Tacitus's other writings discuss oratory (in dialogue format, see '' Dialogus de oratoribus''), Germania (in ''De origine et situ Germanorum''), and the life of his father-in-law, Agricola (the general responsible for much of the Roman conquest of Britain), mainly focusing on his campaign in Britannia ('' De vita et moribus Iulii Agricol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germania (book)
The ''Germania'', written by the Roman historian Publius Cornelius Tacitus around 98 AD and originally entitled ''On the Origin and Situation of the Germans'' ( la, De origine et situ Germanorum), is a historical and ethnographic work on the Germanic peoples outside the Roman Empire. Contents The ''Germania'' begins with a description of the lands, laws, and customs of the Germanic people (chapters 1–27); it then describes individual peoples, beginning with those dwelling closest to Roman lands and ending on the uttermost shores of the Baltic, among the amber-gathering Aesti, the Fenni, and the unknown peoples beyond them. Tacitus says (chapter 2) that physically, the Germanic peoples appear to be a distinct nation, not an admixture of their neighbors, since nobody would desire to migrate to a climate as horrid as that of Germania. They are divided into three large branches, the Ingaevones, the Irminones, and the Istaevones, deriving their ancestry from three sons of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |