|
Locally Cyclic Group
In mathematics, a locally cyclic group is a group (''G'', *) in which every finitely generated subgroup is cyclic. Some facts * Every cyclic group is locally cyclic, and every locally cyclic group is abelian. * Every finitely-generated locally cyclic group is cyclic. * Every subgroup and quotient group of a locally cyclic group is locally cyclic. * Every homomorphic image of a locally cyclic group is locally cyclic. * A group is locally cyclic if and only if every pair of elements in the group generates a cyclic group. * A group is locally cyclic if and only if its lattice of subgroups is distributive . * The torsion-free rank of a locally cyclic group is 0 or 1. * The endomorphism ring of a locally cyclic group is commutative. Examples of locally cyclic groups that are not cyclic Examples of abelian groups that are not locally cyclic * The additive group of real number In mathematics, a real number is a number that can be used to measure a ''continuous'' one-dimension ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finitely Generated Subgroup
In algebra, a finitely generated group is a group ''G'' that has some finite generating set ''S'' so that every element of ''G'' can be written as the combination (under the group operation) of finitely many elements of ''S'' and of inverses of such elements. By definition, every finite group is finitely generated, since ''S'' can be taken to be ''G'' itself. Every infinite finitely generated group must be countable but countable groups need not be finitely generated. The additive group of rational numbers Q is an example of a countable group that is not finitely generated. Examples * Every quotient of a finitely generated group ''G'' is finitely generated; the quotient group is generated by the images of the generators of ''G'' under the canonical projection. * A subgroup of a finitely generated group need not be finitely generated. * A group that is generated by a single element is called cyclic. Every infinite cyclic group is isomorphic to the additive group of the intege ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commutative Ring
In mathematics, a commutative ring is a ring in which the multiplication operation is commutative. The study of commutative rings is called commutative algebra. Complementarily, noncommutative algebra is the study of ring properties that are not specific to commutative rings. This distinction results from the high number of fundamental properties of commutative rings that do not extend to noncommutative rings. Definition and first examples Definition A ''ring'' is a set R equipped with two binary operations, i.e. operations combining any two elements of the ring to a third. They are called ''addition'' and ''multiplication'' and commonly denoted by "+" and "\cdot"; e.g. a+b and a \cdot b. To form a ring these two operations have to satisfy a number of properties: the ring has to be an abelian group under addition as well as a monoid under multiplication, where multiplication distributes over addition; i.e., a \cdot \left(b + c\right) = \left(a \cdot b\right) + \left(a \c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Direct Sum Of Groups
In mathematics, a group ''G'' is called the direct sumHomology. Saunders MacLane. Springer, Berlin; Academic Press, New York, 1963.László Fuchs. Infinite Abelian Groups of two normal subgroups with trivial intersection if it is generated by the subgroups. In abstract algebra, this method of construction of groups can be generalized to direct sums of vector spaces, modules, and other structures; see the article direct sum of modules for more information. A group which can be expressed as a direct sum of non-trivial subgroups is called ''decomposable'', and if a group cannot be expressed as such a direct sum then it is called ''indecomposable''. Definition A group ''G'' is called the direct sum of two subgroups ''H''1 and ''H''2 if * each ''H''1 and ''H''2 are normal subgroups of ''G'', * the subgroups ''H''1 and ''H''2 have trivial intersection (i.e., having only the identity element e of ''G'' in common), * ''G'' = ⟨''H''1, ''H''2⟩; in other words, ''G'' is genera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Group Isomorphism
In abstract algebra, a group isomorphism is a function between two groups that sets up a one-to-one correspondence between the elements of the groups in a way that respects the given group operations. If there exists an isomorphism between two groups, then the groups are called isomorphic. From the standpoint of group theory, isomorphic groups have the same properties and need not be distinguished. Definition and notation Given two groups (G, *) and (H, \odot), a ''group isomorphism'' from (G, *) to (H, \odot) is a bijective group homomorphism from G to H. Spelled out, this means that a group isomorphism is a bijective function f : G \to H such that for all u and v in G it holds that f(u * v) = f(u) \odot f(v). The two groups (G, *) and (H, \odot) are isomorphic if there exists an isomorphism from one to the other. This is written (G, *) \cong (H, \odot). Often shorter and simpler notations can be used. When the relevant group operations are understood, they are omitted and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Real Number
In mathematics, a real number is a number that can be used to measure a ''continuous'' one-dimensional quantity such as a distance, duration or temperature. Here, ''continuous'' means that values can have arbitrarily small variations. Every real number can be almost uniquely represented by an infinite decimal expansion. The real numbers are fundamental in calculus (and more generally in all mathematics), in particular by their role in the classical definitions of limits, continuity and derivatives. The set of real numbers is denoted or \mathbb and is sometimes called "the reals". The adjective ''real'' in this context was introduced in the 17th century by René Descartes to distinguish real numbers, associated with physical reality, from imaginary numbers (such as the square roots of ), which seemed like a theoretical contrivance unrelated to physical reality. The real numbers include the rational numbers, such as the integer and the fraction . The rest of the real ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
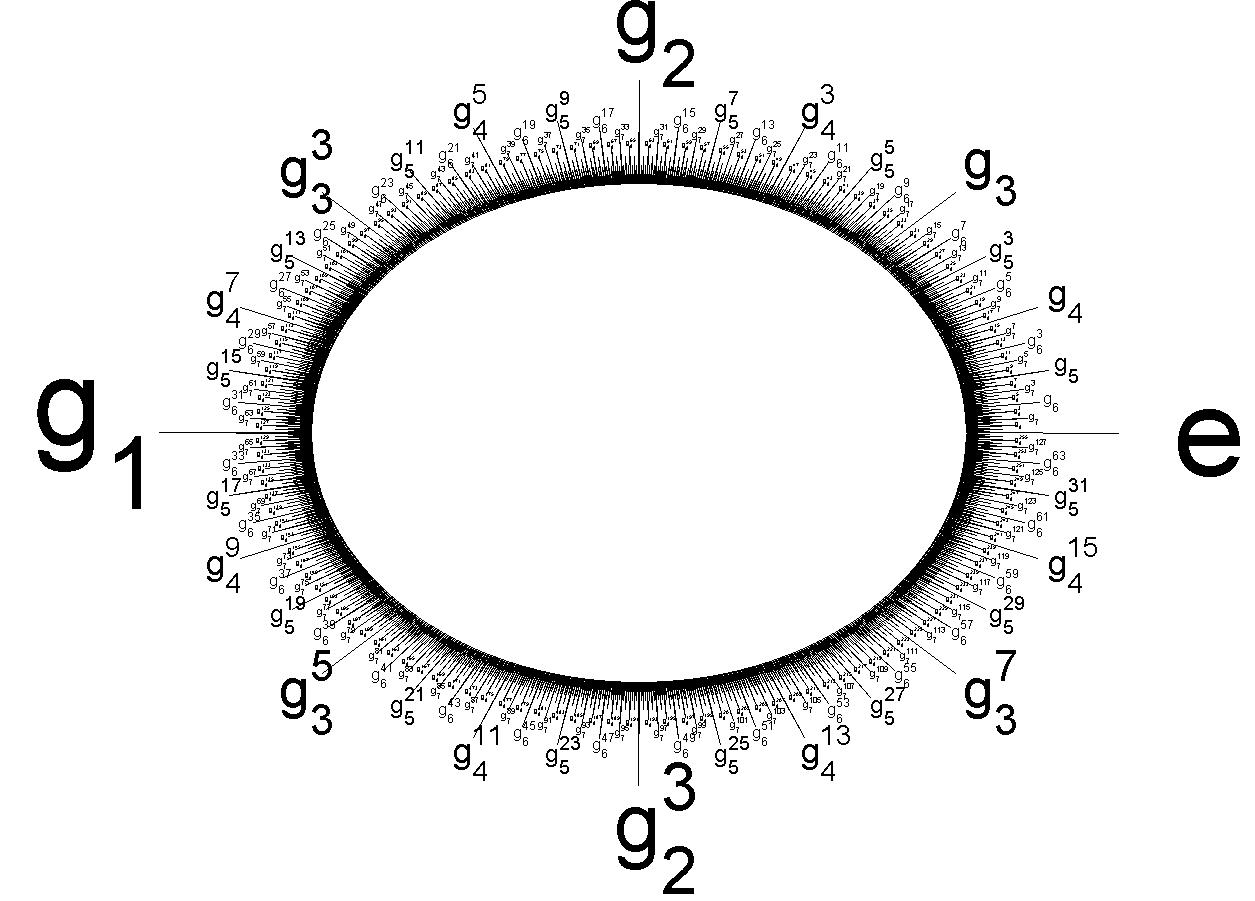
Prüfer Group
In mathematics, specifically in group theory, the Prüfer ''p''-group or the ''p''-quasicyclic group or ''p''∞-group, Z(''p''∞), for a prime number ''p'' is the unique ''p''-group in which every element has ''p'' different ''p''-th roots. The Prüfer ''p''-groups are countable abelian groups that are important in the classification of infinite abelian groups: they (along with the group of rational numbers) form the smallest building blocks of all divisible groups. The groups are named after Heinz Prüfer, a German mathematician of the early 20th century. Constructions of Z(''p''∞) The Prüfer ''p''-group may be identified with the subgroup of the circle group, U(1), consisting of all ''p''''n''-th roots of unity as ''n'' ranges over all non-negative integers: :\mathbf(p^\infty)=\ = \.\; The group operation here is the multiplication of complex numbers. There is a presentation :\mathbf(p^\infty) = \langle\, g_1, g_2, g_3, \ldots \mid g_1^p = 1, g_2^p = g_1, g_3^p = g_ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Root Of Unity
In mathematics, a root of unity, occasionally called a de Moivre number, is any complex number that yields 1 when raised to some positive integer power . Roots of unity are used in many branches of mathematics, and are especially important in number theory, the theory of group characters, and the discrete Fourier transform. Roots of unity can be defined in any field. If the characteristic of the field is zero, the roots are complex numbers that are also algebraic integers. For fields with a positive characteristic, the roots belong to a finite field, and, conversely, every nonzero element of a finite field is a root of unity. Any algebraically closed field contains exactly th roots of unity, except when is a multiple of the (positive) characteristic of the field. General definition An ''th root of unity'', where is a positive integer, is a number satisfying the equation :z^n = 1. Unless otherwise specified, the roots of unity may be taken to be complex number ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dyadic Rational Number
In mathematics, a dyadic rational or binary rational is a number that can be expressed as a fraction whose denominator is a power of two. For example, 1/2, 3/2, and 3/8 are dyadic rationals, but 1/3 is not. These numbers are important in computer science because they are the only ones with finite binary representations. Dyadic rationals also have applications in weights and measures, musical time signatures, and early mathematics education. They can accurately approximate any real number. The sum, difference, or product of any two dyadic rational numbers is another dyadic rational number, given by a simple formula. However, division of one dyadic rational number by another does not always produce a dyadic rational result. Mathematically, this means that the dyadic rational numbers form a ring, lying between the ring of integers and the field of rational numbers. This ring may be denoted \Z tfrac12/math>. In advanced mathematics, the dyadic rational numbers are central to the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rational Number
In mathematics, a rational number is a number that can be expressed as the quotient or fraction of two integers, a numerator and a non-zero denominator . For example, is a rational number, as is every integer (e.g. ). The set of all rational numbers, also referred to as "the rationals", the field of rationals or the field of rational numbers is usually denoted by boldface , or blackboard bold \mathbb. A rational number is a real number. The real numbers that are rational are those whose decimal expansion either terminates after a finite number of digits (example: ), or eventually begins to repeat the same finite sequence of digits over and over (example: ). This statement is true not only in base 10, but also in every other integer base, such as the binary and hexadecimal ones (see ). A real number that is not rational is called irrational. Irrational numbers include , , , and . Since the set of rational numbers is countable, and the set of real numbers is uncou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endomorphism Ring
In mathematics, the endomorphisms of an abelian group ''X'' form a ring. This ring is called the endomorphism ring of ''X'', denoted by End(''X''); the set of all homomorphisms of ''X'' into itself. Addition of endomorphisms arises naturally in a pointwise manner and multiplication via endomorphism composition. Using these operations, the set of endomorphisms of an abelian group forms a (unital) ring, with the zero map 0: x \mapsto 0 as additive identity and the identity map 1: x \mapsto x as multiplicative identity. The functions involved are restricted to what is defined as a homomorphism in the context, which depends upon the category of the object under consideration. The endomorphism ring consequently encodes several internal properties of the object. As the resulting object is often an algebra over some ring ''R,'' this may also be called the endomorphism algebra. An abelian group is the same thing as a module over the ring of integers, which is the initial object in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclic Group
In group theory, a branch of abstract algebra in pure mathematics, a cyclic group or monogenous group is a group, denoted C''n'', that is generated by a single element. That is, it is a set of invertible elements with a single associative binary operation, and it contains an element ''g'' such that every other element of the group may be obtained by repeatedly applying the group operation to ''g'' or its inverse. Each element can be written as an integer power of ''g'' in multiplicative notation, or as an integer multiple of ''g'' in additive notation. This element ''g'' is called a '' generator'' of the group. Every infinite cyclic group is isomorphic to the additive group of Z, the integers. Every finite cyclic group of order ''n'' is isomorphic to the additive group of Z/''n''Z, the integers modulo ''n''. Every cyclic group is an abelian group (meaning that its group operation is commutative), and every finitely generated abelian group ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torsion-free Rank
In mathematics, the rank, Prüfer rank, or torsion-free rank of an abelian group ''A'' is the cardinality of a maximal linearly independent subset. The rank of ''A'' determines the size of the largest free abelian group contained in ''A''. If ''A'' is torsion-free then it embeds into a vector space over the rational numbers of dimension rank ''A''. For finitely generated abelian groups, rank is a strong invariant and every such group is determined up to isomorphism by its rank and torsion subgroup. Torsion-free abelian groups of rank 1 have been completely classified. However, the theory of abelian groups of higher rank is more involved. The term rank has a different meaning in the context of elementary abelian groups. Definition A subset of an abelian group ''A'' is linearly independent (over Z) if the only linear combination of these elements that is equal to zero is trivial: if : \sum_\alpha n_\alpha a_\alpha = 0, \quad n_\alpha\in\mathbb, where all but finitely many c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |