|
Mandrill
The mandrill (''Mandrillus sphinx'') is a large Old World monkey native to west central Africa. It is one of the most colorful mammals in the world, with red and blue skin on its face and posterior. The species is sexually dimorphic, as males have a larger body, longer canine teeth and brighter coloring. Its closest living relative is the drill with which it shares the genus '' Mandrillus''. Both species were traditionally thought to be baboons, but further evidence has shown that they are more closely related to white-eyelid mangabeys. Mandrills mainly live in tropical rainforests but will also travel across savannas. They are active during the day and spend most of their time on the ground. Their preferred foods are fruit and seeds, but mandrills will consume leaves, piths, mushrooms, and animals from insects to juvenile antelope. Mandrills live in large, stable groups known as "hordes" which can number in the hundreds. Females form the core of these groups, while adul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandrillus
''Mandrillus'' is a genus of large Old World monkeys distributed throughout central and southern Africa, consisting of two species: ''M. sphinx'' and ''M. leucophaeus'', the mandrill and drill, respectively. ''Mandrillus'', originally placed under the genus ''Papio'' as a type of baboon, is closely related to the genus ''Cercocebus''. They are characterised by their large builds, elongated snouts with furrows on each side, and stub tails. Both species occupy the west central region of Africa and live primarily on the ground. They are frugivores, consuming both meat and plants, with a preference for plants. ''M. sphinx'' is classified as vulnerable and ''M. leucophaeus'' as endangered on the ''IUCN Red List of Threatened Species''. Taxonomy ''Mandrillus'' is a genus within the tribe Papionini, which in turn is under the subfamily Cercopithecinae. This subfamily is classified under the family of Old World monkeys (Cercopithecidae) within the infraorder Simiiformes. The Papioni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drill (animal)
The drill (''Mandrillus leucophaeus'') is a primate of the family Cercopithecidae (Old World monkeys), related to baboons and even more closely to mandrills. Description The drill is a short-tailed monkey up to long, similar in appearance to the mandrill, but lacks the bright blue and red on the face of that species. It has high sexual dimorphism in weight, with males weighing up to and females up to .ARKive Drill (''Mandrillus leucophaeus'') The body is overall a dark grey-brown. Mature males have a pink lower lip and white chin on a dark grey to black face with raised grooves on the nose. The rump is pink, mauve and blue. Female drills lack the pink chin. Taxonomy Two subspecies of drill are accepted by some authorities, but are not considered distinct by others:Primate Info NetDrill/ref> * Mainland drill, ''Mandrillus leucophaeus leucophaeus'' * Bioko drill, ''Mandrillus leucophaeus poensis'' Their closest relative is the mandrill (''Mandrillus sphinx''), found from s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
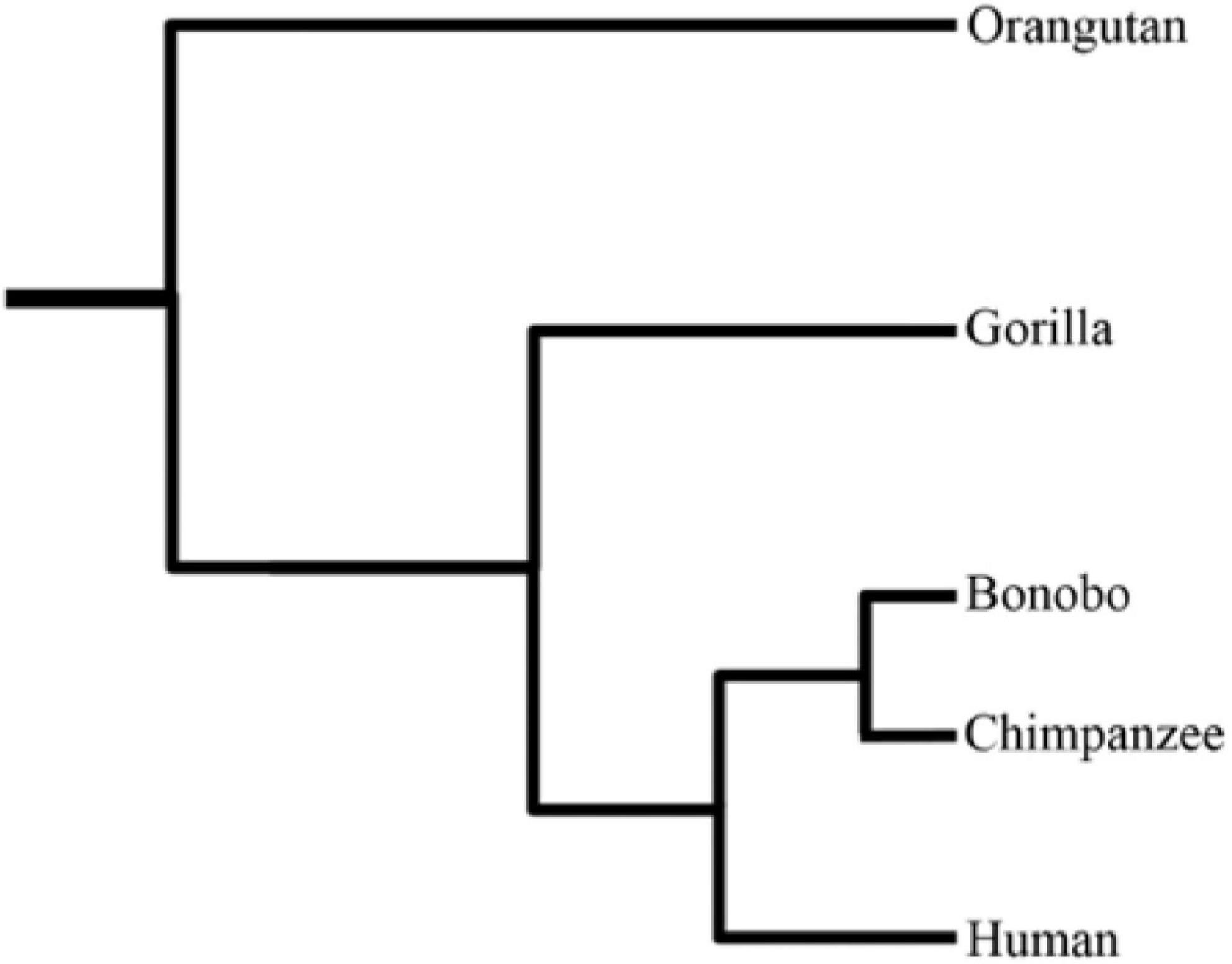
Old World Monkey
Old World monkey is the common English name for a family of primates known taxonomically as the Cercopithecidae (). Twenty-four genera and 138 species are recognized, making it the largest primate family. Old World monkey genera include baboons (genus ''Papio''), red colobus (genus '' Piliocolobus'') and macaques (genus '' Macaca''). Common names for other Old World monkeys include the talapoin, guenon, colobus, douc (douc langur, genus '' Pygathrix''), vervet, gelada, mangabey (a group of genera), langur, mandrill, surili ('' Presbytis''), patas, and proboscis monkey. Phylogenetically, they are more closely related to apes than to New World monkeys. They diverged from a common ancestor of New World monkeys around 45 to 55 million years ago. The smallest Old World monkey is the talapoin, with a head and body 34–37 cm in length, and weighing between 0.7 and 1.3 kg. The largest is the male mandrill, around 70 cm in length, and weighing up to 50&nbs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bushmeat
Bushmeat is meat from wildlife species that are hunted for human consumption, most often referring to the meat of game in Africa. Bushmeat represents a primary source of animal protein and a cash-earning commodity for inhabitants of humid tropical forest regions in Africa, Latin America and Asia. Bushmeat is an important food resource for poor people, particularly in rural areas. The numbers of animals killed and traded as bushmeat in the 1990s in West and Central Africa were thought to be unsustainable. By 2005, commercial harvesting and trading of bushmeat was considered a threat to biodiversity. As of 2016, 301 terrestrial mammals were threatened with extinction due to hunting for bushmeat including primates, even-toed ungulates, bats, diprotodont marsupials, rodents and carnivores occurring in developing countries. Bushmeat provides increased opportunity for transmission of several zoonotic viruses from animal hosts to humans, such as Ebolavirus and HIV. Nomenclature ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papio
Baboons are primates comprising the genus ''Papio'', one of the 23 genera of Old World monkeys. There are six species of baboon: the hamadryas baboon, the Guinea baboon, the olive baboon, the yellow baboon, the Kinda baboon and the chacma baboon. Each species is native to one of six areas of Africa and the hamadryas baboon is also native to part of the Arabian Peninsula. Baboons are among the largest non- hominoid primates and have existed for at least two million years. Baboons vary in size and weight depending on the species. The smallest, the Kinda baboon, is in length and weighs only , while the largest, the chacma baboon, is up to in length and weighs . All baboons have long, dog-like muzzles, heavy, powerful jaws with sharp canine teeth, close-set eyes, thick fur except on their muzzles, short tails, and nerveless, hairless pads of skin on their protruding buttocks called ischial callosities that provide for sitting comfort. Male hamadryas baboons have large w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baboon
Baboons are primates comprising the genus ''Papio'', one of the 23 genera of Old World monkeys. There are six species of baboon: the hamadryas baboon, the Guinea baboon, the olive baboon, the yellow baboon, the Kinda baboon and the chacma baboon. Each species is native to one of six areas of Africa and the hamadryas baboon is also native to part of the Arabian Peninsula. Baboons are among the largest non- hominoid primates and have existed for at least two million years. Baboons vary in size and weight depending on the species. The smallest, the Kinda baboon, is in length and weighs only , while the largest, the chacma baboon, is up to in length and weighs . All baboons have long, dog-like muzzles, heavy, powerful jaws with sharp canine teeth, close-set eyes, thick fur except on their muzzles, short tails, and nerveless, hairless pads of skin on their protruding buttocks called ischial callosities that provide for sitting comfort. Male hamadryas baboons have large whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chimpanzee
The chimpanzee (''Pan troglodytes''), also known as simply the chimp, is a species of great ape native to the forest and savannah of tropical Africa. It has four confirmed subspecies and a fifth proposed subspecies. When its close relative the bonobo was more commonly known as the pygmy chimpanzee, this species was often called the common chimpanzee or the robust chimpanzee. The chimpanzee and the bonobo are the only species in the genus ''Pan''. Evidence from fossils and DNA sequencing shows that ''Pan'' is a sister taxon to the human lineage and is humans' closest living relative. The chimpanzee is covered in coarse black hair, but has a bare face, fingers, toes, palms of the hands, and soles of the feet. It is larger and more robust than the bonobo, weighing for males and for females and standing . The chimpanzee lives in groups that range in size from 15 to 150 members, although individuals travel and forage in much smaller groups during the day. The species lives in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cameroon
Cameroon (; french: Cameroun, ff, Kamerun), officially the Republic of Cameroon (french: République du Cameroun, links=no), is a country in west-central Africa. It is bordered by Nigeria to the west and north; Chad to the northeast; the Central African Republic to the east; and Equatorial Guinea, Gabon and the Republic of the Congo to the south. Its coastline lies on the Bight of Biafra, part of the Gulf of Guinea and the Atlantic Ocean. Due to its strategic position at the crossroads between West Africa and Central Africa, it has been categorized as being in both camps. Its nearly 27 million people speak 250 native languages. Early inhabitants of the territory included the Sao civilisation around Lake Chad, and the Baka hunter-gatherers in the southeastern rainforest. Portuguese explorers reached the coast in the 15th century and named the area ''Rio dos Camarões'' (''Shrimp River''), which became ''Cameroon'' in English. Fulani soldiers founded the Adamawa Emirate in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equatorial Guinea
Equatorial Guinea ( es, Guinea Ecuatorial; french: Guinée équatoriale; pt, Guiné Equatorial), officially the Republic of Equatorial Guinea ( es, link=no, República de Guinea Ecuatorial, french: link=no, République de Guinée équatoriale, pt, link=no, República da Guiné Equatorial), *french: link=no, République de Guinée équatoriale * pt, link=no, República da Guiné Equatorial is a country on the west coast of Central Africa, with an area of . Formerly the colony of Spanish Guinea, its post-independence name evokes its location near both the Equator and the Gulf of Guinea. , the country had a population of 1,468,777. Equatorial Guinea consists of two parts, an insular and a mainland region. The insular region consists of the islands of Bioko (formerly ''Fernando Pó'') in the Gulf of Guinea and Annobón, a small volcanic island which is the only part of the country south of the equator. Bioko Island is the northernmost part of Equatorial Guinea and is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Republic Of The Congo
The Republic of the Congo (french: République du Congo, ln, Republíki ya Kongó), also known as Congo-Brazzaville, the Congo Republic or simply either Congo or the Congo, is a country located in the western coast of Central Africa to the west of the Congo river. It is bordered to the west by Gabon, to its northwest by Cameroon and its northeast by the Central African Republic, to the southeast by the Democratic Republic of the Congo, to its south by the Angolan exclave of Cabinda and to its southwest by the Atlantic Ocean. The region was dominated by Bantu-speaking tribes at least 3,000 years ago, who built trade links leading into the Congo River basin. Congo was formerly part of the French colony of Equatorial Africa. The Republic of the Congo was established on 28 November 1958 and gained independence from France in 1960. It was a Marxist–Leninist state from 1969 to 1992, under the name People's Republic of the Congo. The country has had multi-party elections sin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Historia Animalium (Gessner Book)
''Historia animalium'' ("History of the Animals"), published at Zurich in 1551–1558 and 1587, is an encyclopedic "inventory of renaissance zoology" by Conrad Gessner (1516–1565). Gessner was a medical doctor and professor at the Carolinum in Zürich, the precursor of the University of Zurich. The ''Historia animalium'', after Aristotle's work of the same name. is the first modern zoological work that attempts to describe all the animals known, and the first bibliography of natural history writings. The five volumes of natural history of animals cover more than 4500 pages. Overview The ''Historia animalium'' was Gessner's magnum opus, and was the most widely read of all the Renaissance natural histories. The generously illustrated work was so popular that Gessner's abridgement, ''Thierbuch'' ("Animal Book"), was published in Zurich in 1563, and in England Edward Topsell translated and condensed it as a ''Historie of foure-footed beastes'' (London: William Jaggard, 1607). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)




_anubis_baboon%2C_Ngorongoro_National_Park%2C_Tanzania%2C_2014.png)