|
Mangalesha
Mangalesha (IAST: Maṅgaleśa, r. c. 592-610 CE) was a king of the Chalukya dynasty of Vatapi in Karnataka, India. He succeeded his brother Kirttivarman I on the throne, and ruled a kingdom that stretched from southern Gujarat in north to Bellary-Kurnool region in the south, in the western part of the Deccan region. It included parts of present-day Gujarat, Maharashtra, Goa, Karnataka, and Andhra Pradesh. Mangalesha expanded the Chalukya power in present-day Gujarat and Maharashtra after defeating the Kalachuri king Buddharaja. He also consolidated his rule in the Konkan coastal region of Maharashtra and Goa after conquering Revati-dvipa from the rebel Chalukya governor Svamiraja. His reign ended when he lost a war of succession to his nephew Pulakeshin II, a son of Kirttivarman I. Mangalesha was a Vaishnavite, and constructed a Vishnu temple during the reign of his brother Kirttivarman I. He was tolerant of other sects, as evident by the Mahakuta Pillar inscription, which rec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulakeshin II
Pulakeshin II (IAST: Pulakeśin, r. c. 610–642 CE) was the most famous ruler of the Chalukya dynasty of Vatapi (present-day Badami in Karnataka, India). During his reign, the Chalukya kingdom expanded to cover most of the Deccan region in peninsular India. A son of the Chalukya king Kirttivarman I, Pulakeshin overthrew his uncle Mangalesha to gain control of the throne. He suppressed a rebellion by Appayika and Govinda, and decisively defeated the Kadambas of Banavasi in the south. The Alupas and the Gangas of Talakadu recognized his suzerainty. He consolidated the Chalukya control over the western coast by subjugating the Mauryas of Konkana. His Aihole inscription also credits him with subjugating the Latas, the Malavas, and the Gurjaras in the north. The most notable military achievement of Pulakeshin was his victory over the powerful northern emperor Harshavardhana, whose failure to conquer the Chalukya kingdom is attested by the Chinese pilgrim Xuanzang. In the eas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kirttivarman I
Kirttivarman I (IAST: Kīrtti-varman; r. c. 566-592) was a ruler of the Chalukya dynasty of Vatapi (present-day Badami) in India. He ruled parts of present-day Karnataka, Goa, Maharashtra and Andhra Pradesh. Kirttivarman was the son of his predecessor Pulakeshin I, the first sovereign ruler of the dynasty. He expanded the Chalukya kingdom by defeating the Nalas, the Mauryas of Konkana, the Kadambas, the Alupas, and the Gangas of Talakad. Names and titles Some of the dynasty's inscriptions call him Kirtti-raja. The Godachi inscription calls him Katti-arasa, which is probably a Kannada language variant of his name. Besides the regal title ''Maharaja'', the dynasty's inscriptions accord him the Chalukya family epithets '' Shri-prithvi-vallabha'', ''Vallabha'', and ''Satyashraya''. The Mahakuta pillar inscription of his brother Mangalesha compares him to the legendary king Puru, calling him ''Puru-rana-parakrama'' ("valourous in war like Puru"). Early life Kirttivarman I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Revatidvipa
Revatidvipa or Govapuri was a province under the Chalukya dynasty, encompassing parts of modern-day Goa and Maharashtra, India. Revatidvipa was an important trading port of the dynasties that controlled it, including the Chalukyas. It was conquered by the Rashtrakuta ruler Krishna I in 753 AD. It flourished as a maritime port with a flow of traders and foreign mercantile communities developing. The most significant communist among them were the Pahlavi-speaking Christian merchants from Persis (modern-day Fars) History The town of Gopakapattana is identified with modern-day Redi in Maharashtra. The region was successfully ruled by the Kadambas, Bhojas, Mauryas of Konkana, Chalukyas, Rashtrakutas, Shilaharas, Kadambas of Goa and Seunas of Devagiri. Revatidvipa was an important territory of the Mauryas of Konkan. The Chalukya ruler Kirttivarman I attacked the Konkan Mauryas with his main objective being to occupy the port of Revatidvipa. Kirttivarman I's conquest of Revati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mahakuta Pillar
Mahakuta Pillar ( kn, ಮಹಾಕೂಟ ಸ್ತಂಭ), also known as Makuta pillar, Magada stambha or Mangalesa Dharma Jayastambha, is a deep red sandstone pillar with an early 7th-century inscription of Early Western Chalukya era. It was found near Mahakuta group of Hindu temples near Badami, Karnataka, India. Inscribed with 16 lines of Sanskrit in Old Kannada script by king Mangalesha, it is an important and partly disputed source of historic information about the times of Badami Chalukya, the dynasty, and his influential father Pulakeshin I. Location The pillar was found in the 19th-century lying on the ground near the ruins of Mahakutesvara temple, one of the 7th-century group of temples at the Mahakuta natural springs (Bagalkot district). The site is about east from the historic cave temples of Badami. Its significance was re-discovered by colonial era archaeologists and scholars in the 1880s. The pillar was moved to Bijapur about 1920, and is now housed in the Gol Gum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chalukyas Of Vatapi
The Chalukya dynasty () was a Classical Indian dynasty that ruled large parts of southern and central India between the 6th and the 12th centuries. During this period, they ruled as three related yet individual dynasties. The earliest dynasty, known as the "Badami Chalukyas", ruled from Vatapi (modern Badami) from the middle of the 6th century. The Badami Chalukyas began to assert their independence at the decline of the Kadamba kingdom of Banavasi and rapidly rose to prominence during the reign of Pulakeshin II. After the death of Pulakeshin II, the Eastern Chalukyas became an independent kingdom in the eastern Deccan. They ruled from Vengi until about the 11th century. In the western Deccan, the rise of the Rashtrakutas in the middle of the 8th century eclipsed the Chalukyas of Badami before being revived by their descendants, the Western Chalukyas, in the late 10th century. These Western Chalukyas ruled from Kalyani (modern Basavakalyan) until the end of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aihole Inscription
The Aihole Inscription, also known as the Aihole '' prashasti'', is a nineteen line Sanskrit inscription at Meguti Jain temple in Aihole, Karnataka, India. An eulogy dated 634–635 CE, it was composed by the Jain poet Ravikirti in honor of his patron king Pulakesin Satyasraya (Pulakeshin II) of the Badami Chalukya dynasty. The inscription is partly damaged and corrupted – its last two lines were added at a later date.Kielhorn (1901), pp. 1–11 Since the 1870s, the inscription was recorded several times, revised, republished and retranslated by Fleet, Kielhorn and others. The inscription is a '' prashasti'' for the early Western Chalukyas. It is notable for its historical details mixed in with myth, and the scholarly disagreements it has triggered. It is also an important source of placing political events and literature – such as of Kalidasa – that must have been completed well before 634 CE, the date of this inscription. Location and history The Aihole inscription of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vatapi
Badami, formerly known as Vatapi, is a town and headquarters of a taluk by the same name, in the Bagalkot district of Karnataka, India. It was the regal capital of the Badami Chalukyas from CE 540 to 757. It is famous for its rock cut monuments such as the Badami cave temples, as well as the structural temples such as the Bhutanatha temples, Badami Shivalaya and Jambulingesvara Temple, Badami, Jambulingesvara temple. It is located in a ravine at the foot of a rugged, red sandstone outcrop that surrounds Agastya lake. Badami has been selected as one of the heritage cities for HRIDAY - Heritage City Development and Augmentation Yojana scheme of Government of India. Nearest Railway Station is Badami Railway Station which is just 2 km from Badami city. Nearest Airport is Hubli Airport which is 109 km away from Badami. History Pre-historic and epic The Badami region was settled in pre-historic times, with evidence by megalithic dolmens. In the local tradition, the Bad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kalachuri Dynasty
The Kalachuris (IAST: Kalacuri), also known as Kalachuris of Mahishmati, were an Indian dynasty that ruled in west-central India between 6th and 7th centuries. They are also known as the Haihayas or as the Early Kalachuris to distinguish them from their later namesakes, especially the Kalachuris of Tripuri. The Kalachuri territory included parts of present-day Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, and Maharashtra. Their capital was probably located at Mahishmati. Epigraphic and numismatic evidence suggests that the earliest of the Ellora and Elephanta cave monuments were built during the Kalachuri rule. The origin of the dynasty is uncertain. In the 6th century, the Kalachuris gained control of the territories formerly ruled by the Guptas, the Vakatakas and the Vishnukundinas. Only three Kalachuri kings are known from inscriptional evidence: Shankaragana, Krishnaraja, and Buddharaja. The Kalachuris lost their power to the Chalukyas of Vatapi in the 7th century. One theory connects the l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulakeshin I
Pulakeshin (IAST: Pulakeśin, r. c. 540–567) was the first sovereign ruler of the Chalukya dynasty of Vatapi (modern Badami). He ruled parts of the present-day Karnataka, Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh and Telangana states in the western and central Deccan region of India. Pulakeshin established the city of Vatapi, and performed the Ashvamedha sacrifice to assert his sovereign status. The dynasty established by him went on to rule a major part of peninsular India in the subsequent years. Names and titles Various variants of the name "Pulakeshin" appear in the dynasty's inscriptions, including Polekeshin (Polekeśin), Polikeshin (Polikeśin), and Pulikeshin (Pulikeśin). According to historians J. F. Fleet and D. C. Sircar, the name may be a Sanskrit-Kannada hybrid word meaning "tiger-haired". K. A. Nilakanta Sastri, on the other hand, derived the name from the Sanskrit words ''pula'' or ''pola'' ("great") and ''keśin'' ("lion"). The 'Badami Chalukyas' published by Kannad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prithvi-vallabha
Prithvi-vallabha (IAST: ), or , was a title adopted by several kings that ruled in present-day India, including the Chalukyas of Vatapi, the Rashtrakutas and their successors. Chalukyas of Vatapi All the sovereign rulers of the Chalukyas of Vatapi, Vatapi Chalukya dynasty bore the title ''Shri-prithvi-vallabha'', which means "the husband of the goddess of fortune and the Earth" (that is, Vishnu). Mangalesha bore the exact title ''Prithvi-vallabha'', as attested by the Mahakuta group of temples, Mahakuta inscriptions. The Manor, India, Manor inscription of the Chalukya governor Chalukyas of Navasarika#Jayashraya Mangalarasa, Jayashraya Mangalarasa, dated to 7 April 691 (year 613 of the Shaka era), also mentions ''Prithvi-vallabha'' as one of his titles. His son Avanijanashraya Pulakeshin also bore the title. Rashtrakutas Among the Rashtrakutas, the title was first adopted by Dantidurga, an 8th-century ruler of the Deccan Plateau, Deccan and the founder of the Rashtrakuta dynast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Redi, Maharashtra
Redi is a village in the district of Sindhudurg in Maharashtra. Originally known as Rewati, Redi is located close to the shores of the Arabian Sea. Cashew and coconut trees grow in the region. The village belongs to the Vengurla Taluka of the Konkan region and was a significant sea port during the earlier times. Redi has now evolved into a tourist hub because of its long virgin and unspoiled beaches alongside archaic historic monuments like the Yashwantgad Fort. Redi is merely 566 km away from Mumbai and can be easily reached. History Redi was built by the Marathas in the sixteenth century and, in 1746, was captured by the Portuguese. The previous citadel-holders, the Sawant clan of Maharashtra, attempted to recapture Redi by poisoning the Portuguese garrison's fish supply, but the attack was unsuccessful. Redi was eventually returned to the Sawants following a peace treaty, but the peace was short-lived; in 1765 the fort was captured by the British who sold the land ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
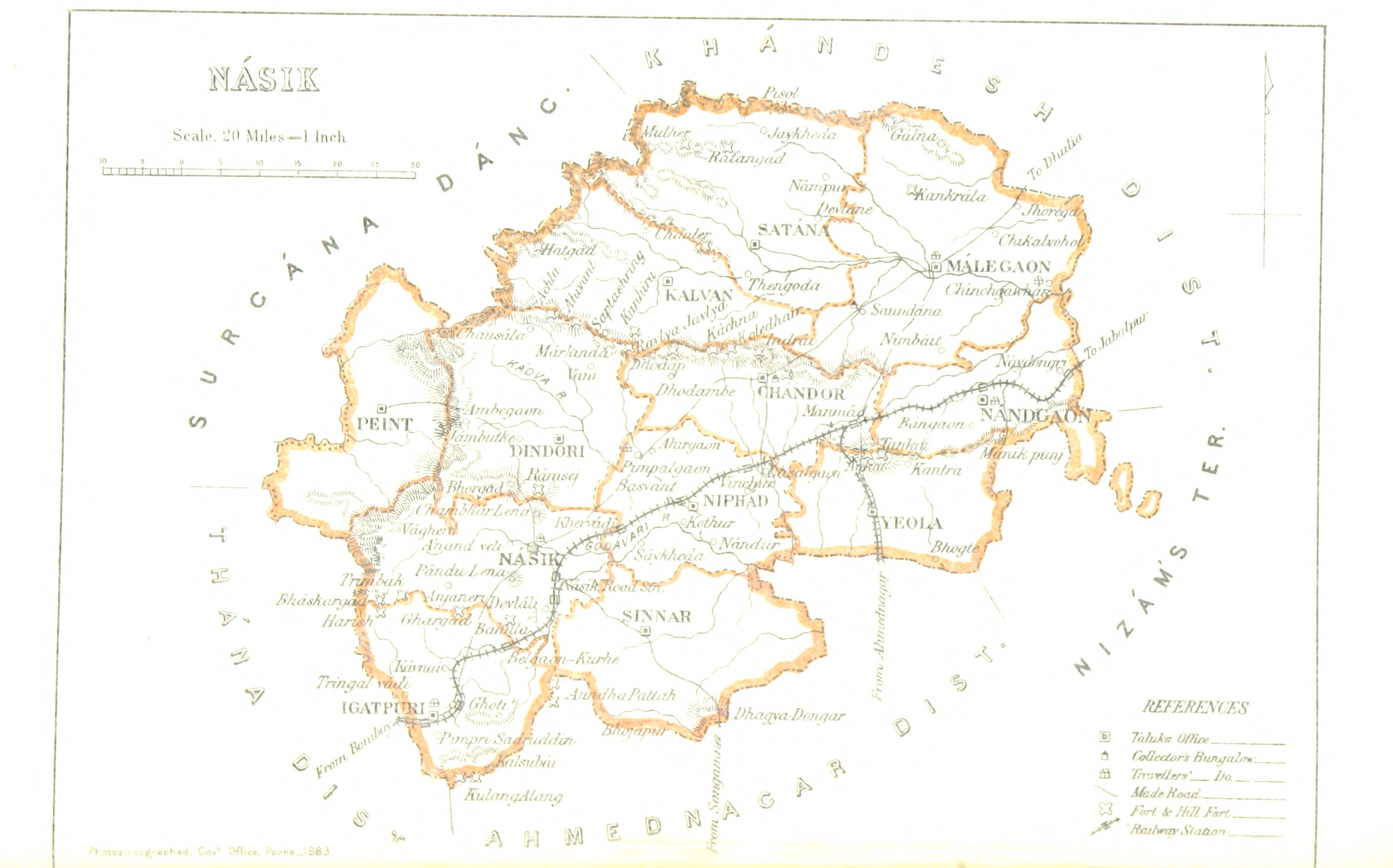
Nashik District
Nashik district, also known as Nasik district, is a district in Maharashtra, India. The city of Nashik is the administrative headquarters of the district. Nashik is well known for the production of wine. Nashik is also known as Mini Maharashtra, because the climate and soil conditions of Surgana, Peth, Igatpuri resembles with Konkan. Niphad, Sinnar, Dindori, Baglan blocks are like Western Maharashtra and Yeola, Nandgaon, Chandwad blocks are like Vidarbha Region. Nashik is the biggest city in the district while Malegaon is the second biggest city. Manmad, Igatpuri, sinnar are some of the big cities situated in the Nashik District. Manmad is one of the biggest railway junction in india while the city of Malegaon is famous for its powerloom. Nashik district is the third largest district in Maharashtra state in terms of population of 8,107,187 and occupying an area of 15,582 square kilometres in the north Maharashtra region. It is bounded by Dhule District to the north, Jalgaon Dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |